2017-08-25 10:39:35
Prelude
Today's Topics
- Levels of analysis in the study of brain and behavior
- Spatial
- Temporal
- Methods to the madness
Review of key concepts
What does the practice of trephining suggest about our human ancestors?
- A. That they knew nothing about how to treat mental illness
- B. That they knew a lot about how to treat mental illness
- C. That they had some notion about the link between mental illness and the brain
What does the practice of trephining suggest about our human ancestors?
- A. That they knew nothing about how to treat mental illness
- B. That they knew a lot about how to treat mental illness
- C. That they had some notion about the link between mental illness and the brain
Descartes thought that this brain structure played a central role in linking sensory information with the actions it triggers.
- A. The cerebral ventricles
- B. The pineal gland
- C. Cerebro-spinal fluid
Descartes thought that this brain structure played a central role in linking sensory information with the actions it triggers.
- A. The cerebral ventricles.
- B. The pineal gland.
- C. Cerebro-spinal fluid.
Which of the following statements about the Egyptians is false?
- A. They employed a word meaning "brain".
- B. They removed the brain in the process of mummification.
- C. They created detailed drawings of human brain anatomy.
Levels of analysis
"If understanding everything we need to know about the brain is a mile, how far have we walked?"
J. Lichtman, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nvXuq9jRWKE&feature=youtu.be
Spatial resolution
Spatial and Temporal Resolution

What causes behavior?
Spatial Resolution in Detail
- Within an individual
- molecular
- genetic
- receptor
- chemical
- neurotransmitter/hormonal
- cellular
- neuronal firing
- molecular
Spatial Resolution in Detail
- Internal to individuals
- network
- lateral inhibition
- area
- region
- system
- network
Spatial Resolution in Detail
- External to individuals
- Social
- Friends, family, teachers, others
- Non-social
- neighborhood, school, state/region, country
- Physical environment
- Social
Temporal Resolution in Detail
- Within one lifetime
- Microseconds
- detection position from acoustic stimulation
- Milliseconds
- action potential
- Seconds
- changes in EEG power
- short-term memory
- Microseconds
Temporal Resolution in Detail
- Within one lifetime
- Minutes
- synaptic plasticity
- Hours
- memory consolidation
- Hormone (melatonin, cortisol) levels
- Days
- Minutes
Temporal Resolution in Detail
- Within one lifetime
- Weeks
- Months
- Years
- education & training
- disease processes
- cultural change
Temporal Resolution in Detail
- Across lifetimes
- Centuries
- cultural changes
- Millenia
- Natural & sexual selection
- Centuries
Why does this matter?
- Different methods, different levels of analysis
- Challenge of interpretation
- Challenge of linking phenomena across levels
- How does the micro affect macro or vice versa?
Neuroscience methods
Methods to the madness
- Tools in the neuroscientist’s toolkit
- What they tell us, and what they don’t
Evaluating methods
- What is the question?
- What are we measuring?
- Structure
- Activity
- Strengths & Weaknesses
- Cost
- Invasiveness
- Spatial/temporal resolution
Spatial and Temporal Resolution
Types of methods
- Structural
- Mapping the circuitry
- Anatomy & connectivity
- Functional (next time)
- What does it do?
- Physiology/Activity
Mapping structures
- Cell/axon stains
- Golgi stain – whole cells
- Nissl stain – cell bodies only
- Cellular distribution, concentration, microanatomy
Golgi stain
Nissl stain
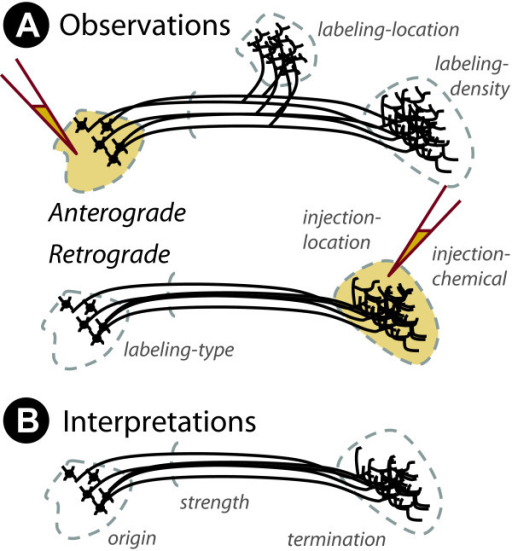
Retrograde vs. anterograde histochemical tracers
- Neuron information flow polarized–flows in one direction
- Retrograde (from axon terminal to cell body); anterograde (from cell body to axon terminal)
- What connects where
Retrograde vs. anterograde tracers
Brainbow
Brainbow
Eyewire.org
Clarity
Evaluating cellular tracing techniques
- Invasive (in humans post-mortem only)
- High spatial resolution, but poor temporal
Mapping structures
- Computed axial tomography (CAT), computed tomography CT
- X-ray based
Tomography
Tomography
CT scan of stroke
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic resonance
- Some common isotopes (e.g., H) & complex molecules have a magnetic dipole
- Axes align with strong magnetic field
- When alignment perturbed by radio frequency (RF) pulse, speed of realignment varies by tissue
- Realignment emits RF signals
MRI
How MRI works
Structural MRI
- Reveals tissue density/type differences
- Gray matter (neurons & dendrites & axons & glia) vs. white matter (mostly axons)
- MR Spectroscopy
- Region sizes/volumes
Structural MRI of the brain
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
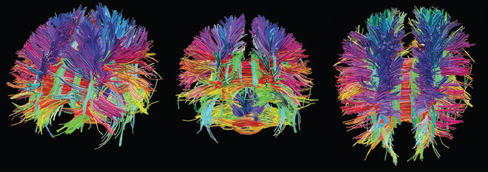
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
- Type of structural MRI
- Reveals integrity/density of axon fibers
- Measure of connectivity
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM)
- Voxels (volume-based elements)
- Morphometry, measure ("metry") form/morphology.
- How does brain size or thickness vary by age, disease status, etc.?
Next time
- Functional methods, including functional MRI (fMRI)
References
Lichtman, Jeff W., Jean Livet, and Joshua R. Sanes. 2008. “A Technicolour Approach to the Connectome.” Nature Reviews Neuroscience 9 (6): 417–22. doi:10.1038/nrn2391.
Sejnowski, Terrence J, Patricia S Churchland, and J Anthony Movshon. 2014. “Putting Big Data to Good Use in Neuroscience.” Nature Neuroscience 17 (11). Nature Publishing Group: 1440–1. doi:10.1038/nn.3839.