2017-08-31 11:24:59
Prelude
Prelude
Today's topics
- Wrap up on functional methods
- Neuroanatomy
- Through song and dance
Wrap-up on functional methods
Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds?
- A. functional MRI
- B. EEG
- C. MEG
- D. single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds?
- A. functional MRI
- B. EEG
- C. MEG
- D. single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has high/fine spatial resolution?
- A. functional MRI
- B. PET
- C. EEG
- D. Optogenetic stimulation
Which of the following methods has high/fine spatial resolution?
- A. functional MRI
- B. PET
- C. EEG
- D. Optogenetic stimulation
Evaluating stimulation methods
- Spatial/temporal resolution?
- Assume stimulation mimics natural activity?
- Optogenetic stimulation highly similar, others less so
- Deep brain stimulation as therapy
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Depression
- Epilepsy
Deep brain stimulation
Simulating the brain
- Computer/mathematical models of brain function
- Example: neural networks
- Cheap, noninvasive, can be stimulated or “lesioned”
Spatial and Temporal Resolution
Neuroanatomy
Brain anatomy through dance
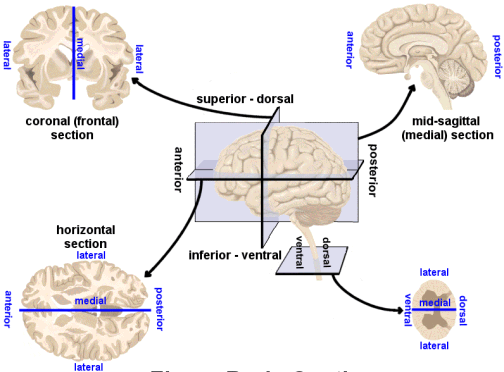
Finding our way around
Anterior/Posterior
Medial/Lateral
Superior/Inferior
Dorsal/Ventral
Rostral/Caudal
Directional image
Bipeds vs. quadripeds
No matter how you slice it
Horizontal/Axial
Coronal/Transverse/Frontal
Sagittal (from the side)
Slice diagram
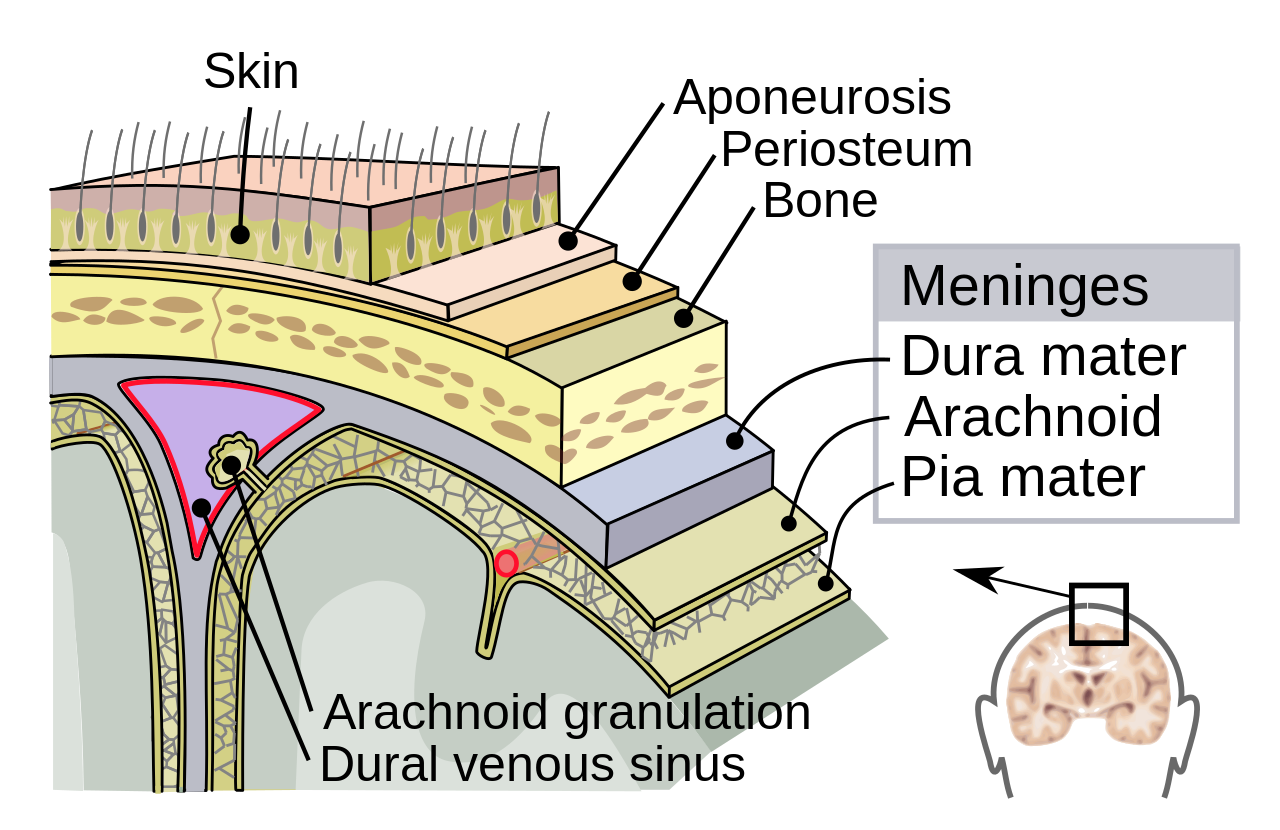
Supporting structures
Meninges
Ventricular system
Blood supply
Meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid membrane
Subarachnoid space
Pia mater
Meninges
Ventricular system
Ventricles
Lateral (1st & 2nd)
3rd
Cerebral aqueduct
4th
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Clears metabolites during sleep (Xie et al. 2013).
Blood Supply
Blood Supply
Arteries
- Circle of Willis
Blood/brain barrier
- Cells forming blood vessel walls tightly packed
- Active transport of molecules typically required
Blood/brain barrier
Area Postrema
- Brainstem, blood-brain barrier thin
Area Postrema
Organization of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Everything encased in bone
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, amygdala | |||
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, tegmentum |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain | 4th | Metencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Mylencephalon | Medulla oblongata |
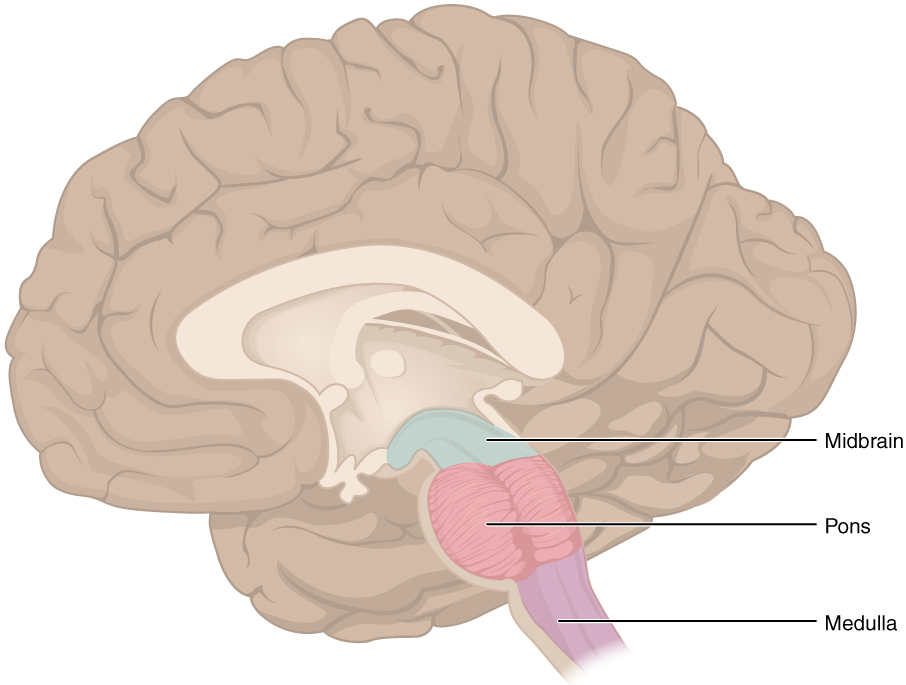
Hindbrain

Structures adjacent to 4th ventricle
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Pons

Medulla oblongata
Medulla
- Cardiovascular regulation
- Muscle tone
- Fibers of passage
- Cranial nerves VI-XII
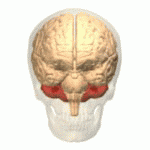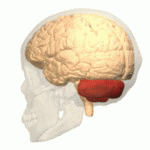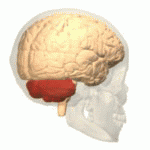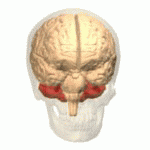
Cerebellum
- “Little brain”
- Dorsal to pons
- Movement coordination, simple learning
Pons
- Bulge on brain stem
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Relay to cerebellum
- Cranial nerve V
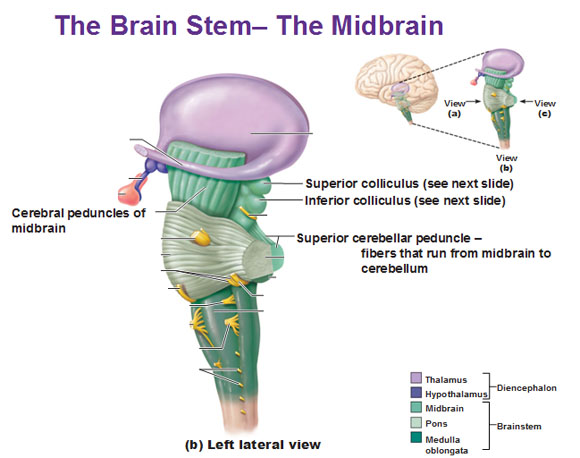
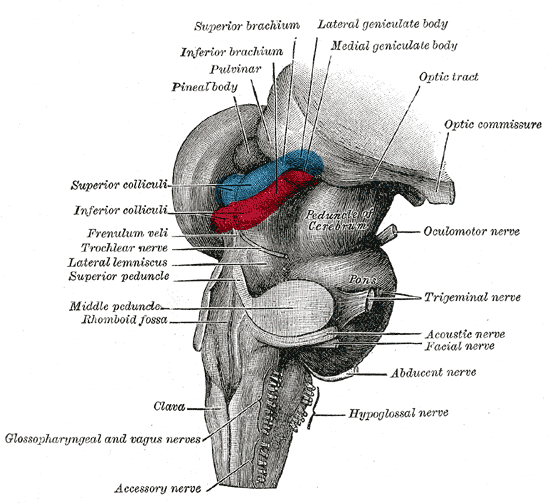
Midbrain
Midbrain components
Tectum
Tegmentum
Tectum
Tectum
- Tectum -> "roof"
- Superior colliculus and inferior colliculus
- Reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears
Tegmentum
- Tegmentum -> "floor"
- Species-typical movement sequences
- Cranial nerves III, IV
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Dopamine (DA)
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
Forebrain
Forebrain Components
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Diencephalon Components
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
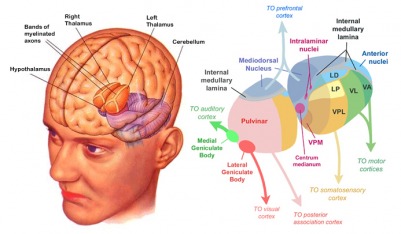
Thalamus
Thalamus functions
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- Posterior (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
Hypothalamus
Next time…
- More neuroanatomy
References
Sejnowski, Terrence J, Patricia S Churchland, and J Anthony Movshon. 2014. “Putting Big Data to Good Use in Neuroscience.” Nature Neuroscience 17 (11). Nature Publishing Group: 1440–1. doi:10.1038/nn.3839.
Xie, Lulu, Hongyi Kang, Qiwu Xu, Michael J Chen, Yonghong Liao, Meenakshisundaram Thiyagarajan, John O’Donnell, et al. 2013. “Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain.” Science 342 (6156). American Association for the Advancement of Science: 373–77. doi:10.1126/science.1241224.