- Resting potential maintained by balance of forces (diffusion, electrostatic)
- Action potential generated when balance is altered
- \([Na^+]\) in: rising phase to + peak
- \([K^+]\) out: falling phase
2022-02-03 07:31:17
Prelude (4:20)
Prelude (2:33)
Announcements
- Exam 1 Thursday, 2/10
- 40 questions
- No in-person/in-class meeting
- On Canvas, live at 3:05 PM; open until 10:00 PM
Today’s Topics
- Electrical communication in neurons
- The action potential
How do neurons communicate?
Types of neural electrical potentials
- Resting potential
- Voltage across neuronal membrane when cell is ‘at-rest’ (not firing)
- Action potential
- Voltage across neuronal membrane when cell is active or firing
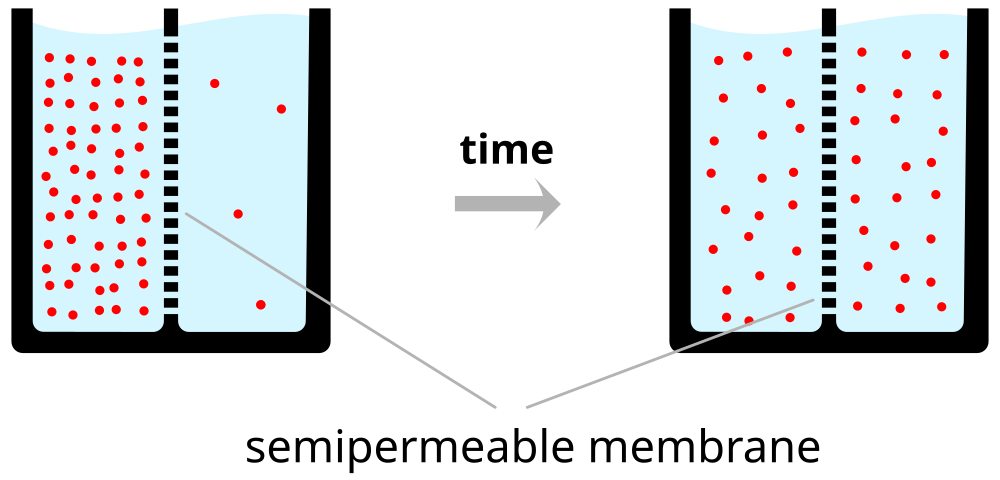
Where does the resting potential come from?
- Ions (charged particles)
- Ion channels
- Separation between charges
- A balance of forces
We are the champIONs, my friend
- Potassium, \(K^+\)
- Sodium, \(Na^+\)
- Chloride, \(Cl^-\)
- Organic anions, \(A^-\)
Party On
- Annie (\(A^-\)) was having a party.
- Used to date Nate (\(Na^+\)), but now sees Karl (\(K^+\))
- Hired bouncers called
- “The Channels”
- Let Karl and friends in or out, keep Nate out
- Annie’s friends (\(A^-\)) and Karl’s (\(K^+\)) mostly inside
- Nate and friends (\(Na^+\)) mostly outside
- Claudia (\(Cl^-\)) tagging along
Resting potential arises from
- A balance of forces
- Force of diffusion
- Electrostatic force
- Forces cause ion flows across membrane
- Force of diffusion consistent (over time)
- Electrostatic force changes
- Ion channels allow ion flow
Ion channels
- Openings in neural membrane
- Selective for specific ions
- Vary in permeability (how readily ions flow)
- Types
- Passive/leak (always open)
- Voltage-gated
- Ligand-gated (chemically-gated)
- Transporters/pumps
Ion channels
Neuron at rest permeable to \(K^+\)
- Permeable: Permits flow across/through
- Passive \(K^+\) channels open
- [\(K^+\)] concentration inside >> outside
- \(K^+\) flows out
- Neuron constantly brings \(K^+\) in
Force of diffusion
Force of diffusion
Neuron at rest permeable to \(K^+\)
- Organic anions (\(A^-\)) too large to move outside of cell
- \(A^-\) and \(K^+\) largely in balance == no net internal charge
- \(K^+\) outflow creates charge separation: \(K^+\) (outside) <-> \(A^-\) (inside)
- Charge separation creates a voltage
- Outside +/inside -
- Voltage build-up stops outflow of \(K^+\)
The resting potential
Balance of forces in the neuron at rest
- Force of diffusion
- \(K^+\) moves from high concentration (inside) to low (outside)
Balance of forces in the neuron at rest
- Electrostatic force
- Voltage build-up stops \(K^+\) outflow
- Specific voltage that stops flow == equilibrium potential for \(K^+\)+
- \(K^+\) positive, so equilibrium potential negative (w/ respect to outside)
- Equilibrium potential close to neuron’s resting potential
Equilibrium potential and Nernst equation
Equilibrium potentials calculated under typical conditions
| Ion | [inside] | [outside] | Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(K^+\) | ~150 mM | ~4 mM | ~ -90 mV |
| \(Na^+\) | ~10 mM | ~140 mM | ~ +55-60 mV |
| \(Cl^-\) | ~10 mM | ~110 mM | - 65-80 mV |
Neuron resting potential ≠ \(K^+\) equilibrium potential
- Resting potential not just due to \(K^+\)
- Other ions flow
- Resting potential == net effects of all ion flows across membrane
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation
\(Na^+\) role
- \(Na^+\) concentrated outside neuron
- Membrane at rest not very permeable to \(Na^+\)
- Some, but not much \(Na^+\) flows in
- \(Na^+\) has equilibrium potential ~ + 60 mV
- Equilibrium potential is positive (with respect to outside)
- Would need positive interior to keep \(Na^+\) from flowing in
Electrical circuit model
Summary of forces in neuron at rest
| Ion | Concentration gradient | Electrostatic force | Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(K^+\) | Inside >> Outside | - (pulls \(K^+\) in) | Higher |
| \(Na^+\) | Outside >> Inside | - (pulls \(Na^+\) in) | Lower |
What happens if something changes?
- Easier for Karl [\(K^+\)] to exit?
- Easier for Nate [\(Na^+\)] to enter?
- Some action!
Action potential
Phases of the action potential
- Threshold of excitation
- Increase (rising phase/depolarization)
- Peak
- at positive voltage
- Decline (falling phase/repolarization)
- Return to resting potential (refractory period)
Action potential break-down
| Phase | Neuron State |
|---|---|
| Rise to threshold | + input makes membrane potential more + |
| Rising phase | Voltage-gated \(Na^+\) channels open, \(Na^+\) flows in |
| Peak | Voltage-gated \(Na^+\) channels close and deactivate; voltage-gated \(K^+\) channels open |
| Falling phase | \(K^+\) flows out |
| Refractory period | \(Na^+\)/\(K^+\) pump restores [\(Na^+\)], [\(K^+\)]; voltage-gated \(K^+\) channels close |
What’s a \(Na^+\)/\(K^+\) pump?
- Enzyme – \(Na^+\)/\(K^+\) ATP-ase – embedded in neuron membrane
- Pumps \(Na^+\) and \(K^+\) against concentration gradients
- \(Na^+\) out; \(K^+\) in
- Uses adensosine triphosphate (ATP) form of chemical energy
Example in another domain
Refractory periods
- Absolute
- Cannot generate action potential (AP) no matter the size of the stimulus
- Voltage-gated \(Na^+\) channels inactivated, reactivate in time.
Refractory periods
- Relative
- Can generate AP with larg(er) stimulus
- Some voltage-gated \(K^+\) channels still open
- Refractory periods put ‘spaces’ between APs
Generating APs
- Axon hillock
- Portion of soma adjacent to axon
- Integrates/sums input to soma
- Axon initial segment
- Umyelinated portion of axon adjacent to soma
- Voltage-gated \(Na^+\) and \(K^+\) channels exposed
- If sum of input to soma > threshold, voltage-gated \(Na^+\) channels open
Axon hillock, axon initial segment

Axon Hillock” by M.aljar3i - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Commons
Nodes of Ranvier
- Regenerate action potential
- \(Na^+\) and \(K^+\) channels exposed to extracellular environment
- Between Nodes of Ranvier, ions can’t move out, so move along
- Nodes of Ranvier -> Action potentials faster & reliable for a given diameter
Main points
Next time
- More on the action potential
- Review for Exam 1