2017-09-28 17:44:18
Prelude
Prelude
Today's Topics
- Wrap-up on neurotransmitters
- Hormonal communication
- Quiz 2 on Monday
- Review Exam 1 on Monday.
Black widow spider venom causes paralysis by impeding the normal function of which neurotransmitter system?
- Glutamate (Glu)
- GABA (GABA)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
Black widow spider venom causes paralysis by impeding the normal function of which neurotransmitter system?
- Glutamate (Glu)
- GABA (GABA)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
- ionotropic
- voltage-gated
- nicotinic
- metabotropic
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
- ionotropic
- voltage-gated
- nicotinic
- metabotropic
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
ionotropicvoltage-gatedvoltage gated Na+, K+, and Ca++nicotinicACh binds to nAChR; ACh not a monoamine- metabotropic
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
- Cl-; IPSP
- K+; IPSP
- Glutamate; EPSP
- GABA; EPSP
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
- Cl-; IPSP
- K+; IPSP
- Glutamate; EPSP
- GABA; EPSP
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
Cl-; IPSPOutward Cl- -> inside less negative = EPSP- K+; IPSP Make inside less positive
Glutamate; EPSPGlu not an ion; transported acrossGABA; EPSPGABA not an ion; transported across
Non-chemical communication between neurons
- Gap junctions
- Electrical coupling
- Connect cytoplasm directly
- Fast, but fixed, hard to modulate
- Examples, retina, cardiac muscle
Gap junctions
Ways to think about synaptic communication
- Specificity: point-to-point vs. broadcast
- Direct vs. modulatory
- Agonists vs. antagonists
Agonists vs. Antagonists
- Agonists
- bind to receptor
- mimic action of endogenous chemical
- Antagonists
- bind to receptor
- block/impede action of endogenous chemical
Valium is a GABA-A receptor agonist. This means:
- It decreases inhibition
- It activates a metabotropic Cl- channel
- It facilitates/increases inhibition
- It blocks an ionotropic channel
Valium is a GABA-A receptor agonist. This means:
- It decreases inhibition
- It activates a metabotropic Cl- channel
- It facilitates/increases inhibition
- It blocks an ionotropic channel
Types of chemical communication
- Neurocrine
- Sending cell -> Receiving cell
- Autocrine
- Sending cell -> itself
- e.g., presynaptic autoreceptors
- Paracrine
- Sending cell -> neighboring cells
- NO and CO NTs
Types of chemical communication
- Endocrine
- Sending cell -> many cells elsewhere in body
- Pheromone
- Sending cell -> other animals of same species
- Allomone
- Sending cell -> cells in other species
Hormones
- Chemical secreted into blood
- Act on specific target tissues
- Produce specific effects
Can a substance be a hormone AND a neurotransmitter?
- Yes, why not?
- No, absolutely not.
Can a substance be a hormone AND a neurotransmitter?
- Yes, why not?
- No, absolutely not.
Examples of substances that are both hormones and neurotransmitters
- Melatonin
- Epinephrine/adrenaline
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
Behaviors under hormonal influence
Behaviors under hormonal influence
- Ingestive (eating/ drinking)
- Fluid levels
- Na, K, Ca levels
- Digestion
- Blood glucose levels
Behaviors under hormonal influence

Behaviors under hormonal influence
- Reproduction
- Sexual Maturation
- Mating
- Birth
- Care giving
Behaviors under hormonal influence
Behaviors under hormonal influence
- Responses to threat/ challenge
- Metabolism
- Heart rate, blood pressure
- Digestion
- Arousal
What do these behaviors have in common?
- Biological imperatives
- Proscribed in space and time
- Foraging/hunting
- Find targets distributed in space, evaluate, act upon
- Often involve others
Differences between neural and hormonal communication
- Point to point vs.“broadcast”
- Wider broadcast than neuromodulators
- Fast vs. slow-acting
- Short-acting vs. long-acting
- Digital (yes-no) vs. analog (graded)
- Voluntary control vs. involuntary
Similarities between neural and hormonal communication
- Chemical messengers stored for later release
- Release follows stimulation
- Action depends on specific receptors
- 2nd messenger systems common
Where are hormones released
Where are hormones released?
- CNS
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Pineal gland
Where are hormones released
Where are hormones released?
- Rest of body
- Thyroid
- Adrenal (ad=adjacent, renal=kidney) gland
- Adrenal cortex
- Adrenal medulla
- Gonads (testes/ovaries)
Two hypothalamus/pituitary release systems
- Direct
- Indirect
Direct hormone release into bloodstream
- Hypothalamus (paraventricular, supraoptic nucleus) to
- Posterior pituitary
- Oxytocin
- Arginine Vasopressin (AVP, vasopressin)
Direct release
Indirect release
- Hypothalamus -> releasing hormones
- Anterior pituitary -> tropic hormones
- End organs
Indirect release
Case studies
Case 1: Responses to threat or challenge
- Neural response
- Sympathetic Adrenal Medulla (SAM) response
- Sympathetic NS activation of adrenal medulla, other organs
- Releases NE and Epi
Case 1: Responses to threat or challenge
- Endocrine response
- Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) axis
- Adrenal hormones released
- Hypothalamus
- Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
- Anterior pituitary
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Case 1: Responses to threat or challenge
- Adrenal cortex
- Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol)
- Mineralocorticoids (e.g. aldosterone)
Adrenal hormones
- Steroids
- Derived from cholesterol
- Cortisol
- increases blood glucose, anti-inflammatory
- negative consequences of prolonged exposure
- Aldosterone
- Regulates Na (and water) retention in kidneys
Case 2: Reproductive behavior – the milk letdown reflex
- Hypothalamus releases oxytocin into posterior pituitary
- Targets milk ducts in breast tissue
Milk letdown reflex
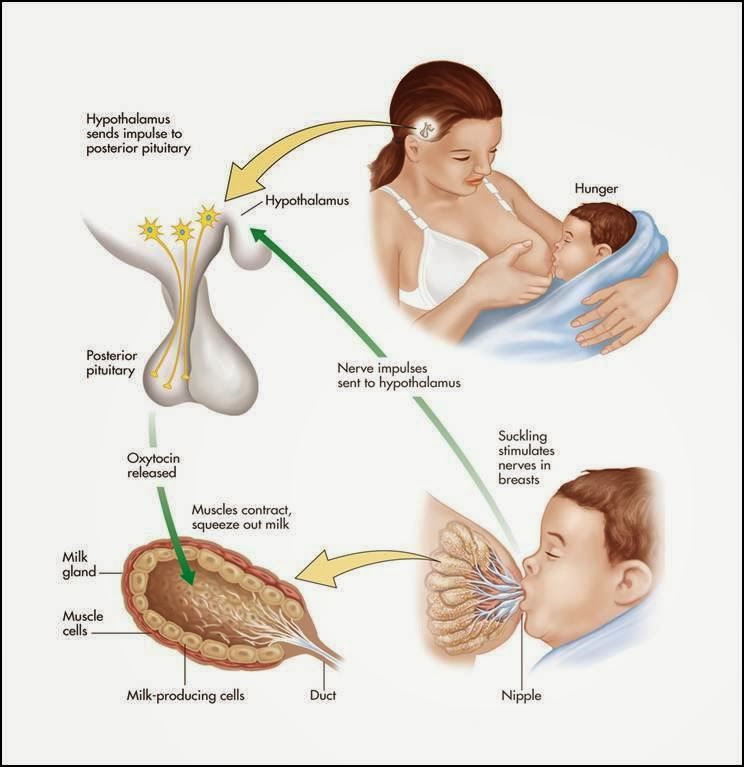
Oxytocin's role
- Sexual arousal
- Released in bursts during orgasm
- Stimulates uterine, vaginal contraction
- Links to social interaction, bonding (Weisman and Feldman 2013)
- Alters face processing in autism (Domes et al. 2013)
Oxytocin
Next time…
- Quiz 2
- Go over Exam 1
References
Domes, Gregor, Markus Heinrichs, Ekkehardt Kumbier, Annette Grossmann, Karlheinz Hauenstein, and Sabine C. Herpertz. 2013. “Effects of Intranasal Oxytocin on the Neural Basis of Face Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorder.” Biological Psychiatry 74 (3): 164–71. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.02.007.
Weisman, Omri, and Ruth Feldman. 2013. “Oxytocin Effects on the Human Brain: Findings, Questions, and Future Directions.” Biological Psychiatry 74 (3): 158–59. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.026.






.png)