- Wrap-up on neurotransmitters
- Quiz 2 on Friday.
- Review Exam 1 on Friday.
2017-02-15 08:39:37
Today's Topics
Black widow spider venom causes paralysis by impeding the normal function of which neurotransmitter system?
- Glutamate (Glu)
- GABA (GABA)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
Black widow spider venom causes paralysis by impeding the normal function of which neurotransmitter system?
- Glutamate (Glu)
- GABA (GABA)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
- ionotropic
- voltage-gated
- nicotinic
- metabotropic
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
- ionotropic
- voltage-gated
- nicotinic
- metabotropic
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
ionotropicvoltage-gatedvoltage gated Na+, K+, and Ca++nicotinicACh binds to nAChR; ACh not a monoamine- metabotropic
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
- Cl-; IPSP
- K+; IPSP
- Glutamate; EPSP
- GABA; EPSP
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
- Cl-; IPSP
- K+; IPSP
- Glutamate; EPSP
- GABA; EPSP
The outward flow of this ion across the neural membrane creates what kind of PSP?
Cl-; IPSPOutward Cl- -> inside less negative = EPSP- K+; IPSP Make inside less positive
Glutamate; EPSPGlu not an ion; transported acrossGABA; EPSPGABA not an ion; transported across
Serotonin (5-HT)
- Released by raphe nuclei in brainstem
- Role in mood, sleep, eating, pain, nausea, cognition, memory
- Modulates release of other NTs
- Most of body's 5-HT regulates digestion
5-HT anatomy
5-HT receptors
- Seven families (5-HT 1-7) with 14 types
- All but one metabotropic
5-HT clinical significance
- Ecstasy (MDMA) disturbs serotonin
- So does LSD
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI)
- Inhibits reuptake -> increases extracellular concentration
- Treats depression, panic, eating disorders, others
- 5-HT3 receptor antagonists are anti-mimetics used in treating nausea
Melatonin
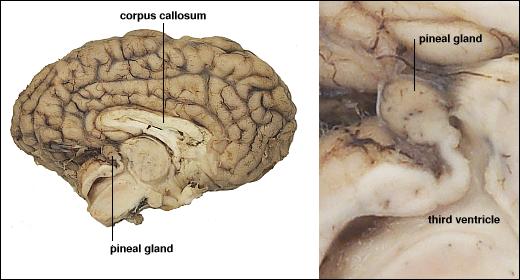
- Released by pineal gland into bloodstream
Pineal gland

By Images are generated by Life Science Databases(LSDB). - from Anatomography, website maintained by Life Science Databases(LSDB). You can get this image through URL below. 次のアドレスからこのファイルで使用している画像を取得できます URL., CC BY-SA 2.1 jp, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=7855244
Histamine
- In brain, released by hypothalamus, projects to whole brain
- Metabotropic receptors
- Role in arousal/sleep regulation
- In body, part of immune response
Other NTs
- Gases
- Nitric Oxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO)
- Neuropeptides
- Substance P and endorphins (endogenous morphine-like compounds) have role in pain
- Orexin/hypocretin, project from lateral hypothalamus across brain, regulate appetite, arousal
Other NTs
- Neuropeptides (continued)
- Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates digestion
- Oxytocin and vasopressin released by posterior hypothalamus onto posterior pituitary, regulate social behavior
Non-chemical communication between neurons
- Gap junctions
- Electrical coupling
- Connect cytoplasm directly
- Fast, but fixed, hard to modulate
- Examples, retina, cardiac muscle
Gap junctions
Ways to think about synaptic communication
- Specificity: point-to-point vs. broadcast
- Direct vs. modulatory
- Agonists vs. antagonists
Agonists vs. Antagonists
- Agonists
- bind to receptor
- mimic action of endogenous chemical
- Antagonists
- bind to receptor
- block/impede action of endogenous chemical
Valium is a GABA-A receptor agonist. This means:
- It decreases inhibition
- It activates a metabotropic Cl- channel
- It facilitates/increases inhibition
- It blocks an ionotropic channel
Valium is a GABA-A receptor agonist. This means:
- It decreases inhibition
- It activates a metabotropic Cl- channel
- It facilitates/increases inhibition
- It blocks an ionotropic channel
Next time…
- Quiz 2
- Go over Exam 1