2017-03-03 08:59:16
Prelude
Prelude
Today's Topics
- Evolution and U.S. public attitudes
- The evolution of the human brain
Public acceptance of evolution
Principles of evolution
- Life forms existing in the Earth's past differed from those living today
- New generations of life forms inherit properties from their predecessors
- New life forms evolved as a result of mutations, selection pressures, and geological events
- Greater survival/reproductive success for some, not others
Types of evidence
- Fossil
- Fossil dating
- Geological
- Where fossils are found relative to one another
- How long it takes to form layers
- Genetic
- Rates of mutation
- Anatomical

Dobzhansky
- "Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution"
Dobzhansky
- "Seen in the light of evolution, biology is, perhaps, intellectually the most satisfying and inspiring science. Without that light, it becomes a pile of sundry facts some of them interesting or curious, but making no meaningful picture as a whole."
Why Gilmore thinks it's controversial (in the U.S.)
- Contradicts verbatim/non-metaphorical reading of some religious texts
- Makes humans seem less special
- Time scales involved beyond human experience
- Scientific method vs. other ways of knowing
- Found in nature ≠ good for human society
Why Gilmore thinks it's controversial (in the U.S.)
- Few negative consequences of 'disbelief'

Why Gilmore thinks it's controversial (in the U.S.)
- U.S. culture individualistic, skeptical
- Lower levels of religious belief among U.S. scientists
- Politics
How we got here
The dawn of time

History of life on Earth
Time scales
Cambrian Explosion
What sparked the explosion? (Fox 2016)
- Behavior requires energy
- Behavior requires perception at a distance
- Behavior requires action
What behaviors are essential for animals to perform?
- Ingestion
- Defense
- Reproduction
What behaviors are essential for animals to perform
- Perception at a distance
- Locomotion
- Object manipulation/consumption
- Signaling/communication
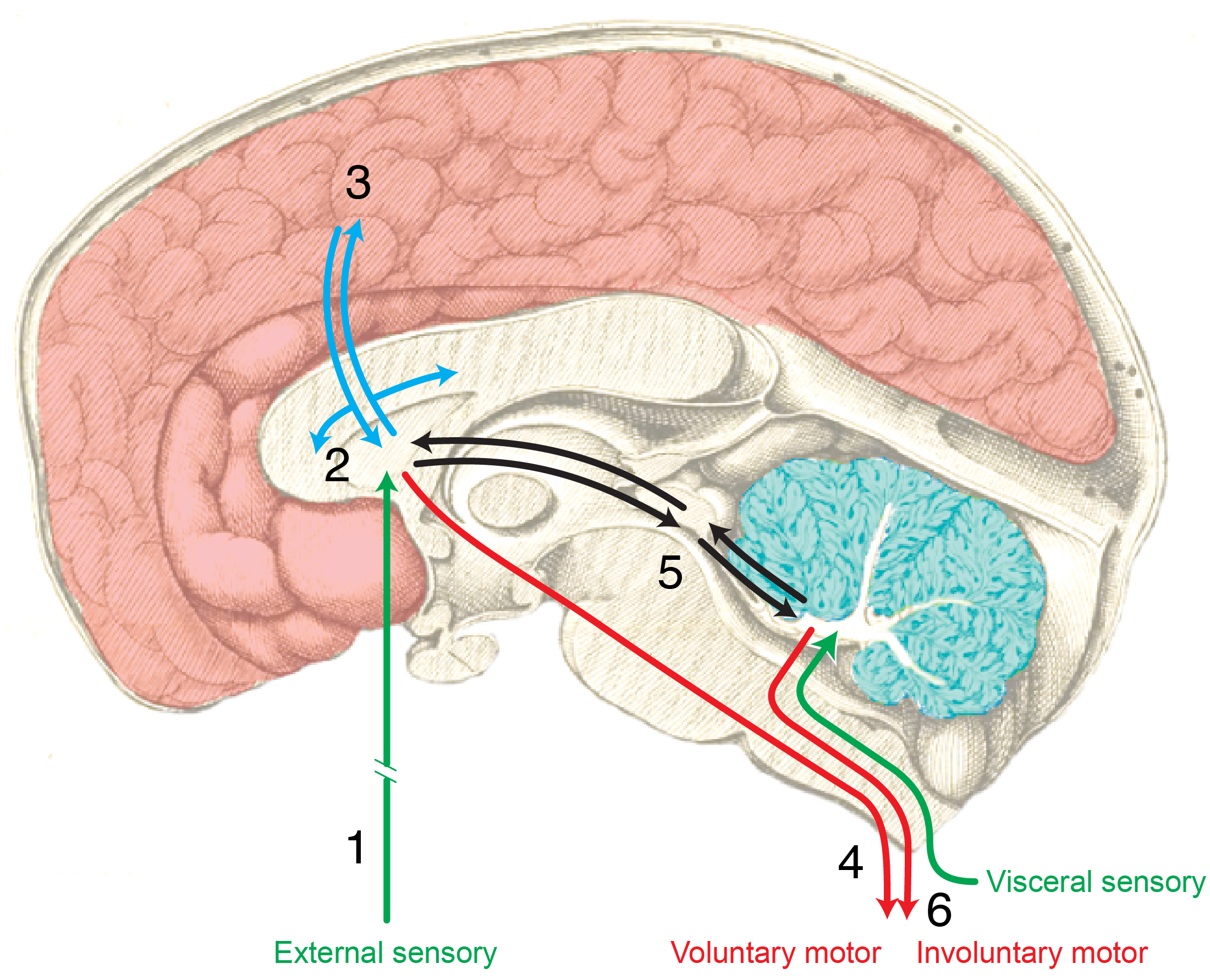
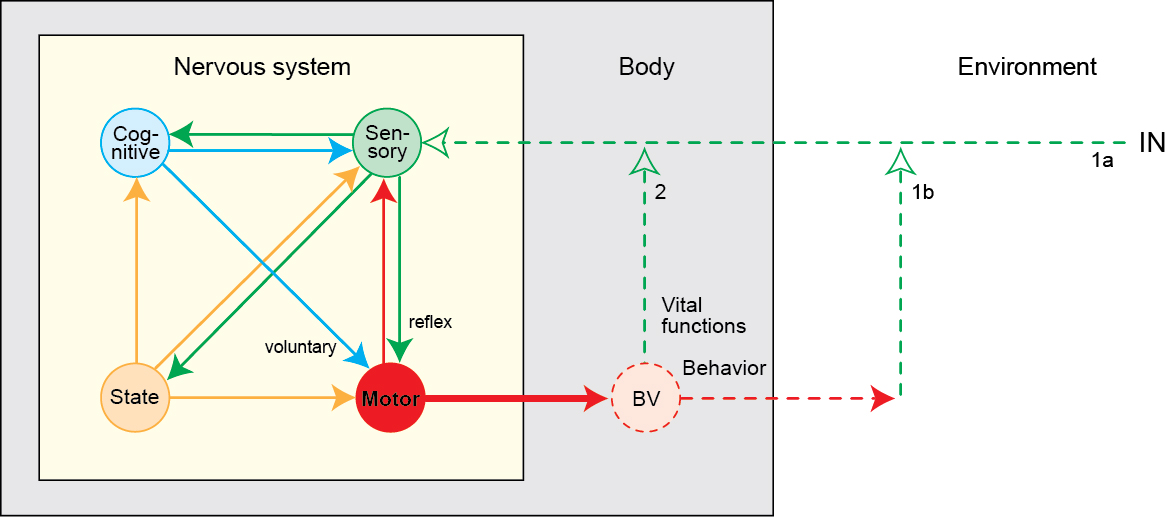
How is the nervous system organized to contribute to these behaviors?
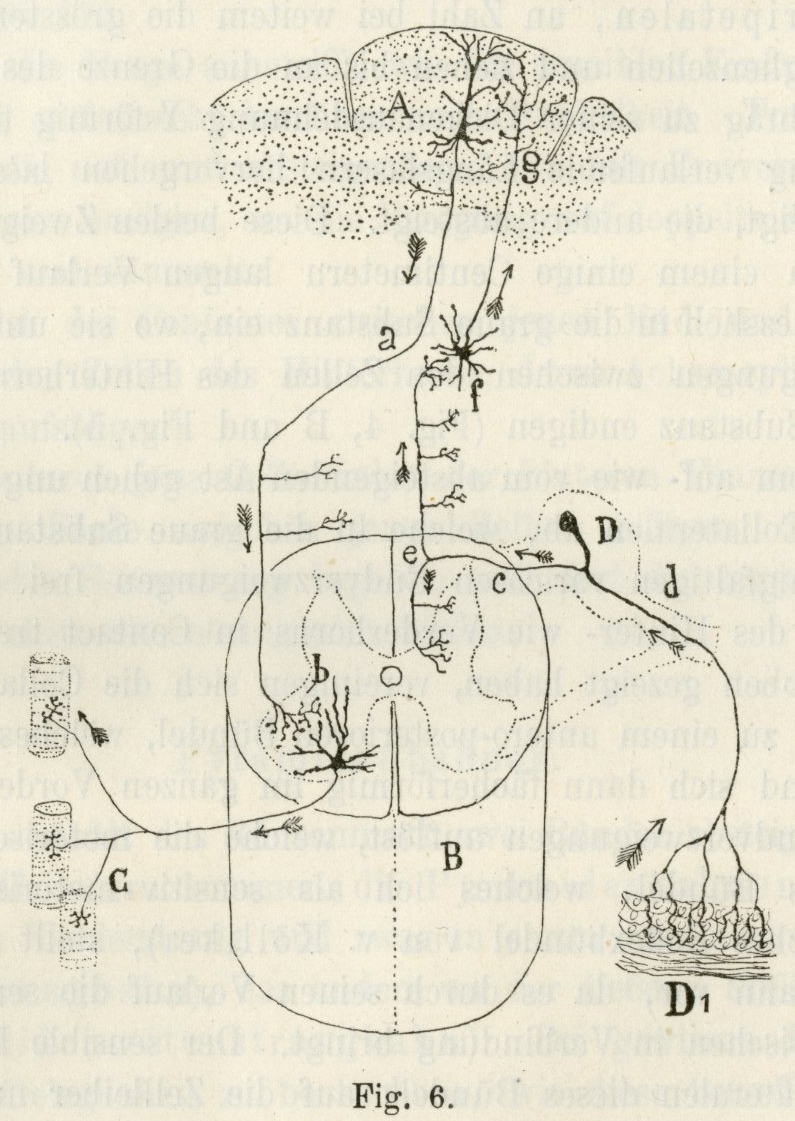
Cajal
Swanson/Cajal Four Systems
How nervous systems differ
- Body symmetry
- radial
- bilateral
- Segmentation
- Centralized vs. distributed function
- Cephalization
- Encasement in bone (vertebrates)
(Arendt, Tosches, and Marlow 2016)
(Arendt, Tosches, and Marlow 2016)
Cellular/molecular mechanisms
- Similarities in patterns of early nervous system development across vastly different species
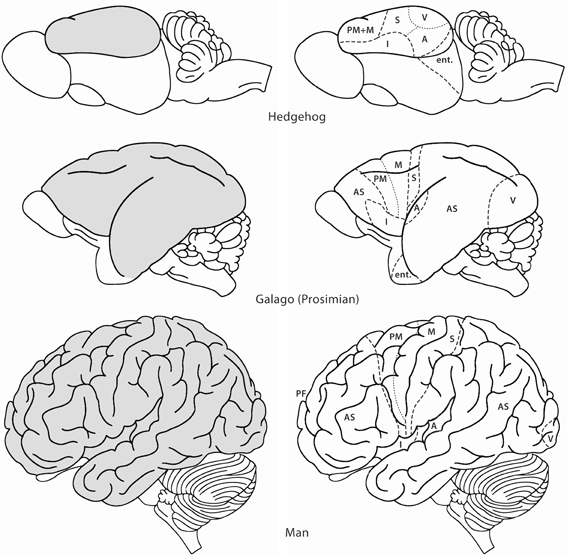
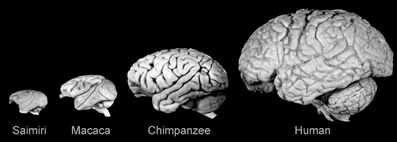
Comparing brain structures
Comparing brain structures
- Vertebrates have similar brain plans
- Species differ in relative size of parts
Brain sizes differ by vertebrate groups
Comparing brain sizes
Brain sizes across vertebrate groups
- Brain size scales with body size
- Mammals and birds have big brains
- Some animals have big brains for their bodies
- Humans
- Crows
- Porpoises
Cortical size within groups
Evolutionary trends in cortical size
| Structural measure | Non-human comparison | Human |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical gray matter %/tot brain vol | insectivores 25% | 50% |
| Cortical gray + white | mice 40% | 80% |
| Cerebellar mass | primates, mammals 10-15% | 10-15% |
Evolutionary trends in cortical size
Evolutionary trends in primate brain size
Evolutionary trends
- In primates, including humans
- Smaller olfactory bulbs
- Cerebellum comparable to other mammals
- Larger cerebral cortex
Selection pressures
- Natural and sexual selection for
- Traits that improve reproductive success
- Physical AND psychological traits
- Hardware and software
Samsung Galaxy S6

Apple iPhone 6s Plus

Virtues of big phones/brains
- More storage
- More processing capacity
- Better sensors
- Better output
- More, better apps
- Do more, faster
Costs of big brains
- Long time to build
- Lots of energy to nourish/maintain
- Long time to program/train/educate
- Head/neck must be strong enough to carry
- How to connect widely, but process info quickly
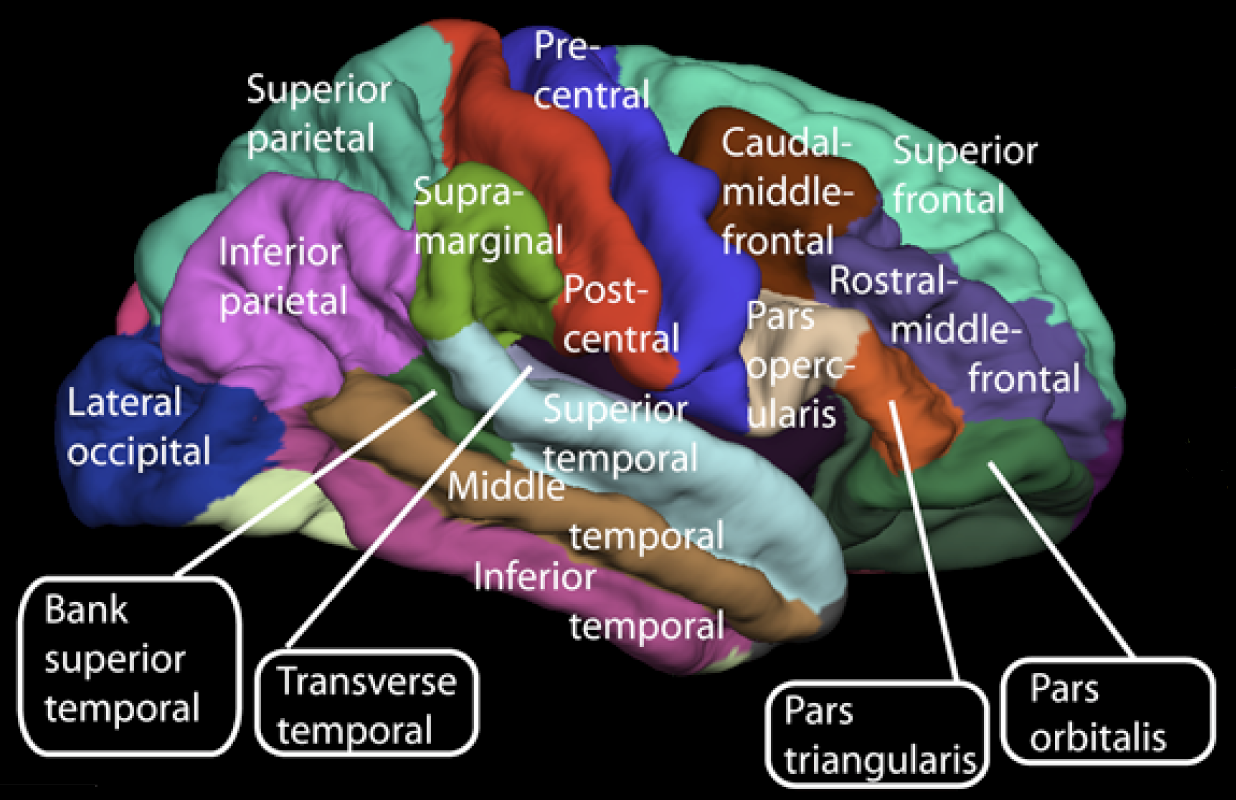
Human brains have
- Significant "folding"
- Dense interconnections
- Large "association" areas
- Large cerebral cortex
- High levels of myelination
Ways human brains differ
- Larger than body size of comparable mammals
- Large cerebral cortex
- Large-scale folding (gyri and sulci)
- Large cortical association areas
- Not primary sensory or motor areas
Association areas
How did it get this way?
- Build upon mammalian/primate norms
- Prolonged (in time) pattern of development
- Specialized pattern of development
- Significant time post-natal/pre-reproductive (childhood)
References
Arendt, Detlev, Maria Antonietta Tosches, and Heather Marlow. 2016. “From Nerve Net to Nerve Ring, Nerve Cord and Brain — Evolution of the Nervous System.” Nature Reviews Neuroscience 17 (1): 61–72. doi:10.1038/nrn.2015.15.
Dobzhansky, Theodosius. 1973. “Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution.” The American Biology Teacher 35 (3). University of California Press on behalf of the National Association of Biology Teachers: pp. 125–29. http://www.jstor.org/stable/4444260.
Fox, Douglas. 2016. “What Sparked the Cambrian Explosion?” Nature 530 (7590): 268–70. doi:10.1038/530268a.
Hofman, Michel A. 2014. “Evolution of the Human Brain: When Bigger Is Better.” Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 8 (March). doi:10.3389/fnana.2014.00015.
Miller, Jon D, Eugenie C Scott, and Shinji Okamoto. 2006. “Public Acceptance of Evolution.” SCIENCE-NEW YORK THEN WASHINGTON- 313 (5788). American Association for the Advancement of Science: 765. doi:10.1126/science.1126746.
Northcutt, R. Glenn. 2002. “Understanding Vertebrate Brain Evolution.” Integrative and Comparative Biology 42 (4): 743–56. doi:10.1093/icb/42.4.743.
Rakic, Pasko. 2009. “Evolution of the Neocortex: A Perspective from Developmental Biology.” Nature Reviews Neuroscience 10 (10). Nature Publishing Group: 724–35. doi:10.1038/nrn2719.