- Quiz 1 Friday
- 13 questions/15 points
- Take-home, take 30 min
2017-09-13 15:42:03
Announcements
Today's Topics
- Cells of the nervous system
- Glia
- Neurons
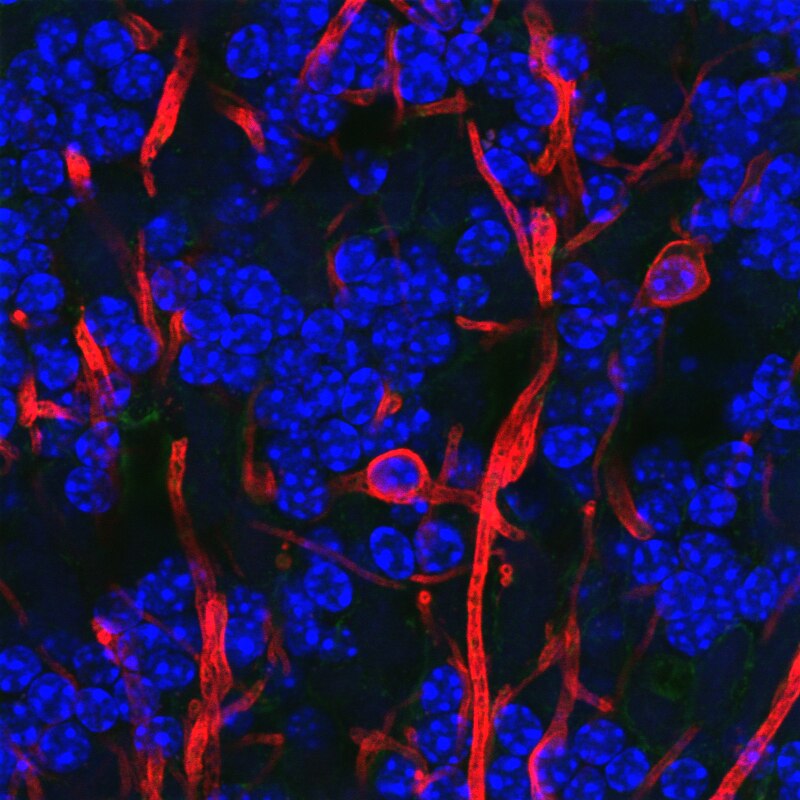
Visualizing the microanatomy of the brain
Crowd-sourcing anatomy research with EyeWire
How many neurons and glia?
- Old "lore": ~100 billion neurons
- New estimate (Azevedo et al. 2009):
- ~86 +/- 8 billion neurons
- 85 +/- 9 billion glia
How many neurons and glia?
"These findings challenge the common view that humans stand out from other primates in their brain composition and indicate that, with regard to numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells, the human brain is an isometrically scaled-up primate brain."
Mass, Neurons, Non-Neurons
Neurons by brain mass
Non-neuronal cells by brain mass
brain %>% ggplot() +
aes(x=mass_g, b_nonneurons, color=portion) +
geom_point() +
xlab("Mass in g") +
ylab("Billions of cells")
The Human Advantage

Could you count to 170 billion?
- How many years to count to 170 billion?
- 60 s/min * 60 min/hr * 24 hrs/day * 365 days/ yr = 31,536,000 s/yr
- 1e11/31,536,000 = 5,390 years
Glia (neuroglia)
- Functions
- Structural support
- Metabolic support
- Brain development
Astrocytes
- "Star-shaped"
- Most numerous cell type in CNS
- Physical and metabolic support
- Blood/brain barrier
- Ion (Ca++/K+) buffering
- Neurotransmitter (e.g., glutamate) buffering
- Regulate local blood flow
Astrocytes
- Shape brain development, synaptic plasticity
- Disruption linked to cognitive impairment, disease (Chung et al. 2015)
Astrocytes
Myelinating cells
- Oligodendrocytes
- In brain and spinal cord (CNS)
- 1:many neurons
- Schwann cells
- In PNS
- 1:1 neuron
- Facilitate neuro-regeneration
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann Cells
Microglia
- Phagocytosis
- Clean-up damaged, dead tissue
- Role in 'pruning' of synapses in normal development
Microglia
What makes neurons "special"?
- Long-lived (most generated b/w 3-25 weeks gestational age)
- Extended branching (dendrites and axons)
- Electrically excitable
- Connect to small #s of other cells via synapses
- Release neurotransmitters
Macrostructure of neurons
- Dendrites
- Soma
- Axons
- Terminal buttons (boutons)
Structure of neurons
Dendrites
- Majority of input to neuron
- Passive vs. active
- Spines
Dendrites
Dendritic Spines
Soma (cell body)
- Varied shapes
- Nucleus
- Chromosomes
- Organelles
- Mitochonrdria
- Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Soma
Axons
- Initial segment
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Terminals
Axons
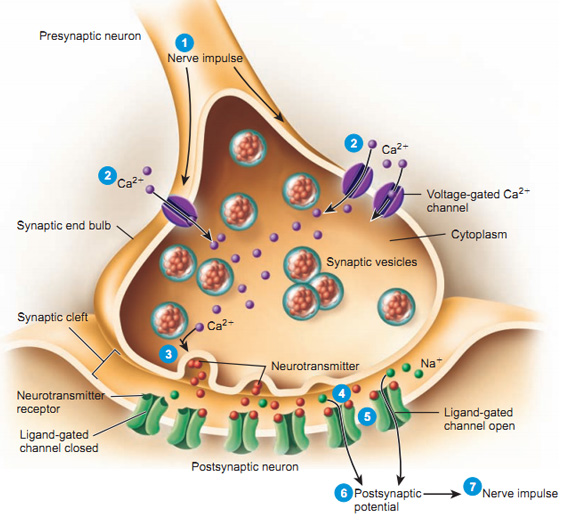
Synaptic bouton (terminal button)
- Synapse (~5-10K per neuron)
- Pre and postsynaptic membranes
- Synaptic cleft
- Synaptic vesicles
- Store/release neurotransmitters
- Autoreceptors & transporters
Synaptic bouton (terminal button)
Classifying neurons
- Functional role
- Input (sensory), output (motor/secretory), interneurons
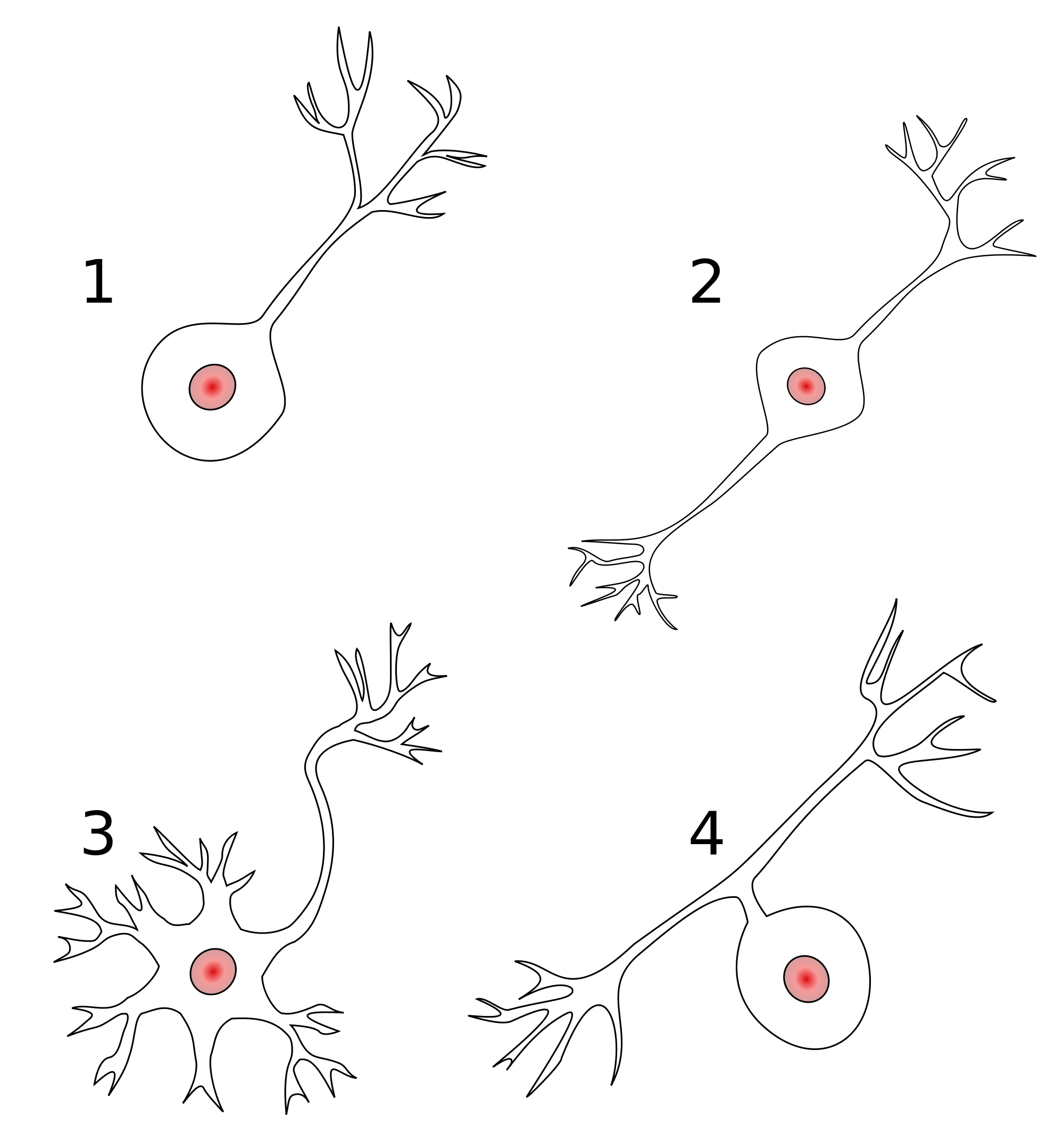
- Anatomy
- Unipolar
- Bipolar
- Multipolar
Branching types
Classifying neurons
- By specific anatomy
- Pyramidal cells
- Stellate cells
- Purkinje cells
- Granule cells
Neurons by type
Morphology, physiology, gene transcription
Next time
- Quiz 1 (available after class)
- Neurophysiology
References
Azevedo, Frederico AC, Ludmila RB Carvalho, Lea T Grinberg, José Marcelo Farfel, Renata EL Ferretti, Renata EP Leite, Roberto Lent, Suzana Herculano-Houzel, and others. 2009. “Equal Numbers of Neuronal and Nonneuronal Cells Make the Human Brain an Isometrically Scaled-up Primate Brain.” Journal of Comparative Neurology 513 (5). Wiley Online Library: 532–41. doi:10.1002/cne.21974.
Chung, Won-Suk, Christina A. Welsh, Ben A. Barres, and Beth Stevens. 2015. “Do Glia Drive Synaptic and Cognitive Impairment in Disease?” Nature Neuroscience 18 (11): 1539–45. doi:10.1038/nn.4142.