Neurochemistry II
2025-10-07
Rick Gilmore
Department of Psychology
Prelude
– Netflix (2025)
Today’s topics
- Wrap-up on synapses
- Neurotransmitters
Warm-up
What ion flows into the presynaptic terminal and triggers neurotransmitter release when the action potential arrives?
- A. potassium, \(K^+\)
- B. organic anions, \(A^-\)
- C. calcium, \(Ca^{++}\)
- D. chloride, \(Cl^-\)
What ion flows into the presynaptic terminal and triggers neurotransmitter release when the action potential arrives?
A. potassium, \(K^+\)B. organic anions, \(A^-\)- C. calcium, \(Ca^{++}\)
D. chloride, \(Cl^-\)
What ion flows into the presynaptic terminal and triggers neurotransmitter release when the action potential arrives?
A. potassium, \(K^+\)flows out not inB. organic anions, \(A^-\)doesn’t flow in or out- C. calcium, \(Ca^{++}\)
D. chloride, \(Cl^-\)flows in, but doesn’t trigger NT release
What ways are neurotransmitters inactivated after they bind with a postsynaptic receptor?
- A. Buffering (e.g., by astrocytes)
- B. Chemical breakdown (enzymatic degradation)
- C. Reuptake (into presynaptic terminal)
- D. All of the above
What ways are neurotransmitters inactivated after they bind with a postsynaptic receptor?
- A. Buffering (e.g., by astrocytes)
- B. Chemical breakdown (enzymatic degradation)
- C. Reuptake (into presynaptic terminal)
- D. All of the above
What sort of PSP would opening a Na+ channel produce?
- Na+ flows in, so Excitatory PSP (EPSP)
- Na+ flows out, so Excitatory PSP (EPSP)
- Na+ flows in, so Inhibitory PSP (IPSP)
- Na+ flows out, so Inhibitory PSP (IPSP)
What sort of PSP would opening a Na+ channel produce?
- Na+ flows in, so Excitatory PSP (EPSP)
Na+ flows out, so Excitatory PSP (EPSP)Na+ flows in, so Inhibitory PSP (IPSP)Na+ flows out, so Inhibitory PSP (IPSP)
Why must NTs be inactivated?
- Or what would happen if they weren’t?
- Or weren’t quickly?
- Concentration gradient wouldn’t be large
- NT flow would be altered
Synapses
Types of synapses
General synapse properties
Neurotransmitters
What are they?
What are they?
Amino acids
| Family | Neurotansmitter |
|---|---|
| Amino acids | Glutamate (Glu) |
| Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) | |
| Glycine | |
| Aspartate |
Amino acids
| Family | Neurotansmitter |
|---|---|
| Amino acids | Glutamate (Glu) |
| Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) | |
| Glycine | |
| Aspartate |
Glutamate
- Primary excitatory NT in CNS (~ 1/2 all synapses)
- Role in learning (via NMDA receptor)
- Transporters on neurons and glia (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes)
- Linked to umami (savory) taste sensation, think monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Dysregulation in schizophrenia McCutcheon, Krystal, & Howes (2020), mood disorders (Małgorzata, Paweł, Iwona, Brzostek, & Andrzej, 2020)
Glutamate
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to |
|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | AMPA | Na+, K+ |
| Kainate | ||
| NMDA | Ca++ | |
| Metabotropic | mGlu |
\(\gamma\)-aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
- Primary inhibitory NT in CNS
- Binding sites for benzodiazepines (e.g., Valium), barbiturates, ethanol, etc.
- Synthesized from glutamate
- Inactivated by transporters
GABA
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to |
|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | GABA-A | Cl- |
| Metabotropic | GABA-B | K+ |
What PSP will occur if we open a K+ channel?
- K+ flows out, so excitatory (EPSP)
- K+ flows out, so inhibitory (IPSP)
What PSP will occur if we open a K+ channel?
K+ flows out, so excitatory (EPSP)- K+ flows out, so inhibitory (IPSP)
Other amino acid NTs
- Glycine
- Spinal cord interneurons
- Also inhibitory
- Aspartate
- Like Glu, stimulates NMDA receptor
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Acetylcholine (ACh)
- Autonomic nervous system
- Sympathetic branch: preganglionic neuron
- Parasympathetic branch: pre/postganglionic
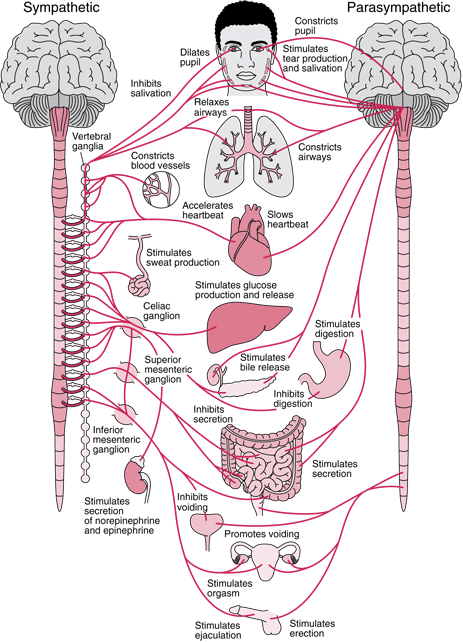
Acetylcholine
| Type | Receptor | Esp Permeable to | Blocked by |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic | Nicotinic (nAChR) | Na+, K+ | e.g., Curare |
| Metabotropic | Muscarinic (mAChR) | K+ | e.g., Atropine |
Curare

Atropine
- also known as (aka), nightshade or belladonna
- blocks ACh receptors in muscles of the iris

Many ways to paralyze your prey
| Substance | Effect |
|---|---|
| Japanese pufferfish toxin | Blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels |
| Black widow spider venom | Accelerates presynaptic ACh release |
| Botulinum toxin (BoTox) | Prevents ACh vesicles from binding presynaptically |
Many ways to paralyze your prey
| Substance | Effect |
|---|---|
| Sarin nerve gas | Impedes ACh breakdown by AChE |
| Pesticides | Impede AChE |
| Tetanus toxin | Blocks release of GABA, glycine |
Monoamines
| Family | Neurotansmitter |
|---|---|
| Monoamines | Dopamine (DA) |
| Norepinephrine (NE)/Noradrenaline (NAd) | |
| Epinephrine (Epi)/Adrenaline (Ad) | |
| Serotonin (5-HT) | |
| Melatonin | |
| Histamine |
Dopamine (DA)
- Released by two pathways
- Both originate in the midbrain tegmentum

Dopamine (DA)
- Substantia nigra -> striatum, meso-striatal projection
- Ventral tegmental area (VTA) -> nucleus accumbens, ventral striatum, hippocampus, amygdala, cortex; meso-limbo-cortical projection

Dopamine (DA)
- Disruption linked to
- Parkinson’s Disease (mesostriatal)
- DA agonists treat (agonists facilitate/increase transmission)
- Schizophrenia (mesolimbocortical)
- DA antagonists treat
- Addiction (mesolimbocortical)
- ADHD (mesolimbocortical)
- Parkinson’s Disease (mesostriatal)
Dopamine (DA)
- Inactivated by
- Chemical breakdown
- Dopamine transporter (DAT)

Dopamine (DA)
| Type | Receptor | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Metabotropic | D1-like (D1 and D5) | more prevalent |
| D2-like (D2, D3, D4) | target of many antipsychotics (drugs that treat schizophrenia symptoms) |
Dopamine (DA)
- Not the pleasure or motivation NT
- One function: signals differences between predicted and actual outcomes

Norepinephrine (NE)
- Role in arousal, mood, eating, sexual behavior
- Released by
- locus coeruleus in pons/caudal tegmentum
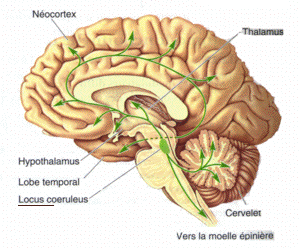
Norepinephrine (NE)
- Released by Sympathetic branch of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) onto targets in PNS

Norepinephrine (NE)
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inactivates monoamines in neurons, glial cells
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) increase NE, DA
- Inhibiting inactivation ~
-(-1) = + 1
- Inhibiting inactivation ~
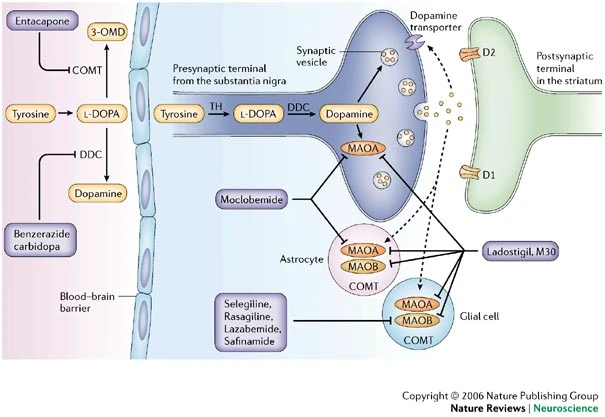
Norepinephrine (NE)
- MAO-Is early treatment for depression, but side effects (dry mouth, nausea, headache, dizziness)

Norepinephrine (NE)
| Type | Receptor | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Metabotropic | \(\alpha\) (1,2) | antagonists treat anxiety, panic |
| \(\beta\) (1,2,3) | ‘beta blockers’ in cardiac disease |
Serotonin (5-HT)
- Released by raphe nuclei in brainstem
- Role in mood, sleep, eating, pain, nausea, cognition, memory
- Modulates release of other NTs

Serotonin (5-HT)
- Most of body’s 5-HT neurons regulate digestion
- via Enteric Nervous System (in PNS)
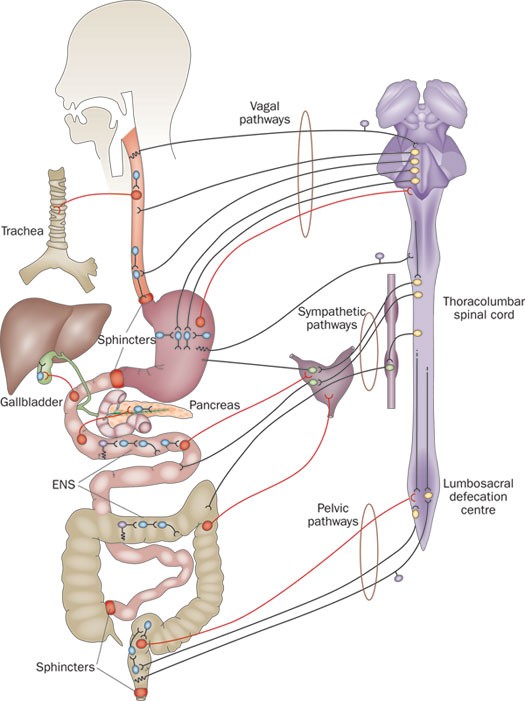
Serotonin (5-HT)
- 5-HT receptors
- Seven families (5-HT 1-7) with 14 types
- All but one metabotropic
Serotonin (5-HT)
- Ecstasy (MDMA) disturbs serotonin
- So does LSD
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI)
- Inhibits reuptake -> increases extracellular concentration
- Treats depression, panic, eating disorders, others
- 5-HT3 receptor antagonists are anti-mimetics used in treating nausea
Melatonin
- Hormone released by pineal gland into bloodstream
- Concentrations vary over the day, peak near bedtime
- Release regulated by inputs from hypothalamus

Key points about monoamines
- Monoamine neurotransmitters–DA, NE, 5-HT–modulate activity of other neurons
- Monoamines are released from specific areas in midbrain and hindbrain
- Monoamines project widely throughout the CNS
- Monamines are inactivated chemically and via transporters
Key points about monoamines
- Many drugs that treat psychiatric illness affect monoamines
- Most monoamines activate metabotropic receptors
Next time
- Wrap-up on neurochemistry
- Hormones
Resources
About
This talk was produced using Quarto, using the RStudio Integrated Development Environment (IDE), version 2025.5.1.513.
The source files are in R and R Markdown, then rendered to HTML using the revealJS framework. The HTML slides are hosted in a GitHub repo and served by GitHub pages: https://psu-psychology.github.io/psych-260-2025-fall/
References
Bell, V. (2013, February 3). The unsexy truth about dopamine. The Guardian. The Guardian. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/science/2013/feb/03/dopamine-the-unsexy-truth
Furness, J. B. (2012). The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 9(5), 286–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.32
Małgorzata, P., Paweł, K., Iwona, M. L., Brzostek, T., & Andrzej, P. (2020). Glutamatergic dysregulation in mood disorders: Opportunities for the discovery of novel drug targets. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 24(12), 1187–1209. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2020.1836160
McCutcheon, R. A., Krystal, J. H., & Howes, O. D. (2020). Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: Biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry: Official Journal of the World Psychiatric Association, 19(1), 15–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20693
McHugh, P. C., & Buckley, D. A. (2015). Chapter eleven - the structure and function of the dopamine transporter and its role in CNS diseases. In G. Litwack (Ed.), Vitamins & hormones (Vol. 98, pp. 339–369). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2014.12.009
Netflix, S. W. (2025). Dr. Jane Goodall’s final message to the world | famous last words | netflix. YouTube. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lfLKHY52ERc
Youdim, M. B. H., Edmondson, D., & Tipton, K. F. (2006). The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 7(4), 295–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1883

PSYCH 260.001 | © Rick Gilmore under CC BY 4.0



