- Mic on
- Zoom share screen
- 2nd computer connected to Zoom
- Projector on
2020-09-07 17:32:48
Pre-check
Prelude (1:22)
Today’s topics
- Quiz 1 on Thursday
- Warm-up
- More neuroanatomy
Warm-up
What hindbrain area’s name means ‘little brain’?
- A. Pons
- B. 4th ventricle
- C. Cerebellum
- D. Tegmentum
What hindbrain area’s name means ‘little brain’?
- A.
Pons - B.
4th ventricle - C. Cerebellum
- D.
Tegmentum
The blood/brain barrier is especially thin in which hindbrain area?
- A. Pons
- B. 4th ventricle
- C. Cerebellum
- D. Medulla oblongata (medulla)
The blood/brain barrier is especially thin in which hindbrain area?
- A.
Pons - B.
4th ventricle - C.
Cerebellum - D. Medulla oblongata (medulla)
Which of the cerebral ventricles is most caudal (closest to the spinal cord)?
- Cerebral aqueduct
- Lateral ventricles
- 3rd ventricle
- 4th ventricle
Which of the cerebral ventricles is most caudal (closest to the spinal cord)?
Cerebral aqueductLateral ventricles3rd ventricle- 4th ventricle
More neuroanatomy
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, amygdala | |||
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, tegmentum |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain | 4th | Metencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Mylencephalon | Medulla oblongata |
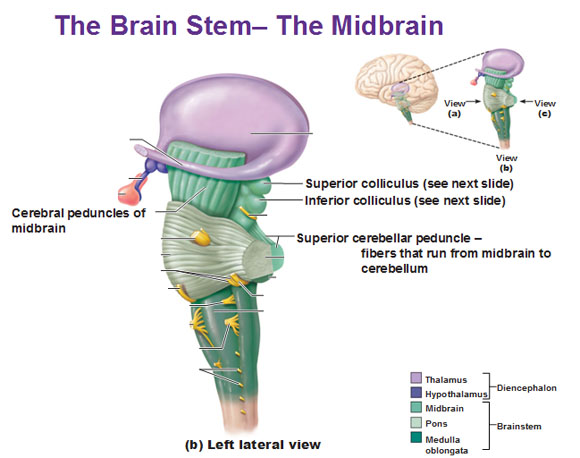
Midbrain
Midbrain components
Tectum
Tegmentum
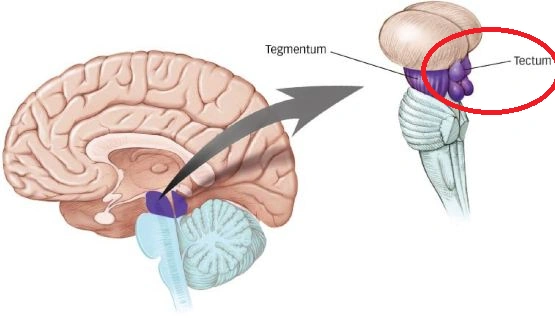
Tectum
- Tectum -> “roof”
- Superior colliculus (reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears)
- Inferior colliculus (sound/auditory processing)
Tegmentum
- Tegmentum -> “floor”
- Species-typical movement sequences (e.g., cat: hissing, pouncing)
- Cranial nerves III, IV
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Dopamine (DA)
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
Forebrain
Forebrain Components
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Diencephalon Components
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
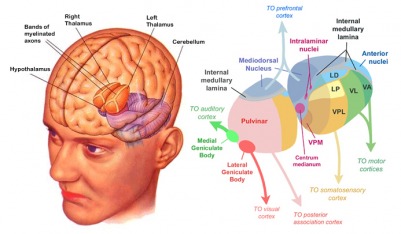
Thalamus
Thalamus functions
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Controls endocrine system via pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- Posterior (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
Hypothalamus
Telencephalon components
- Basal (not basil) ganglia
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
- Skill and habit learning
- Sequencing of movement
- Example: Parkinson’s Disease
Basal ganglia
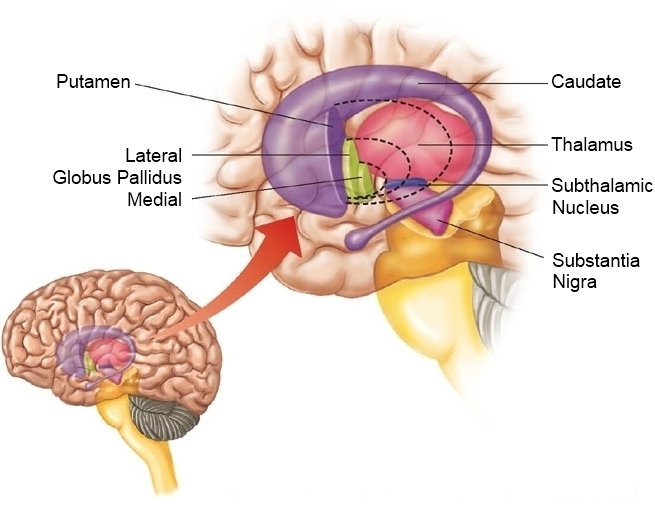
Basal ganglia
- Striatum
- Dorsal
- Ventral
Basal ganglia
- Globus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Substantia nigra (in tegmentum)
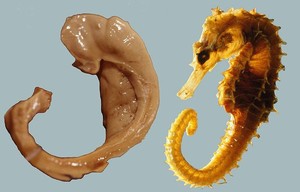
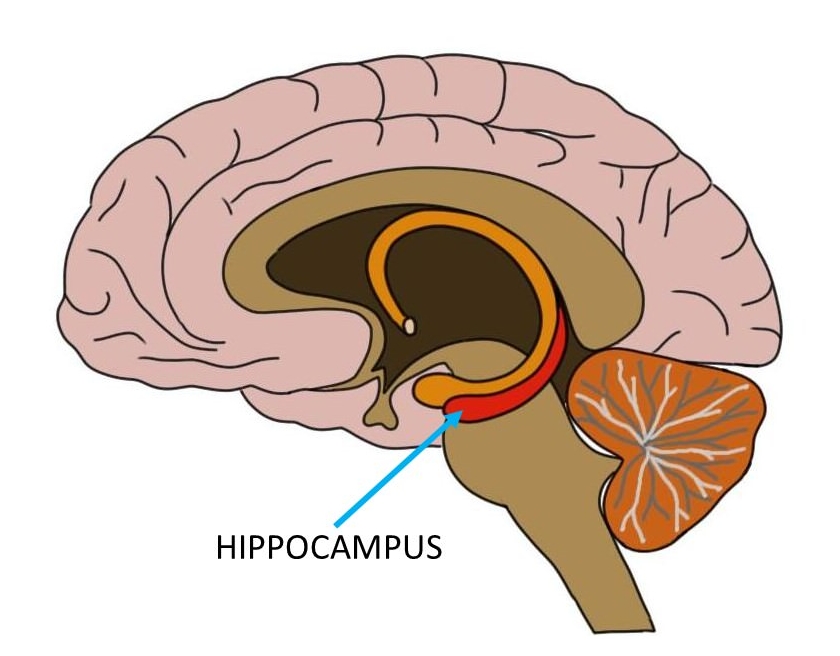
Hippocampus
- From Greek for “sea horse”
- Immediately lateral to lateral ventricles
- Memories of specific facts or events, spatial locations
- Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Fornix projects to hypothalamus
- Mammillary bodies
Amygdala
- “almond”
- Physiological state, behavioral readiness, affect
- NOT the fear center! (LeDoux, 2015).
Cerebral Cortex
- Cerebral hemispheres
- Groove (sulcus or sulci)
- Bumps (gyrus or gyri)
- Grey vs. white matter
- Lobes
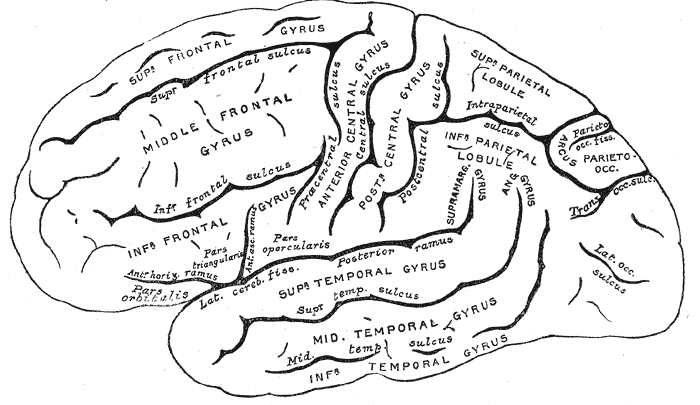
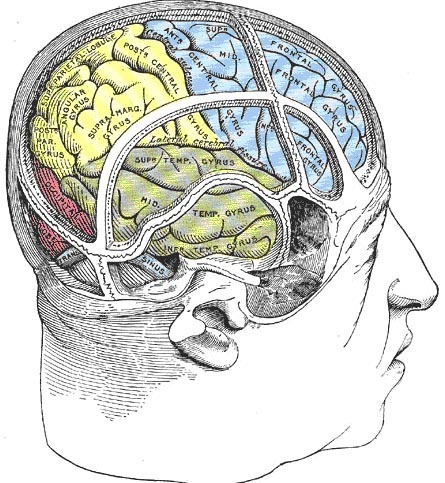
Cortical Gyri – Lateral
Cortical Gyri – Medial
Grey vs. White Matter
- Grey matter
- Cell bodies, dendrites, axons, glia, vessels
- White matter
- Mostly axons (covered in myelin)
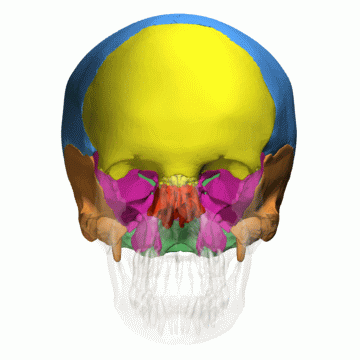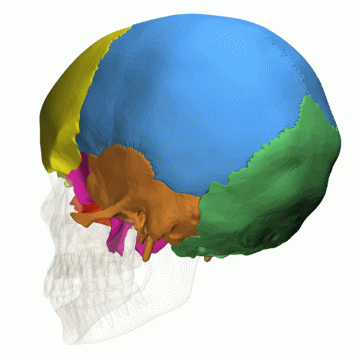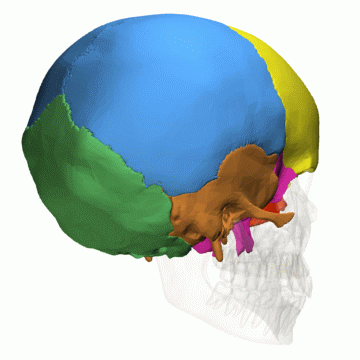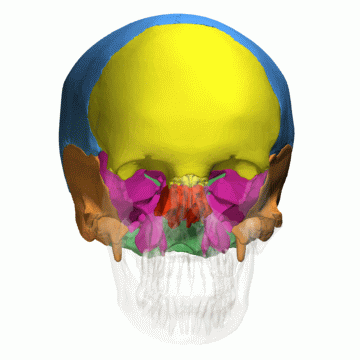
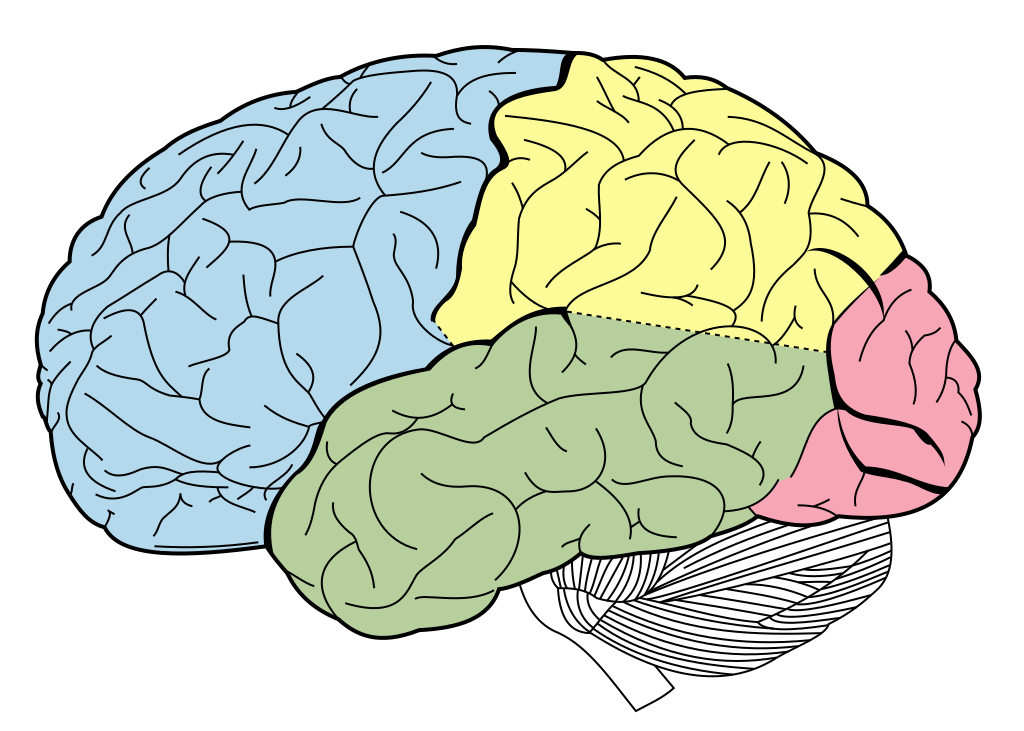
Lobes of the cerebral cortex
- Frontal
- Temporal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Related to cranial bones of the skull
Landmarks of the cortex
| Landmark | Identifies/separates |
|---|---|
| Medial longitudinal fissure (longitudinal fissure) | Divides hemispheres |
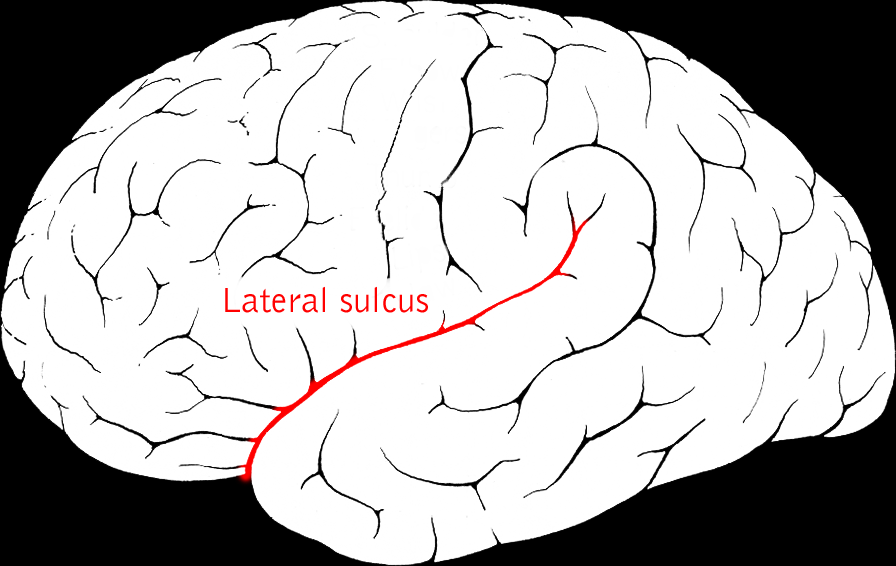
| Lateral sulcus/fissure | Divides temporal lobe from frontal & parietal |
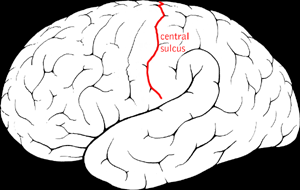
| Central sulcus | Divides frontal from parietal lobe |
Medial longitudinal fissure (longitudinal fissure)
Lateral sulcus/fissure
Central sulcus
Representative interhemispheric fiber tracts in the cortex
- Connect left and right hemispheres
- Corpus callosum
- Anterior, Posterior Commissures
Corpus callosum
Anterior, Posterior Commissures
Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex
Frontal lobe
- Where is it?
- Anterior to central sulcus
- Superior to lateral fissure
- Dorsal to temporal lobe
Frontal lobe
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary motor cortex (M1)
- Pre-central gyrus (pre/anterior to central sulcus)
Frontal lobe
- What does it do/contain?
- Prefrontal cortex
- Planning, problem solving, working memory…?
- Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- Primary olfactory cortex
- Gustatory cortex
- Prefrontal cortex
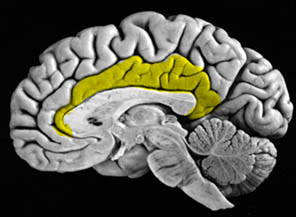
Cingulate Gyrus
Temporal lobe
- Where is it?
- Ventral to frontal, parietal lobes
- Inferior to lateral fissure
Temporal lobe
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary auditory cortex (A1)
- Object, face recognition
- Amygdala, hippocampus
- Storage of memories about events, objects
- Olfactory cortex
Parietal lobe
- Where is it?
- Caudal to frontal lobe
- Dorsal to temporal lobe
- Posterior to central sulcus
Parietal lobe
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary somatosensory cortex
- Perception of spatial relations, action planning
Post-central gyrus
- Post-central -> “posterior to” central sulcus
- Primary somatosensory cortex (S1)
Occipital lobe
- Where is it?
- Caudal to parietal & temporal lobes
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary visual cortex (V1)
Visual Cortex
Insular cortex (insula)
- Where is it?
- medial to temporal lobe
- deep inside lateral fissure
Insula
Insula
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary gustatory cortex
- self-awareness, interpersonal experiences, motor control
Lobes, landmarks, areas
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Central sulcus | Precentral gyrus | motor cortex |
| Corpus callosum | Cingulate gyrus | anterior cingulate cortex | |
| olfactory cortex | |||
| gustatory cortex |
Lobes, landmarks, areas
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal | Lateral fissure | auditory cortex | |
| olfactory cortex | |||
| hipppocampus | |||
| amygdala |
Lobes, landmarks, areas
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parietal | Central sulcus | Postcentral gyrus | somatosensory ctx |
| Occipital | visual ctx | ||
| Insula | Lateral fissure | gustatory ctx |
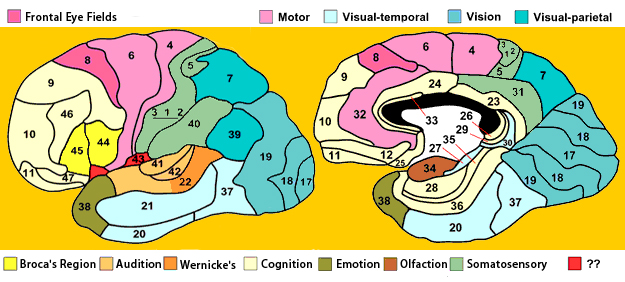
Brodmann Areas
- Korbinian Brodmann
- Cytoarchitectonic differences in cerebral cortex
Brodmann Areas
Brodmann Areas
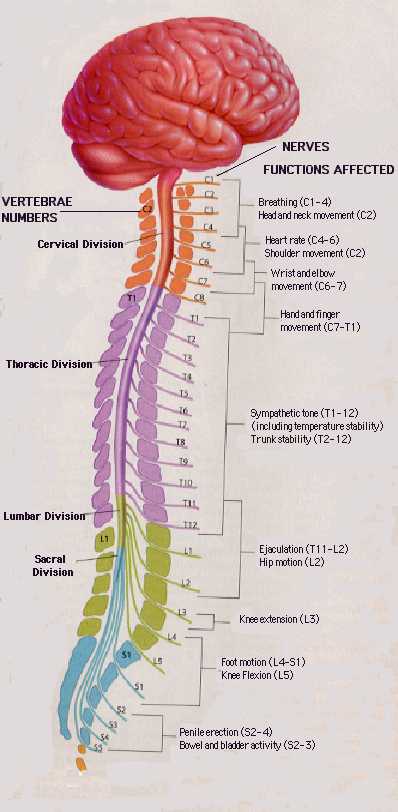
Spinal cord
- Rostral/Caudal axis
- Spinal column w/ vertebrae
- Cervical (8), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5), coccygeal (1)
- Spinal segments & 31 nerve pairs
- Cauda equina
Spinal cord
Spinal cord
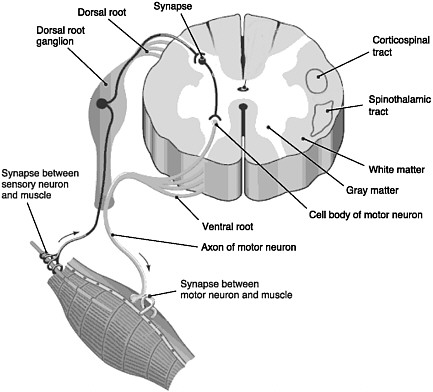
- Organization of the spinal cord
- Dorsal/Ventral
- Dorsal root (sensory)
- Ventral root (mostly motor)
- Grey (interior) vs. white matter (exterior)
- Dorsal/Ventral

Organization of the PNS
Somatic division
Autonomic division
Cranial nerves
Spinal nerves
Cranial nerves
- Afferents (input), efferents (output), or mixed
- Innervate head and neck
- Olfactory (I), optic (II), (VIII) auditory, vagus (X), etc.
- Spinal nerves
Cranial nerves
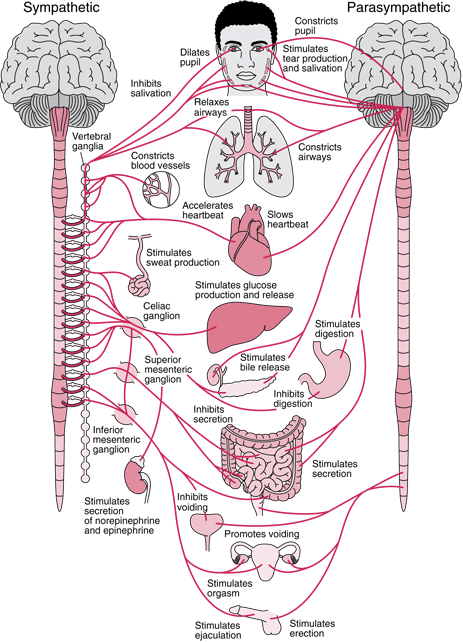
Autonomic nervous system
- CNS & PNS components
- Controls “vegetative functions”"
- Limited voluntary control
- Two divisions
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
ANS
Sympathetic division
- Prepares body for action
- “Fight or flight”"
- Spinal cord
- ganglion chain along spinal column to End organs
- NTs
- Preganglionic: ACh
- Post: NE
Parasympathetic division
- Para -> “around”
- Restorative function
- “Rest & digest”
- Spinal cord -> ganglia near end organs -> end organ
- NT: ACh
Next time…
- Quiz 1
- Neuroanatomy III
References
LeDoux, J. (2015, August 10). The Amygdala Is NOT the Brain’s Fear Center. Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/i-got-mind-tell-you/201508/the-amygdala-is-not-the-brains-fear-center