2020-09-29 08:51:19
Prelude (4:44)
Today’s Topics
- How neurons talk to one another
- Synaptic communication
In the beginning
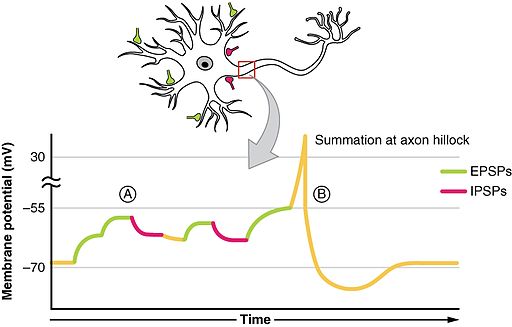
- Soma receives input from dendrites
- Axon hillock sums/integrates
- If sum > threshold, AP “fires”
Illustration of summation
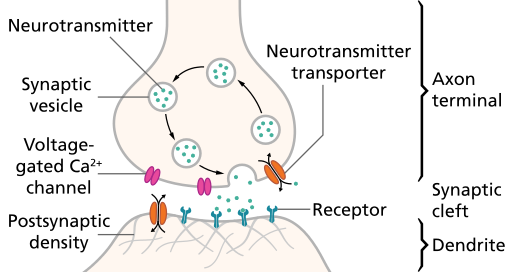
Steps in synaptic transmission
- Rapid change in voltage triggers neurotransmitter (NT) release
- Voltage-gated calcium Ca++ channels open
- Ca++ causes synaptic vesicles to bind with presynaptic membrane, merge, exocytosis
- NTs diffuse across synaptic cleft
Steps in synaptic transmission
- NTs bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane
- Receptors respond
- NTs unbind, are inactivated
Synaptic transmission
Exocytosis
Why do NTs move from presynaptic terminal toward postsynaptic cell?
- Electrostatic force pulls them
- Force of diffusion
Why do NTs move from presynaptic terminal toward postsynaptic cell?
- Electrostatic force pulls them
- Force of diffusion
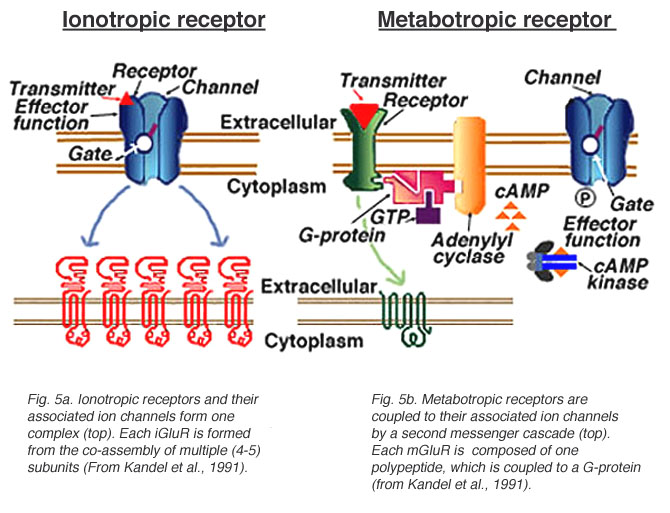
Postsynaptic receptor types
- Ionotropic (receptor + ion channel)
- Ligand-gated
- Open/close ion channel
- Ions flow in/out depending on membrane voltage and ion type
- Faster, but short-acting effects
Postsynaptic receptor types
- Metabotropic (receptor only, no attached ion channel)
- Trigger 2nd messengers
- G-proteins
- Open/close adjacent channels, change metabolism
- Slower, but longer-lasting effects
Receptor types
Receptors generate postsynaptic potentials (PSPs)
- Small voltage changes
- Amplitude scales with # of receptors activated
- Excitatory PSPs (EPSPs)
- Depolarize neuron (make more +)
- Inhibitory (IPSPs)
- Hyperpolarize neuron (make more -)
NTs inactivated
- Buffering
- e.g., glutamate into astrocytes (Anderson & Swanson, 2000)
- Reuptake via transporters
- molecules in membrane that move NTs inside
- e.g., serotonin via serotonin transporter (SERT)
- Enzymatic degradation
- e.g., AChE degrades ACh
Questions to ponder
- Why must NTs be inactivated?
Questions to ponder
- Why must NTs be inactivated?
- Keeps messages discrete, localized in time and space
What sort of PSP would opening a Na+ channel produce?
- Excitatory PSP, Na+ flows in
- Excitatory PSP, Na+ flows out
- Inhibitory PSP, Na+ flows in
- Inhibitory PSP, Na+ flows out
What sort of PSP would opening a Na+ channel produce?
- Excitatory PSP, Na+ flows in
- Excitatory PSP, Na+ flows out
- Inhibitory PSP, Na+ flows in
- Inhibitory PSP, Na+ flows out
What sort of PSP would opening a Cl- channel produce?
Remember [Cl-out]>>[Cl-in]; Assume resting potential ~60 mV
- Excitatory PSP, Cl- flows in
- Excitatory PSP, Cl- flows out
- Inhibitory PSP, Cl- flows in
- Inhibitory PSP, Cl- flows out
What sort of PSP would opening a Cl- channel produce?
Remember [Cl-out]>>[Cl-in]; Assume resting potential ~60 mV
- Excitatory PSP, Cl- flows in
- Excitatory PSP, Cl- flows out
- Inhibitory PSP, Cl- flows in
- Inhibitory PSP, Cl- flows out
Types of synapses
Types of synapses
- Axodendritic (axon to dendrite)
- Axosomatic (axon to soma)
- Axoaxonic (axon to axon)
- Axosecretory (axon to bloodstream)
Synapses on
- dendrites
- usually excitatory
- cell bodies
- usually inhibitory
- axons
- usually modulatory (change p(fire))
Summary of chemical transmission

Neurotransmiters
| Family | Neurotansmitter |
|---|---|
| Amino acids | Glutamate (Glu) |
| Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) | |
| Glycine | |
| Aspartate |
Glutamate
- Primary excitatory NT in CNS
- Role in learning (via NMDA receptor)
- Transporters on neurons and glia (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes)
- Linked to umami (savory) taste sensation, think monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Dysregulation in schizophrenia? (Javitt, 2010)
Glutamate
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to |
|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | AMPA | Na+, K+ |
| Kainate | ||
| NMDA | Ca++ | |
| Metabotropic | mGlu |
GABA
- Primary inhibitory NT in CNS
- Excitatory in developing CNS, [Cl-] in >> [Cl-] out
- Binding sites for benzodiazepines (e.g., Valium), barbiturates, ethanol, etc.
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to |
|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | GABA-A | Cl- |
| Metabotropic | GABA-B | K+ |
GABA

“GABAA-receptor-protein-example” by Chemgirl131 at English Wikipedia - Transferred from
en.wikipedia to Commons by Sreejithk2000 using CommonsHelper.. Licensed under Public Domain via Commons.
Other amino acid NTs
- Glycine
- Spinal cord interneurons
- Aspartate
- Like Glu, stimulates NMDA receptor
Acetylcholine (ACh)
- Primary NT of CNS output
- Somatic nervous system (neuromuscular junction)
- Autonomic nervous system
- Sympathetic branch: preganglionic neuron
- Parasympathetic branch: pre/postganglionic
- Inactivation by acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
ACh anatomy
Acetylcholine
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to | Blocked by |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | Nicotinic (nAChR) | Na+, K+ | e.g., Curare |
| Metabotropic | Muscarinic (mAChR) | K+ | e.g., Atropine |
Curare
Atropine
- aka, nightshade or belladonna
How to stop your prey
| Substance | Effect |
|---|---|
| Japanese pufferfish toxin | Blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels |
| Black widow spider venom | Accelerates presynaptic ACh release |
| Botulinum toxin | Prevents ACh vesicles from binding presynaptically |
| Sarin nerve gas | Impedes ACh breakdown by AChE |
| Pesticides | Impede AChE |
| Tetanus toxin | Blocks release of GABA, glycine |
Next time…
- More on NTs!
References
Anderson, C. M., & Swanson, R. A. (2000). Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia, 32(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-1136(200010)32:1<1::AID-GLIA10>3.0.CO;2-W
Javitt, D. C. (2010). Glutamatergic theories of schizophrenia. Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Sciences, 47(1), 4.