Neuroanatomy I
2025-09-94
Department of Psychology
Prelude
ctdalilah (2006)
Kids Learning Tube (2015)
Today’s topics
- Announcement
- Warm up
- Wrap up on functional methods
- Anatomy of the brain
Announcement
- Quiz 1 next Thursday, September 11
Warm up
Which of the following is not a functional neuroscience method?
- A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI/MRI)
- B. functional MRI (fMRI)
- C. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- D. Single-unit recording
Which of the following is not a functional neuroscience method?
- A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI/MRI)
B. functional MRI (fMRI)C. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)D. Single-unit recording
Which of the following methods measures electromagnetic fields?
- A. Event-related potentials (ERP)
- B. Electroencephalography (EEG)
- C. Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- D. All of the above
Which of the following methods measures electromagnetic fields?
- A. Event-related potentials (ERP)
- B. Electroencephalography (EEG)
- C. Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- D. All of the above
Why is fMRI an indirect measure of brain activity?
- A. fMRI measures change in blood oxygen that stem from activity several seconds earlier
- B. fMRI measures electrical activity of individual neurons
- C. fMRI measures things inside the head
Why is fMRI an indirect measure of brain activity?
- A. fMRI measures changes in blood oxygen that stem from activity several seconds earlier
- B.
fMRI measures electrical activity of individual neurons - C.
fMRI measures things inside the head
Wrap-up on functional methods
Functional methods
Anatomy of the brain
Brain anatomy through dance
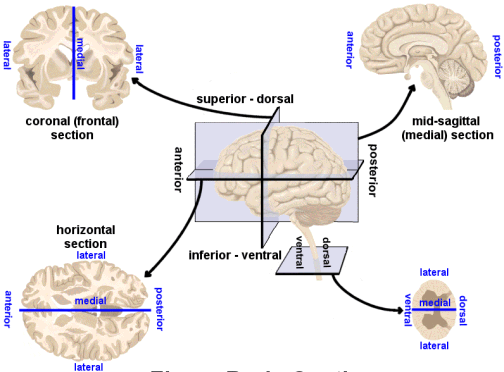
Directional terms
- Anterior/Posterior -> front/back
- Medial/Lateral -> inside/outside
- Superior/Inferior -> upward/downward

Directional terms
- Dorsal/Ventral -> back-ward/belly-ward
- Rostral/Caudal -> head-ward/tail-ward

Planar (slice) terms
- Brain is 3D but view in 2D
- Horizontal/Axial
- Coronal/Transverse/Frontal
- Sagittal (from the side)
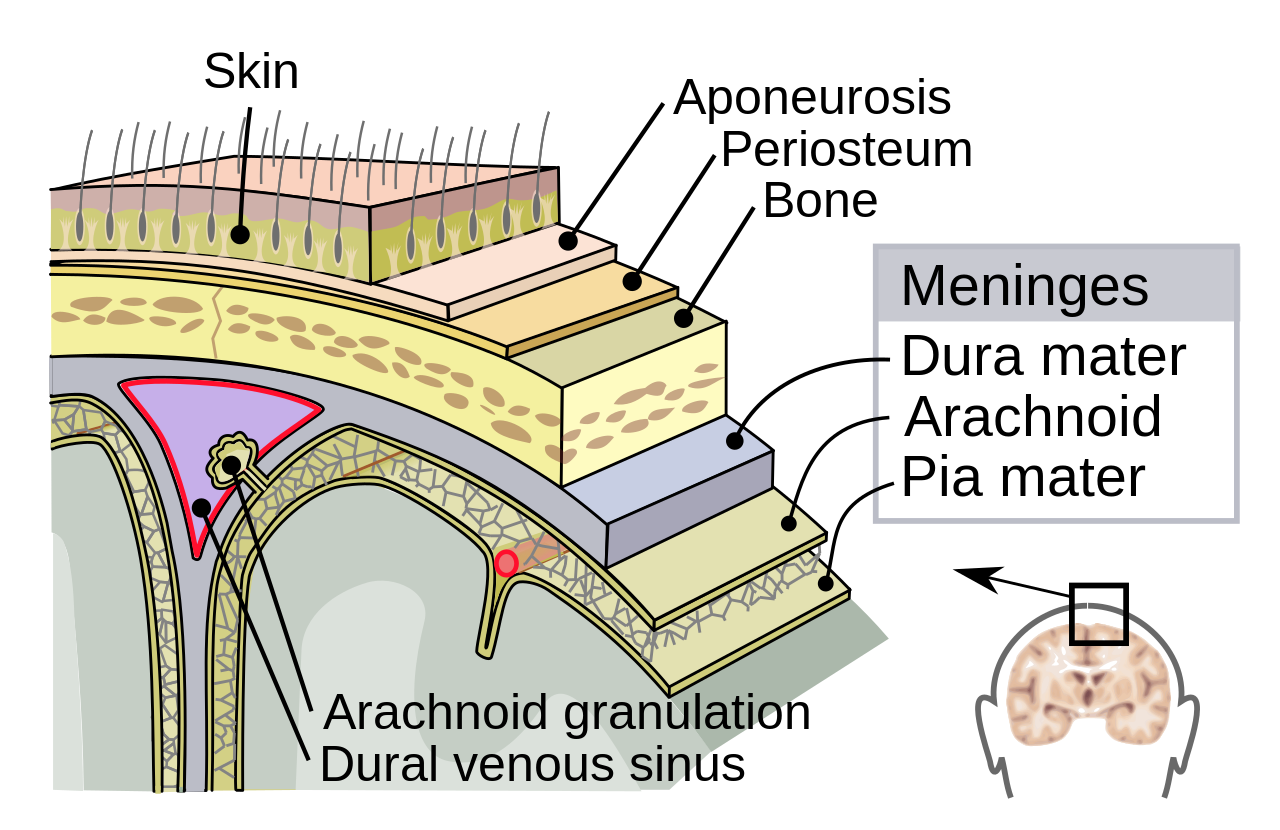
Supporting structures
- Meninges
- Cerebral Ventricles
- Blood supply
- Blood/brain barrier
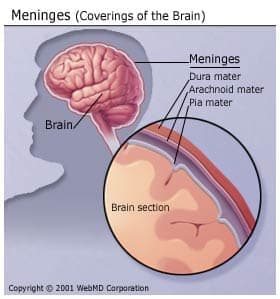
Meninges
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater/membrane
- Subarachnoid space
- Pia mater
Clinical relevance
Q: What disease is associated with inflammation of (e.g., ‘-itis’) of the meninges?
Cerebral Ventricles
- Lateral (1st & 2nd)
- 3rd
- Cerebral aqueduct
- 4th
- Ventricles are filled with Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)

Clinical relevance
Hydrocephalus can occur there is a blockage in the flow of CSF through the cerebral ventricles.

Blood Supply
- Arteries
- external & internal carotid; vertebral -> basilar
- Circle of Willis
- anterior, middle, & posterior cerebral
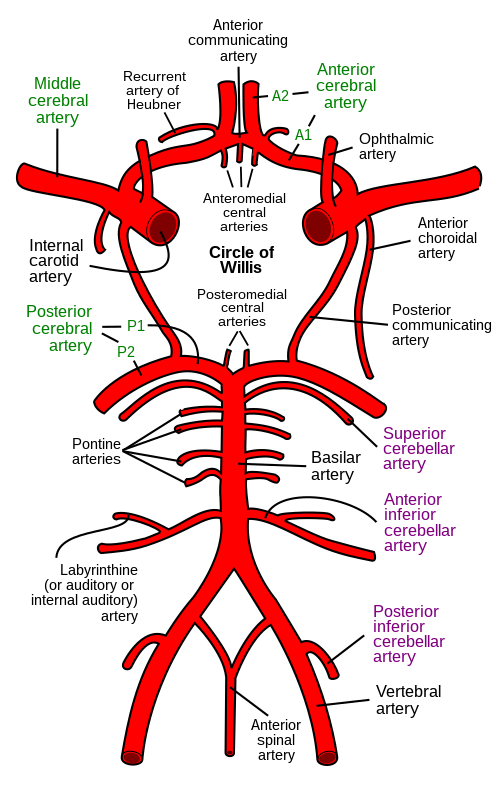
Note
The Circle of Willis helps equalize blood pressures among the ascending arteries from the heart.
Blood/brain barrier
- Isolates CNS from blood stream
- Tighly packed endothelial cells form blood vessel walls
- Astrocytes (a glial cell) participate in transporting substances to the brain
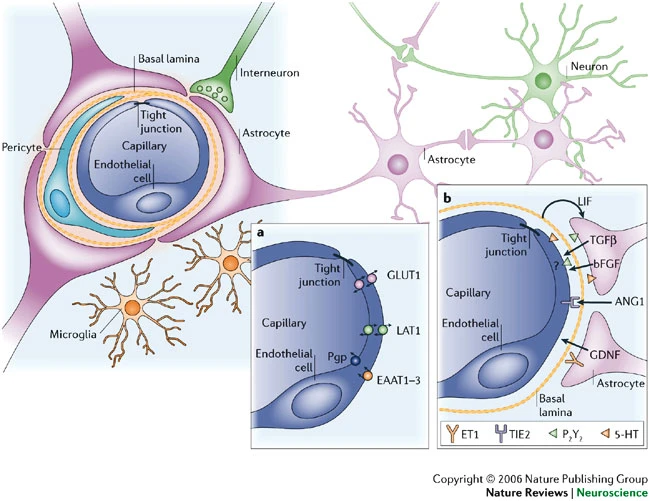
Blood/brain barrier
- Exception is Area Postrema
- In brainstem (see AP in the figure below)
- Blood-brain barrier thin
- Detects toxins, evokes vomiting (emesis)
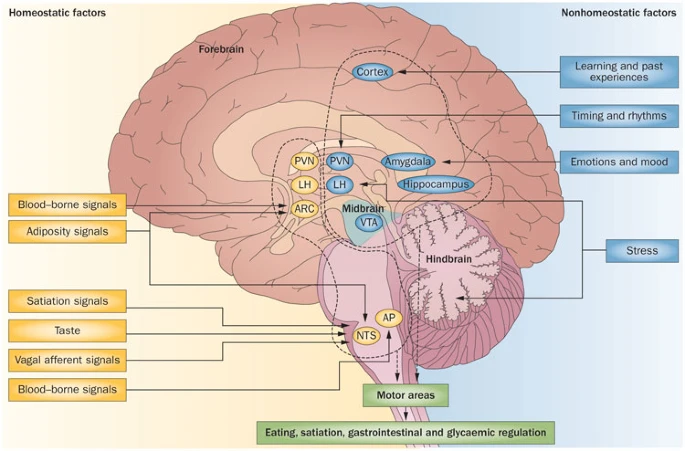
The Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Everything encased in bone
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Everything else!ent

Interactive brain atlas
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, Amygdala |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, Tegmentum |
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain | 4th | Rhombencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Medulla oblongata |
Note
Some of these terms arise from the developmental stages of the human embryo.

Components of the brain
Hindbrain
- Structures adjacent to 4th ventricle 1

Medulla oblongata
- Fibers of passage (to/from spinal cord)
- Cranial nerves VI-XII
- Cardiovascular regulation
- Muscle tone

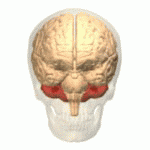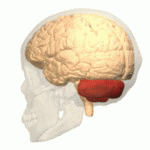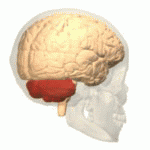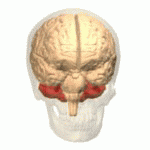
Cerebellum
- “Little brain”
- Dorsal to pons
- Movement coordination, classical conditioning (associative learning), + ???
- 3D atlas

Pons
- Bulge on brain stem
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Relay to cerebellum
- Cranial nerve V

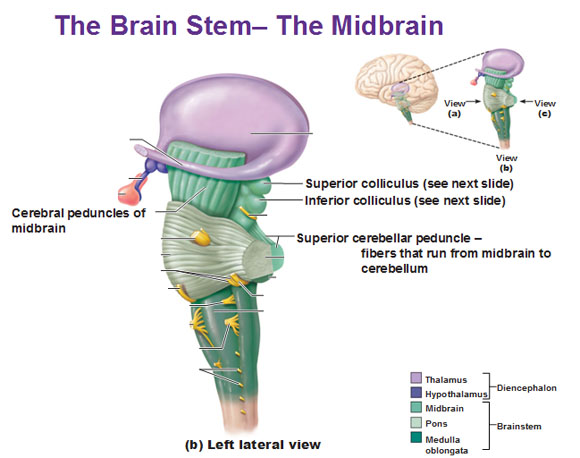
Midbrain
Midbrain
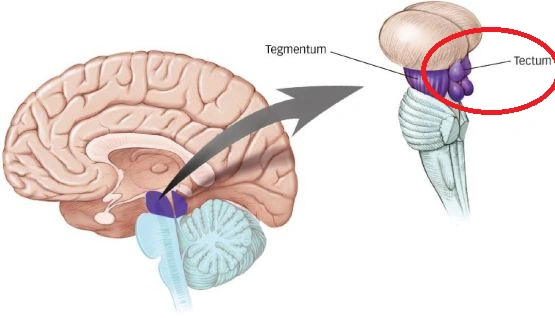
- Tectum
- Tectum -> “roof”
- Superior colliculus (reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears)
- Inferior colliculus (sound/auditory processing)
- Tegmentum
- Tegmentum -> “floor”
- Species-typical movement sequences (e.g., cat: hissing, pouncing)
- Cranial nerves III, IV
Midbrain
- Tectum
- Tectum -> “roof”
- Superior colliculus (reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears)
- Inferior colliculus (sound/auditory processing)
- Tegmentum
- Nuclei that release modulatory neurotransmitters (“neuromodulators”)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- Nuclei that release modulatory neurotransmitters (“neuromodulators”)
Pineal gland
- Releases melatonin (hormone) into bloodstream
- Does not inflate the muscles (sorry Descartes)
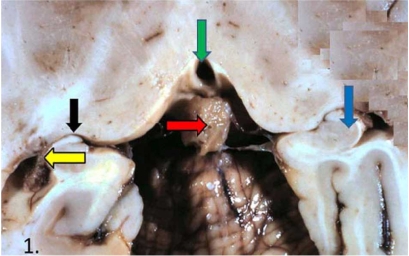
Forebrain

https://www.simplypsychology.org/forebrain-midbrain-hindbrain.html
Diencephalon (“between” brain)
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus

Thalamus
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
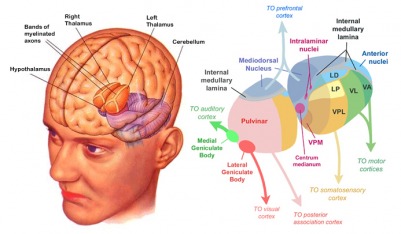
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Sympathetic branch
- Parasympathetic branch

Hypothalamus
- Controls endocrine system via pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- Posterior (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin

Hypothalamus
- Regulates circadian rhythms (via Suprachiasmatic Nucleus)

Telencephalon
- Basal (not basil!) ganglia
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
- Skill and habit learning
- Sequencing of movement
- Example: Parkinson’s Disease
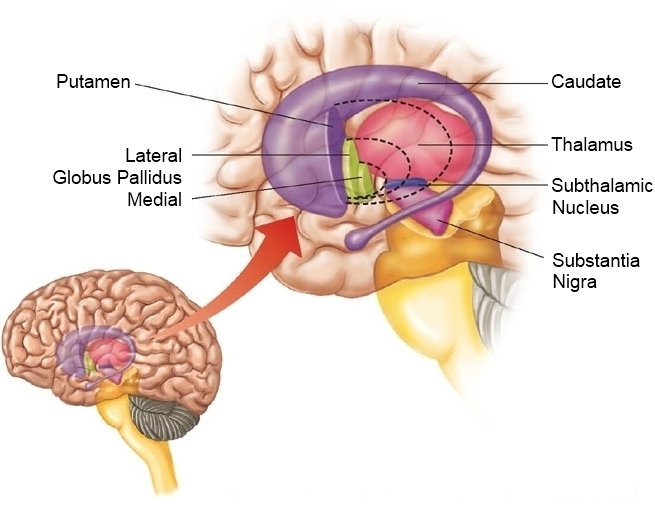
Basal ganglia
- Striatum
- Dorsal
- Ventral

Basal ganglia
- Globus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Substantia nigra (in tegmentum){preview-link=“true”}

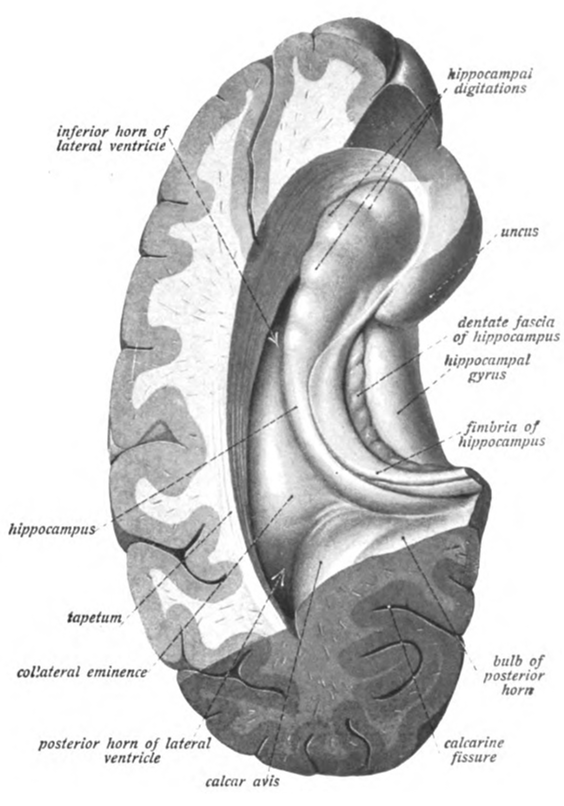
Hippocampus
- From Greek for “sea horse”
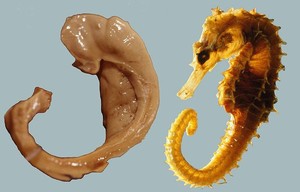
Hippocampus
- Immediately lateral to (inferior) lateral ventricles
- Medial temporal lobe
- Memories of specific facts or events, spatial locations
- Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease
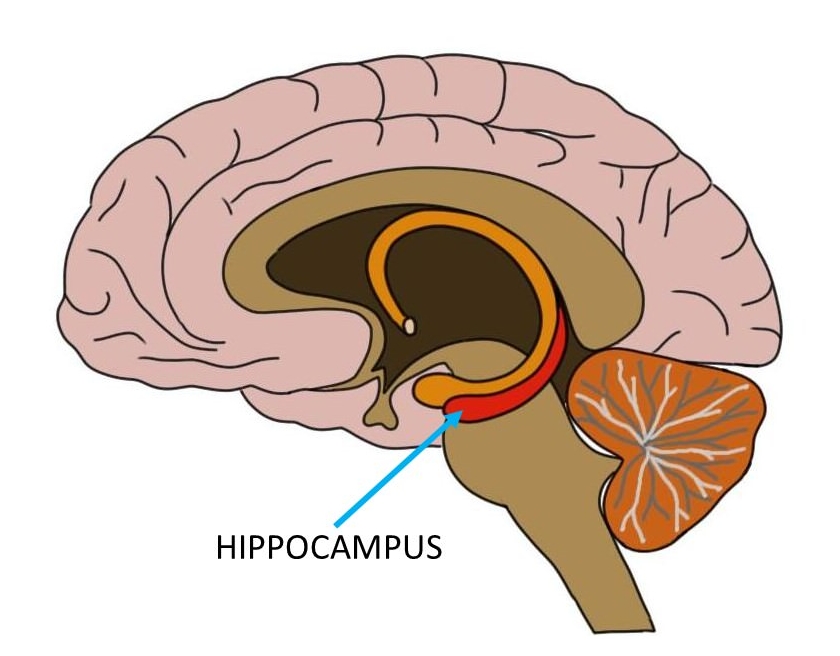
Hippocampus
- Fornix projects to hypothalamus
- Mammillary bodies
Amygdala
- “almond”-shaped
- Influences physiological state, behavioral readiness, affect
- NOT the fear center! (LeDoux, 2015).

Take homes
- CNS (encased in bone) vs. PNS
- Structures defined relative to others using specific anatomical terms
Next time
- Neuroanatomy II – the cerebral cortex
Resources
About
This talk was produced using Quarto, using the RStudio Integrated Development Environment (IDE), version 2025.5.1.513.
The source files are in R and R Markdown, then rendered to HTML using the revealJS framework. The HTML slides are hosted in a GitHub repo and served by GitHub pages: https://psu-psychology.github.io/psych-260-2025-fall/
References

PSYCH 260.001 | © Rick Gilmore under CC BY 4.0