- Mic on
- Zoom share screen
- 2nd computer connected to Zoom
- Projector on
2020-09-03 09:55:37
Pre-check
Prelude (2:01)
Today’s topics
- Announcement: Quiz 1 next Thursday (online via Canvas)
- Warm-up
- Wrap up on functional methods
- Neuroanatomy
- Through song and dance
Warm-up
What kind of brain imaging technique does this image represent?

What kind of structural brain imaging technique does this image represent?
- A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- B. Positron Emission Tomography
- C. Event-related potentials (ERP)
What kind of structural brain imaging technique does this image represent?
- A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- B.
Positron Emission Tomography - C.
Event-related potentials (ERP)
Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds?
- A. functional MRI
- B. EEG
- C. MEG
- D. single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds?
- A. functional MRI
- B.
EEG - C.
MEG - D.
single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has high/fine spatial resolution?
- A. functional MRI
- B. PET
- C. EEG
- D. single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has high/fine spatial resolution?
- A.
functional MRI - B.
PET - C.
EEG - D. single-unit recording
Which measure(s) would you use to map connections between brain areas?
- A. retrograde/anterograde cell tracers
- B. diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
- C. PET neuroimaging
- E. both A & B.
Which measure(s) would you use to measure connections between brain areas?
- A. retrograde/anterograde cell tracers
- B. diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
- C.
PET neuroimaging - E. both A & B.
Wrap-up on functional methods
Manipulating the brain
- Nature’s “experiments”
- Stroke, head injury, tumor
- Neuropsychology
- If damage to X impairs performance on Y -> X critical for/controls Y
- Poor spatial/temporal resolution, limited experimental control
Phineas Gage
Stimulating the brain
- Pharmacological
- Electrical (transcranial Direct Current Stimulation - tDCS)
- Inject low levels of electric current
- Magnetic (Transcranial magnetic stimulation - TMS)
- Inject directed pulses of magnetic energy
- Optically (optogenetics)
- Light activates ion channels in neurons, causes current to flow
tDCS
TMS
Optogenetic stimulation
Evaluating stimulation methods
- Spatial/temporal resolution?
- Assume stimulation mimics natural activity. Does it?
- Optogenetic stimulation similar to natural stimulation, others less so
- Deep (electrical) brain stimulation as therapy
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Depression
- Epilepsy
Deep brain stimulation
Simulating the brain
- Computer/mathematical models of brain function
- Example: neural networks
- Cheap, noninvasive, can be stimulated or “lesioned”
Spatial and Temporal Resolution
Bottom line…
- Neuroscientists…
- need to use many tools
- seek converging evidence
Neuroanatomy
Brain anatomy through dance
Finding our way around
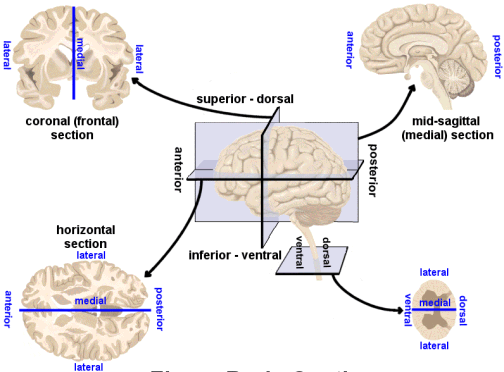
Anterior/Posterior
Medial/Lateral
Superior/Inferior
Dorsal/Ventral
Rostral/Caudal
Finding our way around
Anterior/Posterior -> front/back
Medial/Lateral -> inside/outside
Superior/Inferior -> upward/downward
Dorsal/Ventral -> back-ward/belly-ward
Rostral/Caudal -> head-ward/tail-ward
Directional image
Bipeds vs. quadripeds
No matter how you slice it
Horizontal/Axial
Coronal/Transverse/Frontal
Sagittal (from the side)
Slice diagram
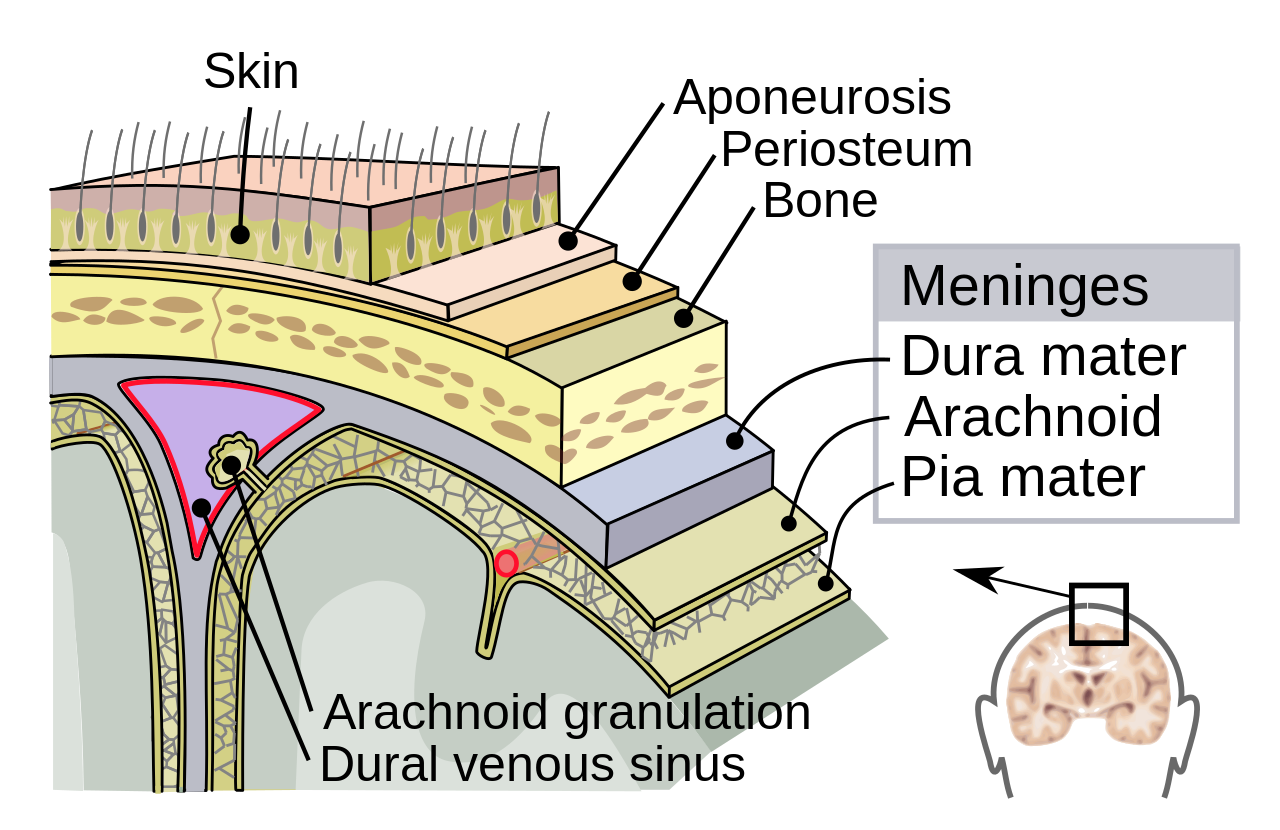
Supporting structures
Meninges
Ventricular system
Blood supply
Meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid membrane
Subarachnoid space
Pia mater
Meninges
Ventricular system
Ventricles
Lateral (1st & 2nd)
3rd
Cerebral aqueduct
4th
(are filled with) Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Blood Supply
Blood Supply
Arteries
- external & internal carotid; vertebral -> basilar
- Circle of Willis
- anterior, middle, & posterior cerebral
Blood/brain barrier
- Isolates CNS from blood stream
- Active transport of molecules typically required
- (endothelial) Cells forming blood vessel walls tightly packed
Blood/brain barrier
exception is Area Postrema
- In brainstem
- Blood-brain barrier thin
- Detects toxins, evokes vomiting
Area Postrema
Organization of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Everything encased in bone
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, amygdala | |||
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, Tegmentum |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain | 4th | Rhombencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Medulla oblongata |
Embryonic brain
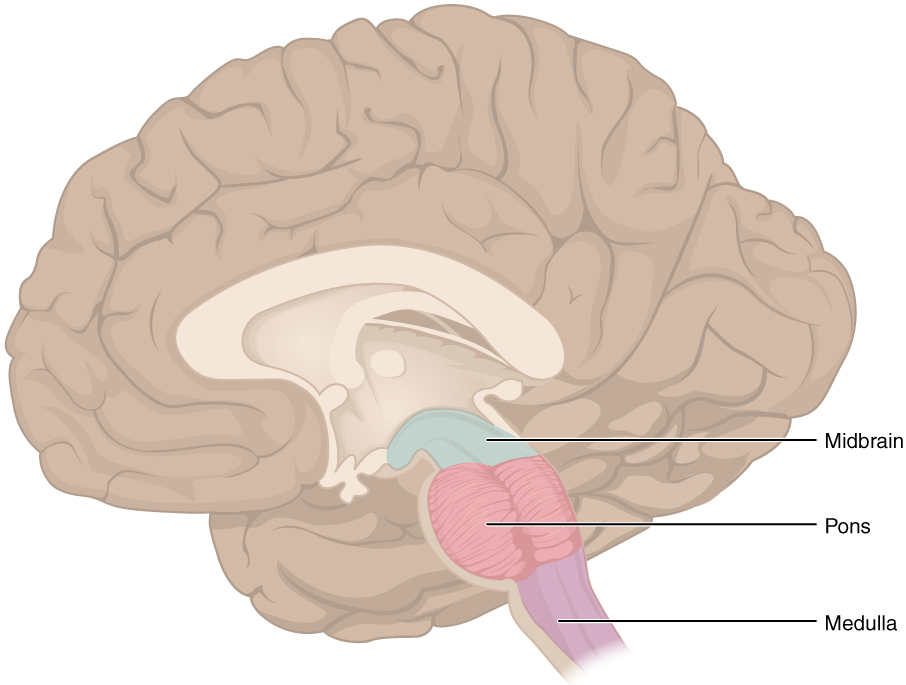
Hindbrain
Structures adjacent to 4th ventricle
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Pons

Medulla oblongata
Medulla
- Cardiovascular regulation
- Muscle tone
- Fibers of passage
- Cranial nerves VI-XII
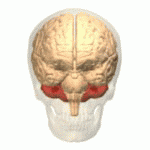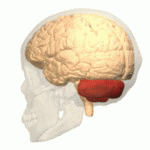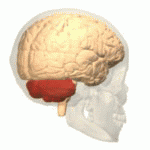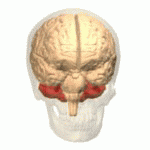
Cerebellum
- “Little brain”
- Dorsal to pons
- Movement coordination, classical conditioning (associative learning), + ???
Pons
- Bulge on brain stem
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Relay to cerebellum
- Cranial nerve V
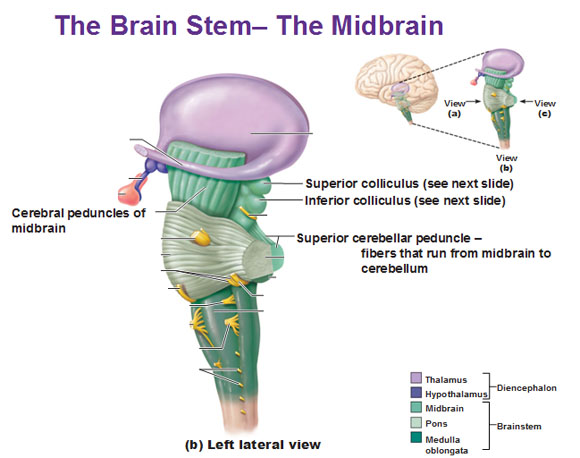
Midbrain
Midbrain components
Tectum
Tegmentum
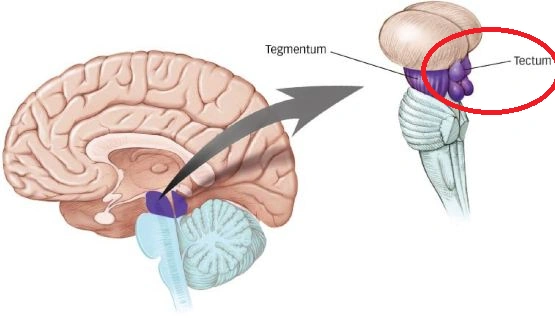
Tectum
- Tectum -> “roof”
- Superior colliculus (reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears)
- Inferior colliculus (sound/auditory processing)
Tegmentum
- Tegmentum -> “floor”
- Species-typical movement sequences (e.g., cat: hissing, pouncing)
- Cranial nerves III, IV
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Dopamine (DA)
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
Forebrain
Forebrain Components
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
Diencephalon (“between” brain)
Diencephalon components
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
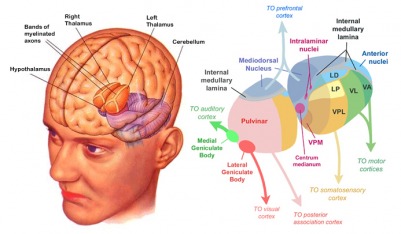
Thalamus
Thalamus functions
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
- others…
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls autonomic nervous system (ANS)
- Controls pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- Posterior (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
- Oxytocin
Hypothalamus
Next time…
- More neuroanatomy…
References
Dayan, E., Censor, N., Buch, E. R., Sandrini, M., & Cohen, L. G. (2013). Noninvasive brain stimulation: From physiology to network dynamics and back. Nature Neuroscience, 16(7), 838–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3422
Sejnowski, T. J., Churchland, P. S., & Movshon, J. A. (2014). Putting big data to good use in neuroscience. Nature Neuroscience, 17(11), 1440–1441. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3839