2022-02-02 09:49:34
Prelude
How to play EyeWire (03:56)
Announcements
- Exam 1 next Thursday, 2/10
- 40 questions
- Complete 1 “component/section” in EyeWire, earn 2 extra credit points.
- Take screen shot, email to Iris via Canvas
- Due before Friday, 2/11
Today’s Topics
- Cells of the nervous system
- Glia
- Neurons
- How do these cells communicate?
Cells of the nervous system
We are human
- ~ 37 trillion (10^9) (Roy & Conroy, 2018) cells
- 10-100 trillion non-human cells (gut, skin/hair, bloodstream, etc.)
How many neurons and glia?
- Old “lore”: ~100 billion neurons
- New estimate (Azevedo et al., 2009)
- ~86 +/- 8 billion neurons
- ~85 +/- 9 billion glia
- 100-500 trillion synapses, 1 billion/mm^3
Could you count to 170 billion?
- How many years to count to 170 billion?
- 60 s/min x 60 min/hr x 24 hrs/day x 365 days/ yr = 31,536,000 s/yr
- 1.7e11/31,536,000 = 5,390 years
Mass, Neurons, Non-Neurons
Non-neuronal cells by brain mass
Neurons by brain mass
Summary
- # glia+ cells scales with brain size/mass
- # neurons doesn’t scale with brain size/mass
- cerebellum small but # of neurons large
The Human Advantage

Glia (neuroglia)
- “Glia” means glue
- Functions
- Structural support
- Metabolic support
- Brain development
- Neural plasticity?
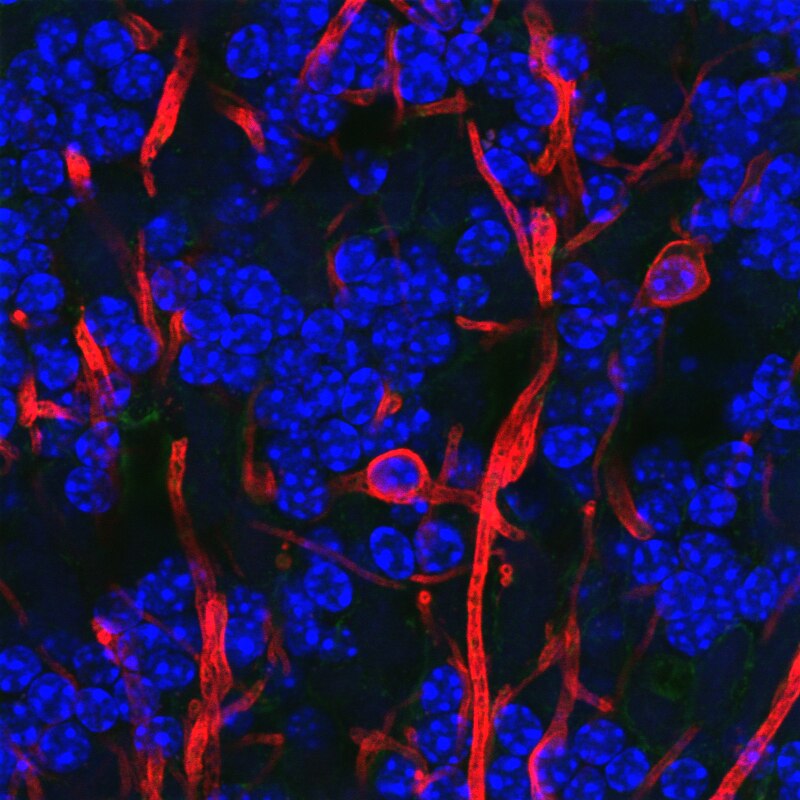
Astrocytes
- “Star-shaped”
- Physical and metabolic support
- Blood/brain barrier
- Regulate concentration of key ions (Ca++/K+) for neural communication
- Regulate concentration of key neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate)
Astrocytes
- Shape brain development, synaptic plasticity
- Regulate local blood flow (part of fMRI’s blood oxygen-dependent BOLD response)
- Regulate/influence communication between neurons, (Bazargani & Attwell, 2016)
- Disruption linked to cognitive impairment, disease (Chung, Welsh, Barres, & Stevens, 2015)
Astrocytes
Myelinating cells
- Produce myelin or myelin sheath
- White, fatty substance
- Surrounds many neurons
- The “white” in white matter
- Provide electrical/chemical insulation
- Make neuronal messages faster, less susceptible to noise
Types of myelin-producing cells
- Oligodendrocytes
- In brain and spinal cord (CNS)
- 1:many neurons
- Schwann cells
- In PNS
- 1:1 neuron
- Facilitate neuro-regeneration
- Mnemonics: COPS/SPOC
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann Cells
Microglia
- Phagocytosis
- Clean-up damaged, dead tissue
- Prune synapses in normal development and disease
- Disruptions in microglia pruning -> impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior, (Zhan et al., 2014)
Microglia
Neurons
Fun facts about neurons
- Specialized for electrical & chemical communication
- Post-mitotic – don’t divide
- Most born early in life, (Bhardwaj et al., 2006)
- Among longest-lived cells in body, may scale with organism lifespan (Magrassi, Leto, & Rossi, 2013)
- Can extend over long distances
Macrostructure of neurons
Structure of neurons
Dendrites
- Branch-like “extrusions” from cell body
- Majority of input to neuron
- Cluster close to cell body/soma
- Usually receive info
- Passive (do not regenerate electrical signal) vs. active (regenerate signal)
- Spines
Dendrites
Dendritic Spines
Soma (cell body)
- Varied shapes
- Nucleus
- Chromosomes
- Organelles
- Mitochonrdria
- Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Soma
Axons
- Another branch-like “extrusion” from soma
- Extend farther than dendrites
- Usually transmit info
Axons
- Parts
- Initial segment (closest to soma, unmyelinated)
- Nodes of Ranvier (unmyelinated segments along axon)
- Terminals, axon terminals, terminal buttons, synaptic terminals, synaptic boutons
Axons
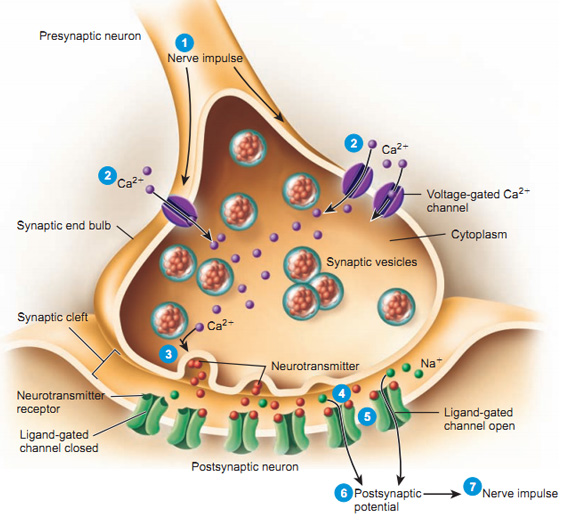
Synaptic bouton (terminal button)
- Synapse (~5-10K per neuron)
- Presynaptic membrane (sending cell) and postsynaptic (receiving cell) membrane
- Synaptic cleft – space between cells
- Synaptic vesicles
- Pouches of neurotransmitters
- Autoreceptors (detect NTs); transporters (transport NTs across membrane)
Synaptic bouton (terminal button)
Classifying neurons
- Functional role
- Input (sensory), output (motor/secretory), interneurons
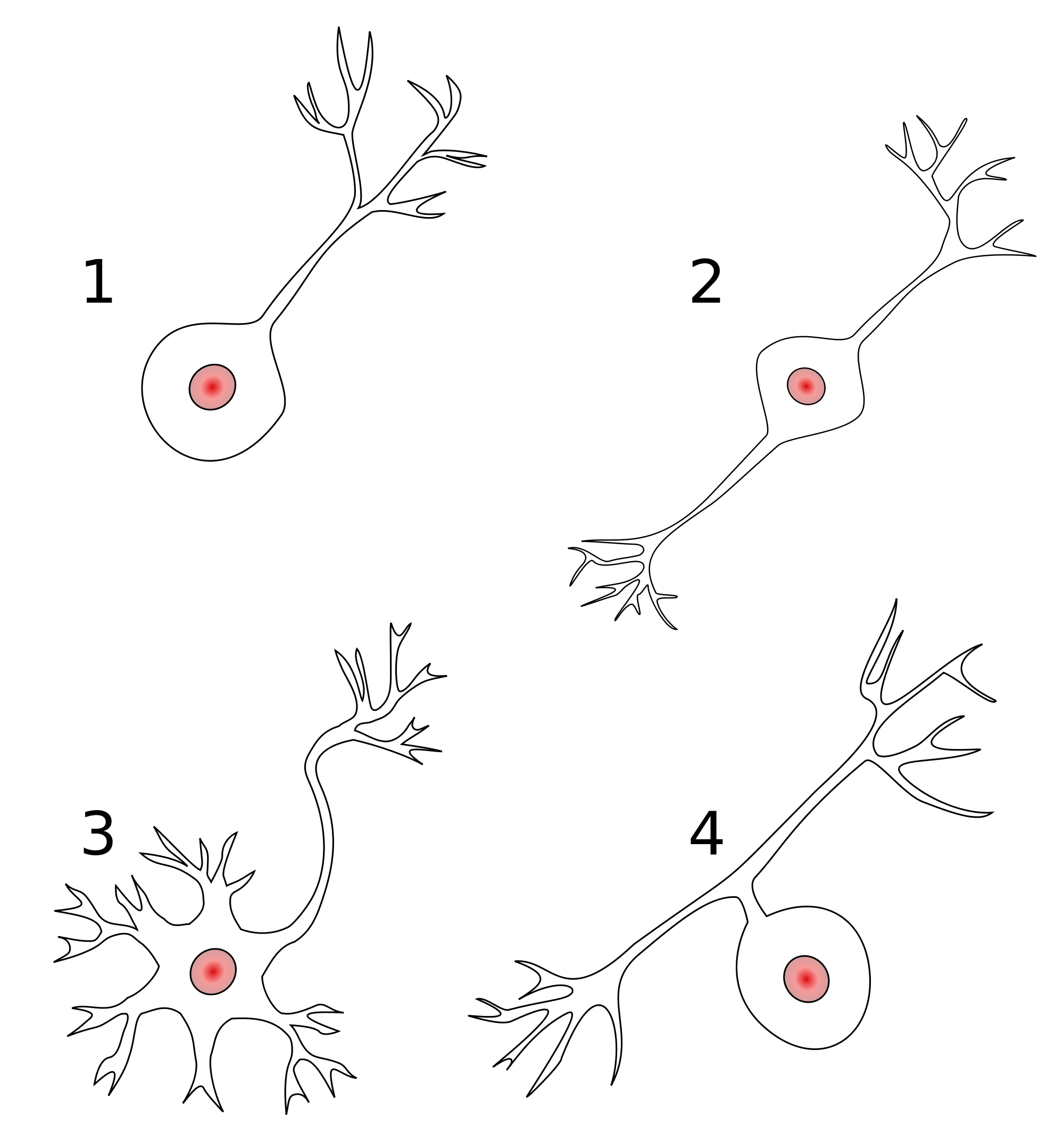
- Anatomy
- Unipolar
- Bipolar
- Multipolar
Classifying neurons
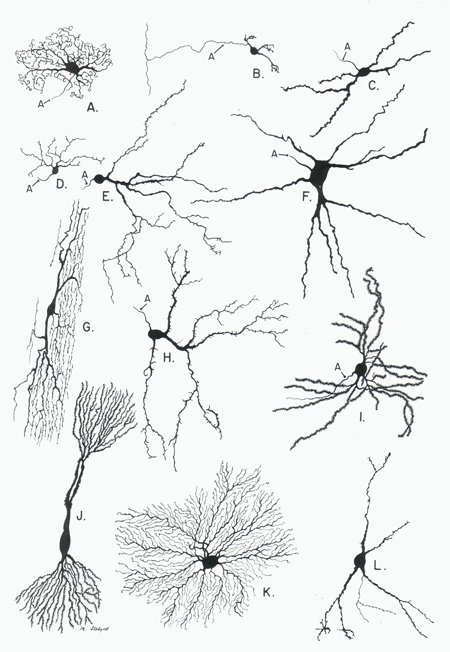
- By specific anatomy
- Pyramidal cells
- Stellate cells
- Purkinje cells
- Granule cells
Neurons by type
Next time
- How neurons communicate
References
Azevedo, F. A., Carvalho, L. R., Grinberg, L. T., Farfel, J. M., Ferretti, R. E., Leite, R. E., … others. (2009). Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 513(5), 532–541.
Bazargani, N., & Attwell, D. (2016). Astrocyte calcium signaling: The third wave. Nature Neuroscience, 19(2), 182–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4201
bbscottvids. (2009, September). Neuronal migration. Youtube. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t-8bxeWqSV4
Bhardwaj, R. D., Curtis, M. A., Spalding, K. L., Buchholz, B. A., Fink, D., Björk-Eriksson, T., … Frisén, J. (2006). Neocortical neurogenesis in humans is restricted to development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(33), 12564–12568. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605177103
Chung, W.-S., Welsh, C. A., Barres, B. A., & Stevens, B. (2015). Do glia drive synaptic and cognitive impairment in disease? Nature Neuroscience, 18(11), 1539–1545. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4142
Magrassi, L., Leto, K., & Rossi, F. (2013). Lifespan of neurons is uncoupled from organismal lifespan. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(11), 4374–4379. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217505110
Roy, A. L., & Conroy, R. S. (2018). Toward mapping the human body at a cellular resolution. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 29(15), 1779–1785. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E18-04-0260
Zhan, Y., Paolicelli, R. C., Sforazzini, F., Weinhard, L., Bolasco, G., Pagani, F., … Gross, C. T. (2014). Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nature Neuroscience, 17(3), 400–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3641