- Multiple structural, functional methods
- Different levels of spatial & temporal analysis
- Functional tools have different strengths & weaknesses
2018-09-03 08:32:47
Prelude
Today's Topics
- Wrap-up on functional methods
- Gross neuroanatomy
Neuroscience Seminar
"Combinatorial Strategies for the Plasticity and Regeneration of the Injured Spinal Cord"
Dr. Xiao-Ming Xu Indiana University
Wednesday, September 5, 2018 4:00 - 5:00 P.M.
108 Wartik Lab
Wrap-up on functional methods
Stimulating the brain


Stimulating the brain
- Spatial/temporal resolution?
- Assume stimulation mimics natural activity?
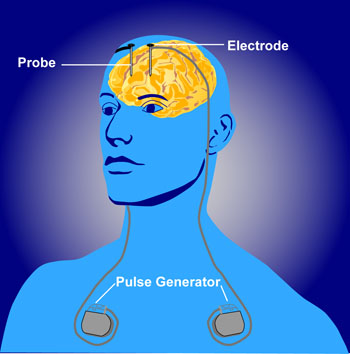
Deep brain stimulation as therapy
- Depression
- Epilepsy
- Parkinson’s Disease
Optogenetics
Optogenetics
- Gene splicing techniques insert light-sensitive molecules into neuronal membranes
- Application of light at specific wavelengths alters neuronal function
- Cell-type specific and temporally precise control
Simulating the brain
- Computer/mathematical models of brain function
- Example: neural networks
- Cheap, noninvasive, can be stimulated or “lesioned”
Main points
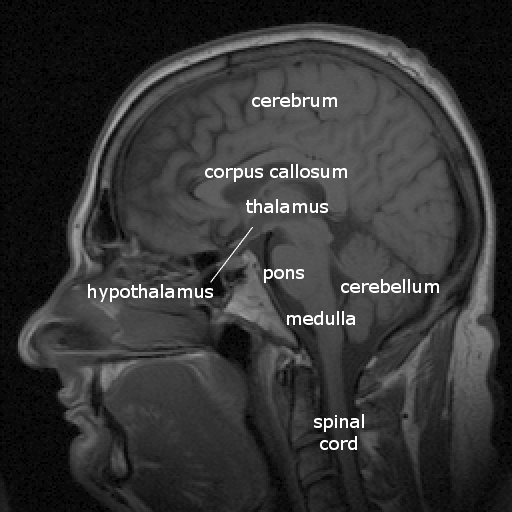
Gross neuroanatomy
Brain anatomy through dance
Finding our way around
Anterior/Posterior
Medial/Lateral
Superior/Inferior
Dorsal/Ventral
Rostral/Caudal
Directional image
Bipeds vs. quadripeds
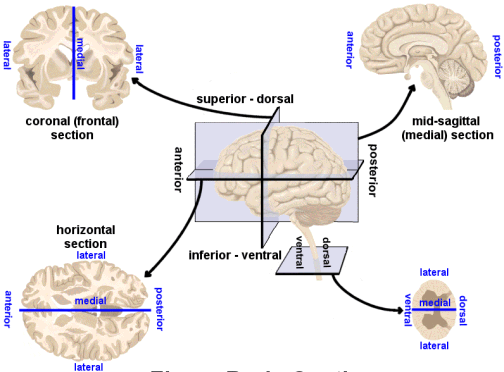
No matter how you slice it
Horizontal/Axial
Coronal/Transverse/Frontal
Sagittal (from the side)
Slice diagram
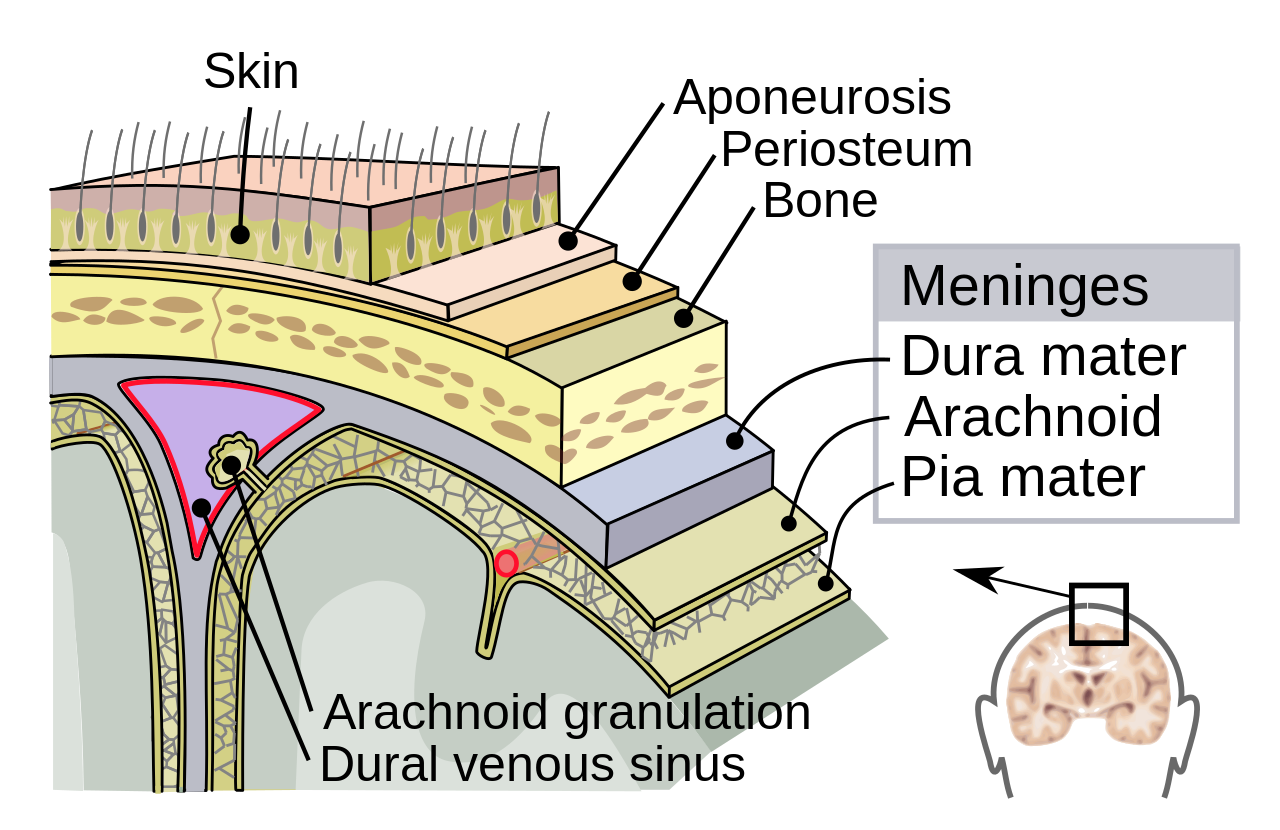
Supporting structures
Meninges
Ventricular system
Blood supply
Meninges
Dura mater ('tough mother')
Arachnoid membrane
Subarachnoid space
Pia mater ('gentle mother')
Meninges
Ventricular system
Ventricles
Lateral (1st & 2nd)
3rd
Cerebral aqueduct
4th
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Clears metabolites during sleep (Xie et al., 2013).
Blood Supply
Blood Supply
Arteries
- Circle of Willis
Blood/brain barrier
- Cells forming blood vessel walls tightly packed
- Active transport of molecules typically required
Blood/brain barrier
Area Postrema
- Brainstem, blood-brain barrier thin
Organization of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Everything encased in bone
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, amygdala | |||
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, tegmentum |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain | 4th | Metencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Mylencephalon | Medulla oblongata |
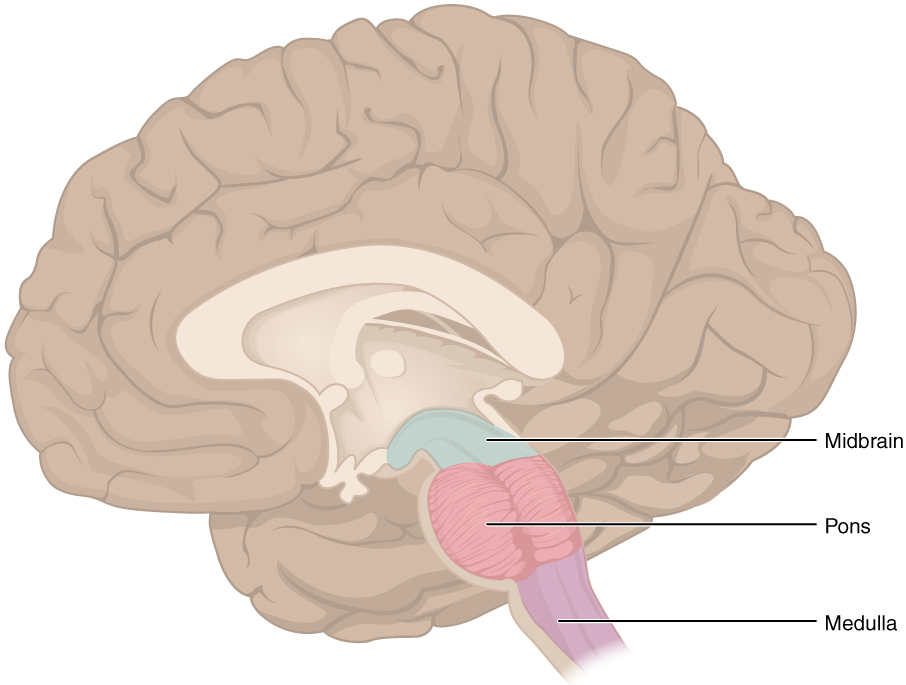
Hindbrain

Hindbrain
- Structures adjacent to 4th ventricle
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Pons

Medulla oblongata
Medulla
- Cardiovascular regulation
- Muscle tone
- Fibers of passage
- Ascending fibers (from body), a.k.a. afferents
- Descending fibers (exiting brain), a.k.a., efferents
Cerebellum
- “Little brain”
- Dorsal to pons
- Movement coordination, simple learning
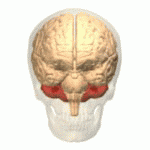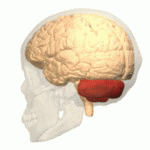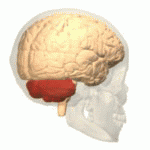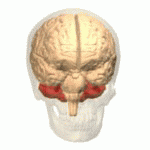
Pons
- Bulge on brain stem
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Relay to cerebellum
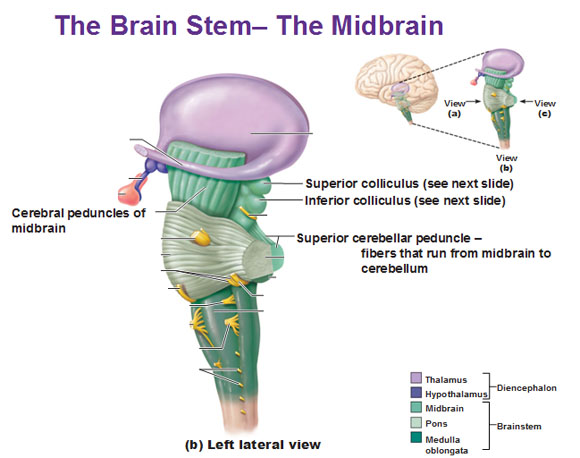
Midbrain
Midbrain components
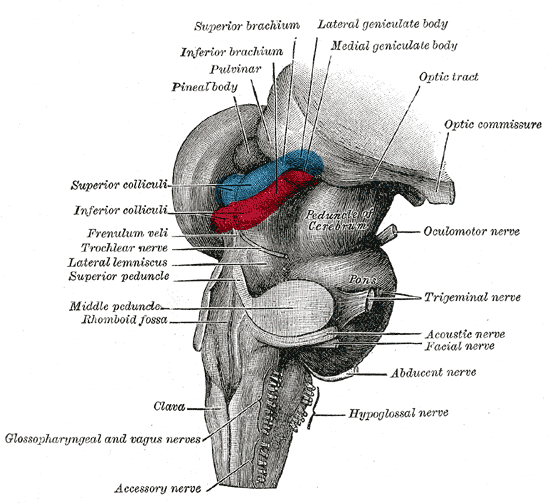
Tectum
Tegmentum
Tectum
Tectum
- "Roof" of the midbrain
- Superior and inferior colliculus
- Reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears
Tegmentum
- "Floor" of the midbrain
- Species-typical movement sequences
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
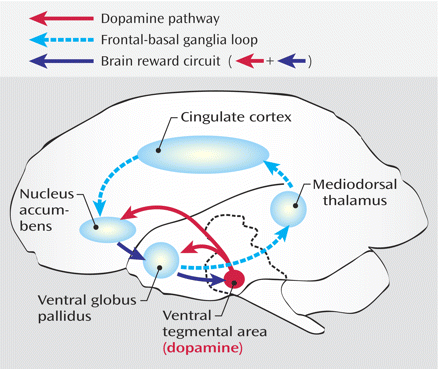
- Dopamine (DA) – from ventral tegmental area (VTA)
Forebrain
Forebrain Components
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Diencephalon Components
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus

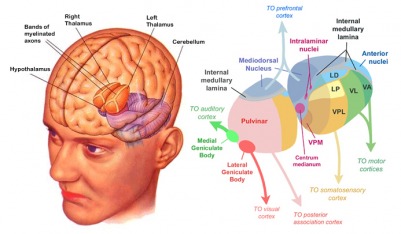
Thalamus
Thalamus functions
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
- Pulvinar, attention?
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- e.g., Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH) -> release of cortisol from Adrenal Cortex
- Posterior pituitary (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin (aka, Arginine Vasopressin – AVP; Anti-diuretic Hormone – ADH)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
Hypothalamus

Telencephalon
- Basal ganglia
- Hippocampus, amygdala
- Cerebral cortex
Basal Ganglia
- Skill and habit learning
- Linked to Tourette syndrome, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), addiction, movement disorders
- Example: Parkinson's Disease
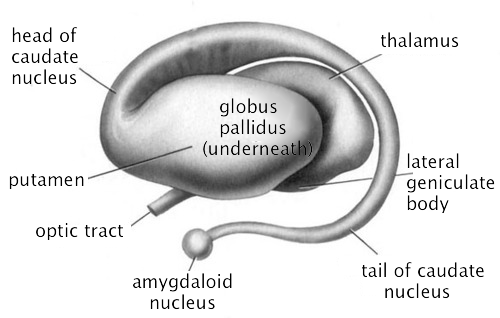
Basal ganglia
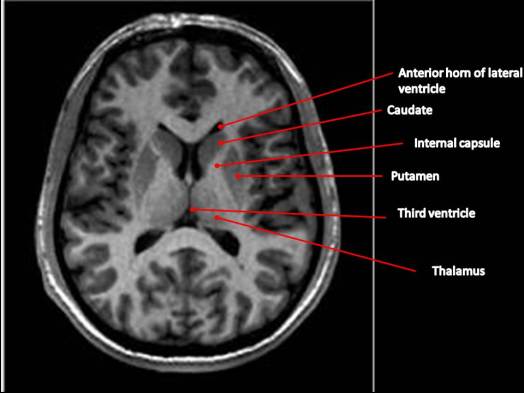
Basal ganglia
- Striatum
- Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Globus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Substantia nigra (tegmentum)
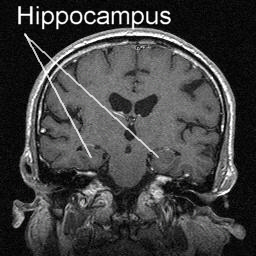
Hippocampus
- Immediately lateral to lateral ventricles
- Memories of specific facts or events
- Fornix projects to hypothalamus
- Mammillary bodies
Hippocampus
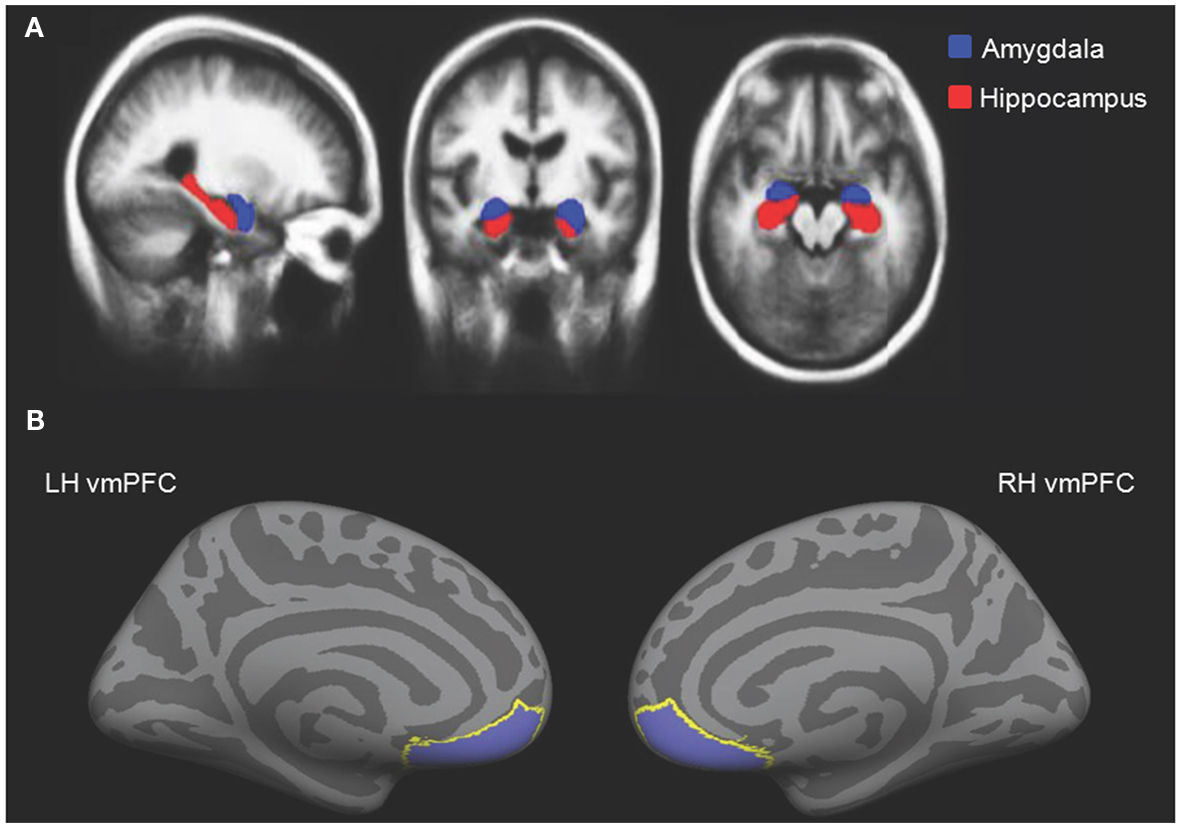
Amygdala (“almond”)
- Physiological state, behavioral readiness, affect
- NOT the fear center! (LeDoux, 2015).
Amygdala
Next time
- Gilmore's cautionary notes
- The cerebral cortex
- The peripheral nervous system
References
LeDoux, J. (2015, August 10). The Amygdala Is NOT the Brain’s Fear Center. Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/i-got-mind-tell-you/201508/the-amygdala-is-not-the-brains-fear-center
Xie, L., Kang, H., Xu, Q., Chen, M. J., Liao, Y., Thiyagarajan, M., … others. (2013). Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science, 342(6156), 373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224