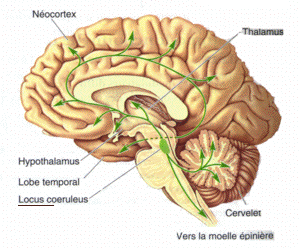
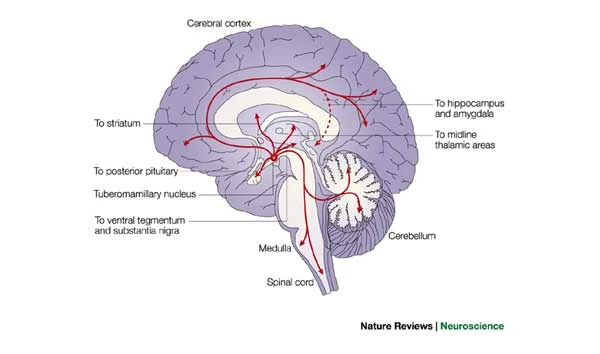
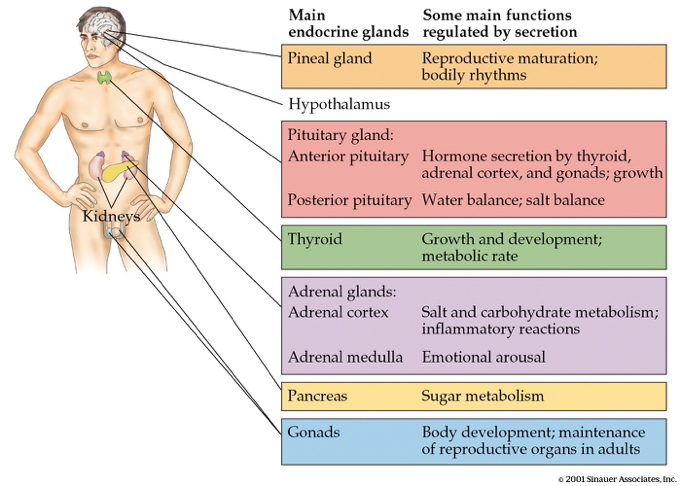
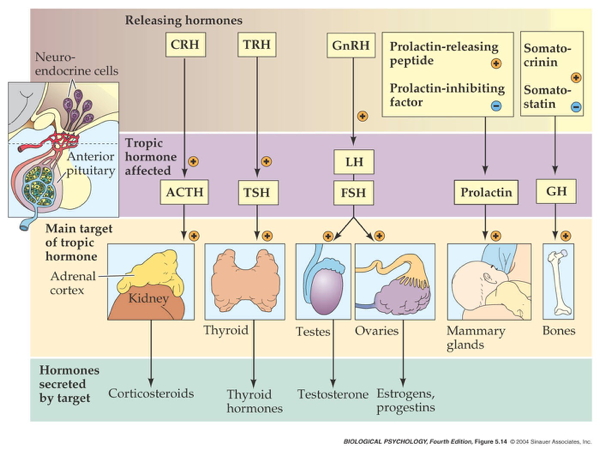
Deussing, J. M., & Chen, A. (2018). The
Corticotropin-Releasing Factor family: Physiology of the stress response.
Physiological Reviews,
98(4), 2225–2286.
https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00042.2017
Domes, G., Heinrichs, M., Kumbier, E., Grossmann, A., Hauenstein, K., & Herpertz, S. C. (2013). Effects of intranasal oxytocin on the neural basis of face processing in autism spectrum disorder.
Biological Psychiatry,
74(3), 164–171. https://doi.org/
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.02.007
Haas, H., & Panula, P. (2003). The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system.
Nature Reviews. Neuroscience,
4(2), 121–130.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1034
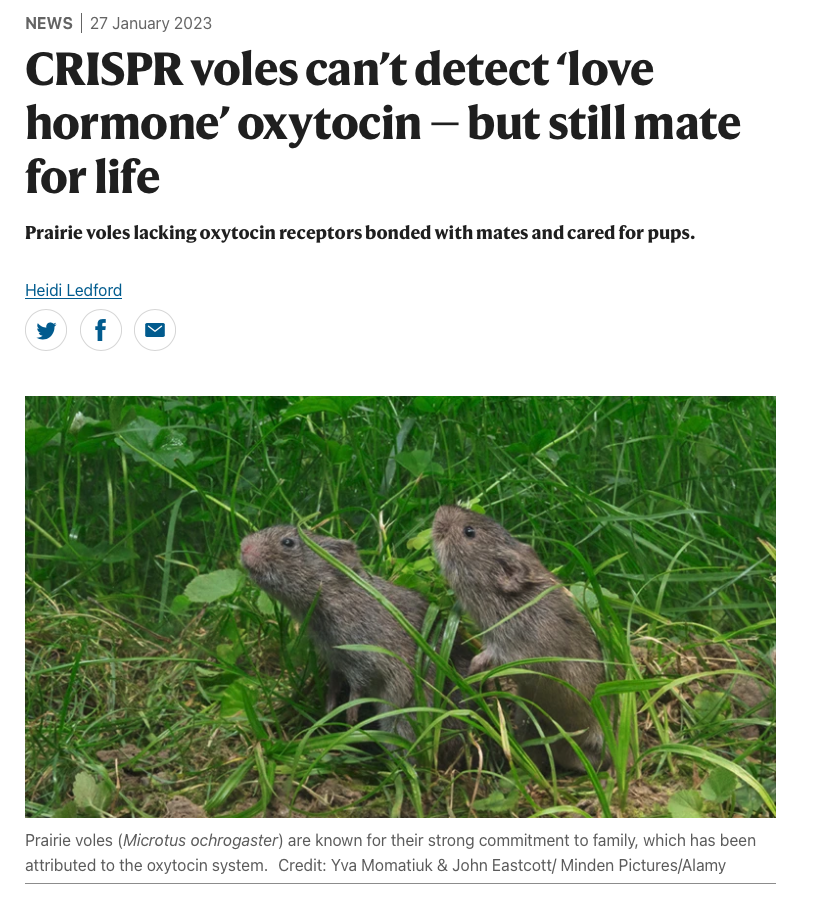
Ledford, H. (2023, January 27).
CRISPR voles can’t detect
“love hormone” oxytocin — but still mate for life.
https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-00197-9
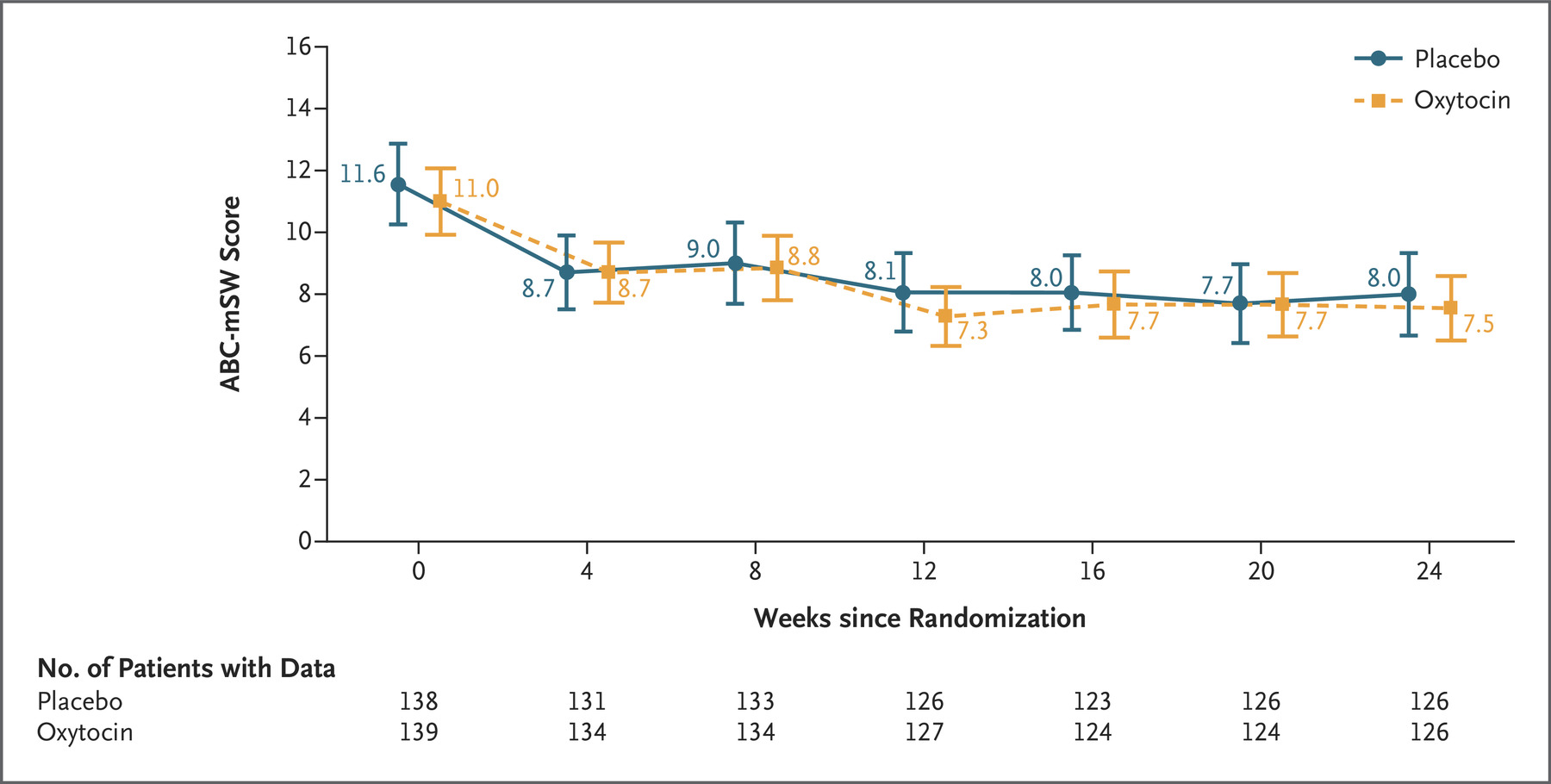
Sikich, L., Kolevzon, A., King, B. H., McDougle, C. J., Sanders, K. B., Kim, S.-J., … Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. (2021). Intranasal oxytocin in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.
The New England Journal of Medicine,
385, 1462–1473.
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2103583
Songs, M. (2018).
Muppet songs: Mahna mahna (muppet show - 1976). You
Tube. Retrieved from
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TbZ_hTEOKZc
Weisman, O., & Feldman, R. (2013). Oxytocin effects on the human brain: Findings, questions, and future directions.
Biological Psychiatry,
74(3), 158–159. https://doi.org/
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.026