From sensation to perception
2025-02-13
Prelude
MarvinGayeVEVO (2019)
Overview
Announcements
- Assigned next Tuesday, February 18: Final Project proposal.
Last time…
- Light informs
- Spatial perception: Where, how far, how big?
- Object perception: What is it, what form, color, etc.
- Eye
- High resolution info only in center
- Samples different categories of light wavelength
- Moves to stablize retina, scan environment
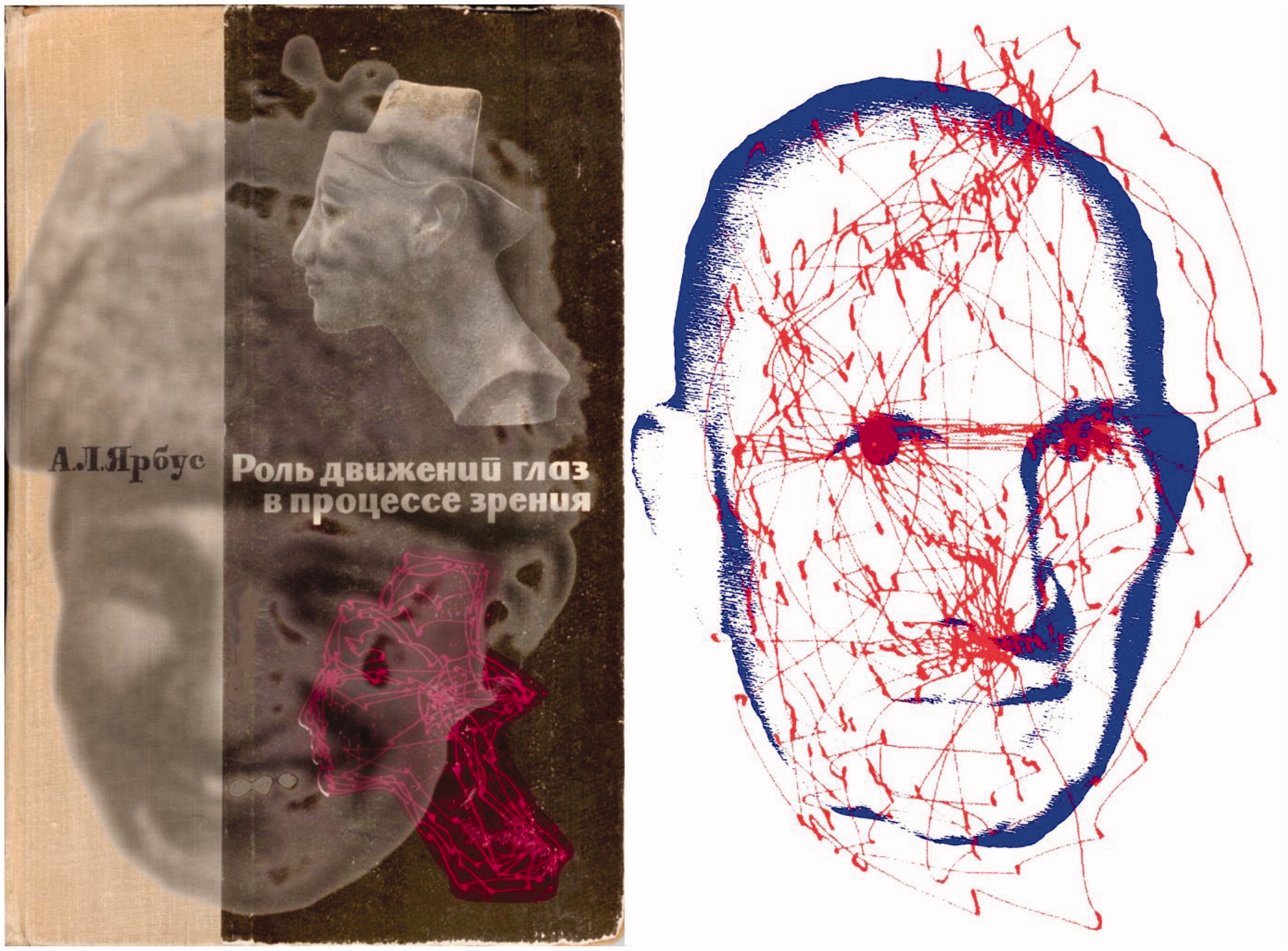
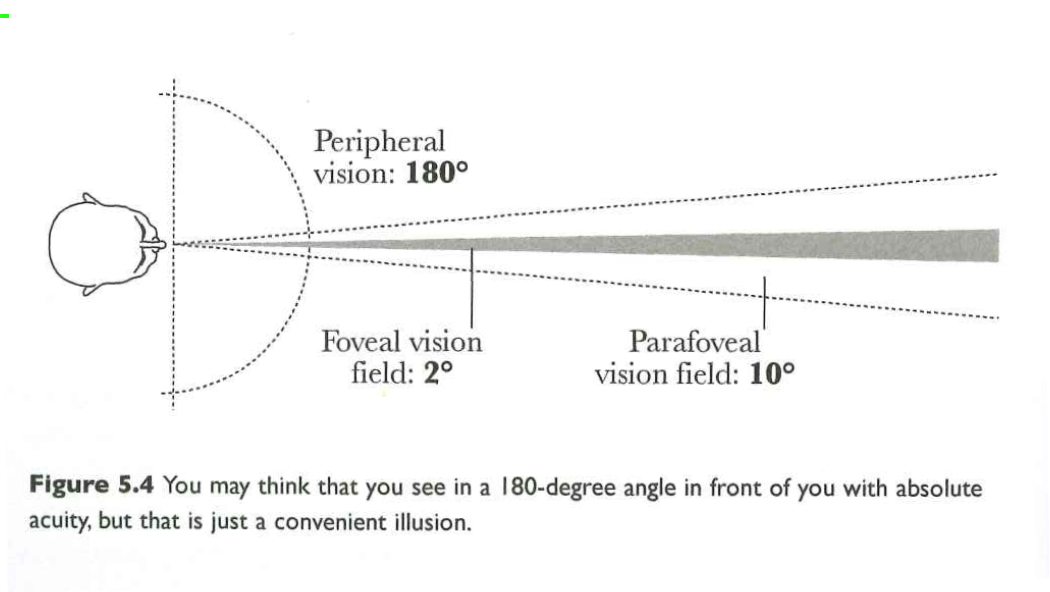

Wade (2015)
Today
- Wrap-up on sensation
- From sensation to perception
Wrap-up on sensation
Color perception
- Perceived color a function of activity in “R”, “G”, and “B” photoreceptors

Source: Wikipedia
Wavelengths are continuous, but are perceived colors?
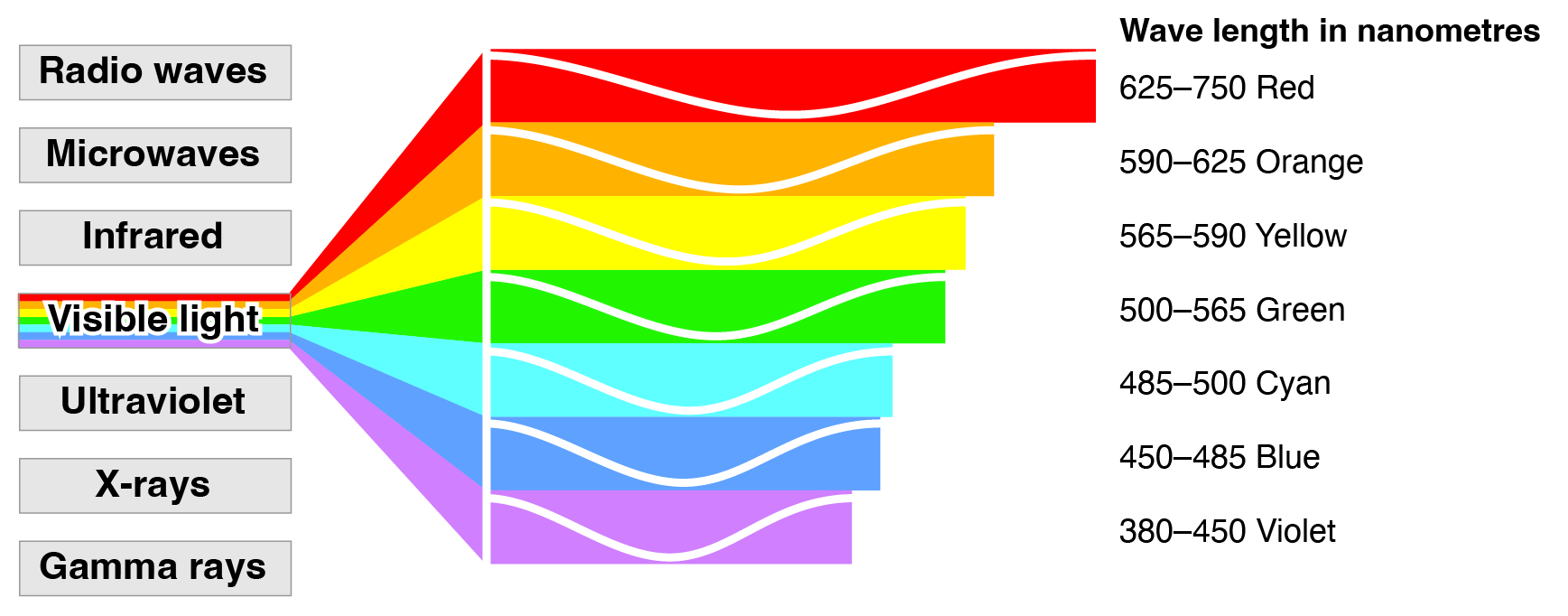
https://rmit.pressbooks.pub/colourtheory1/part/2-colour-theory-the-visible-spectrum/
Perceived colors seem ordinal, but…

- Color is a neuropsychological construct
What’s a reddish-green look like?
What’s a reddish-green look like?
Explanation
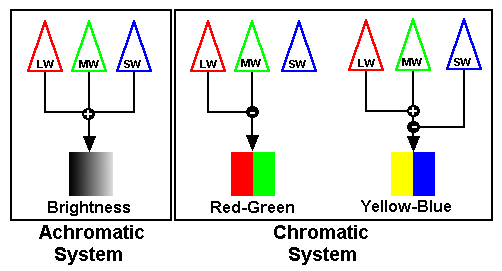
Color vision anomalies
- Absence of or anomalies in photoreceptors
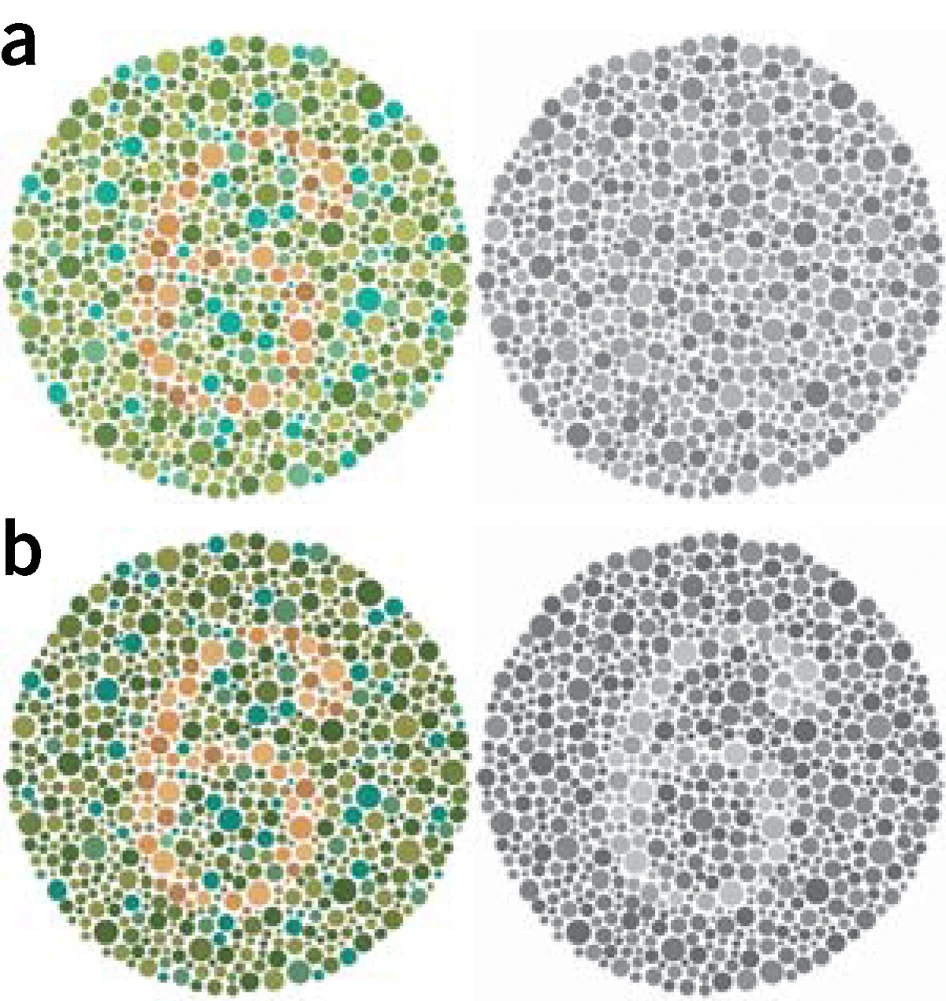
Wong (2011) Figure 1
Types
- Protanopia (impaired R/long wavelength)
- Deuteranopia (impaired G/medium wavelength)
- Tritanopia (impaired B/short wavelength)
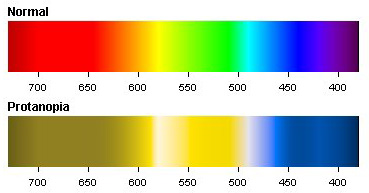
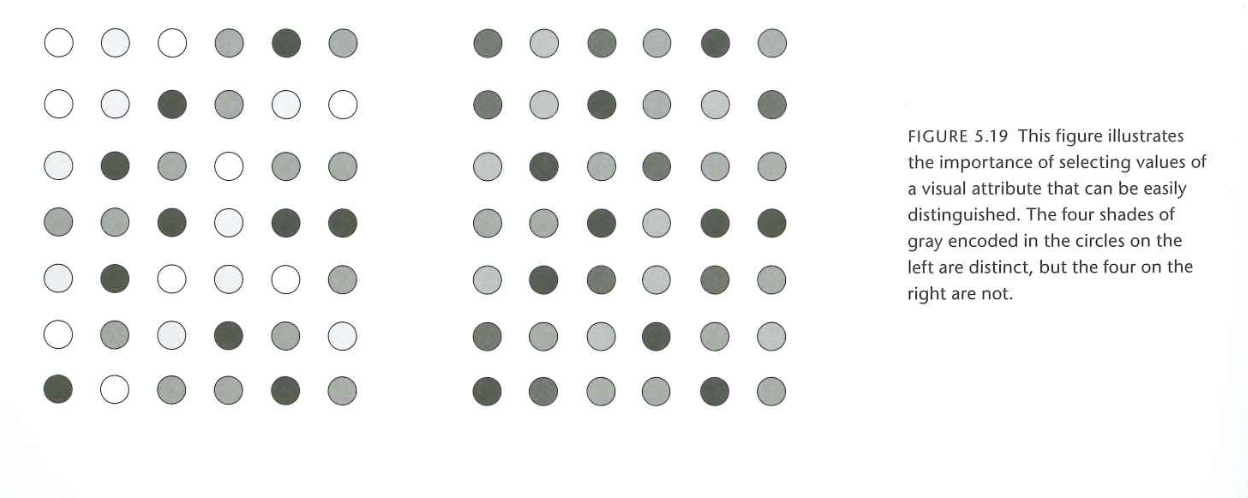
Color palettes
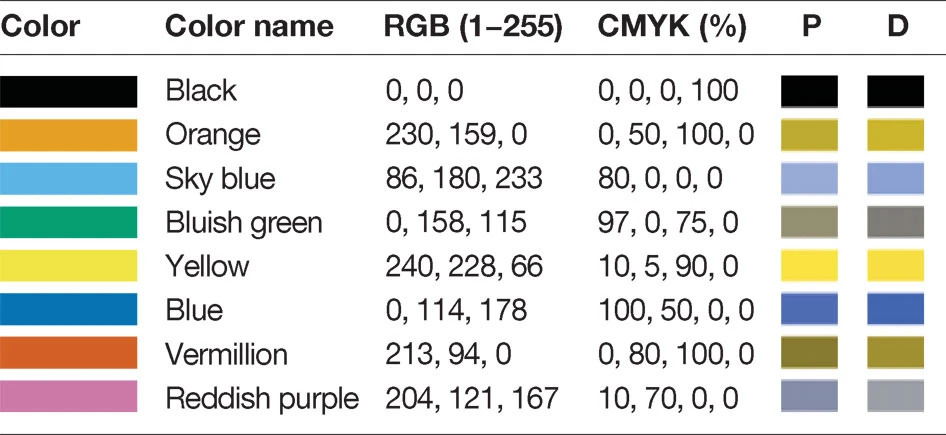
Wong (2011) Figure 2
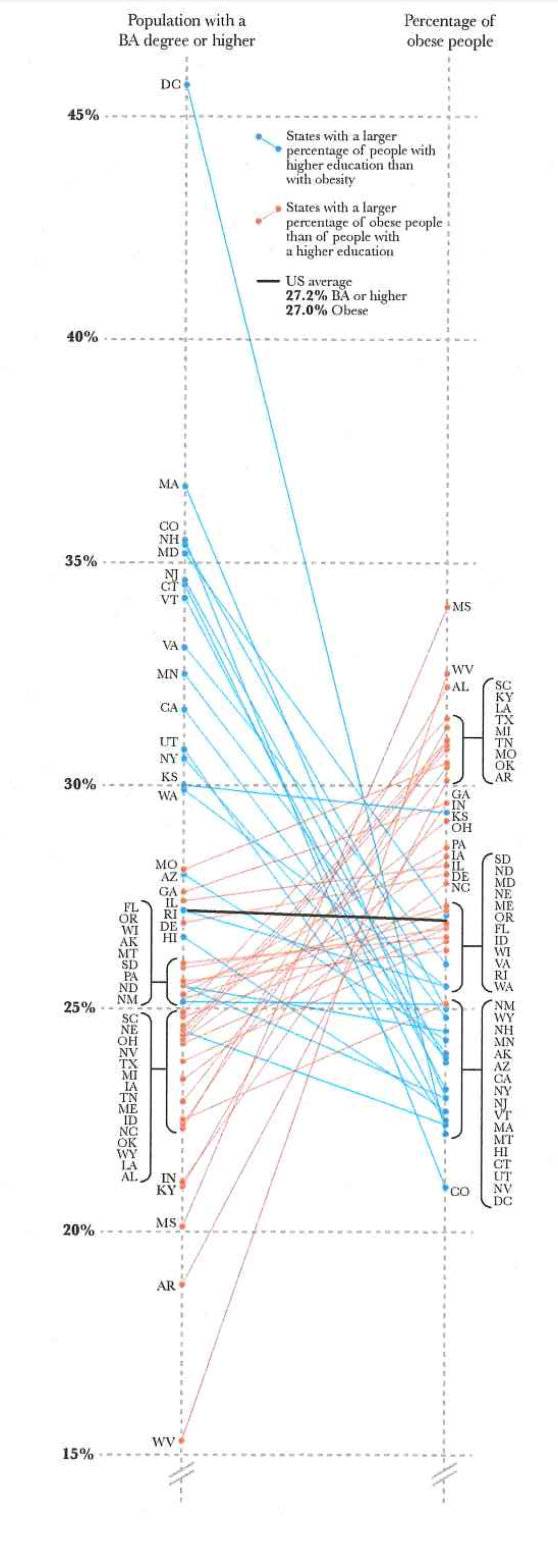
Some consequences for data figures
- Size of visual elements (symbols, including text)
- Contrast (light/dark or color)
- Textures of visual patterns
- Some colors more visible than others
- How much visual scanning (# of eye movements) required?
From sensation to perception
Visual brains love differences
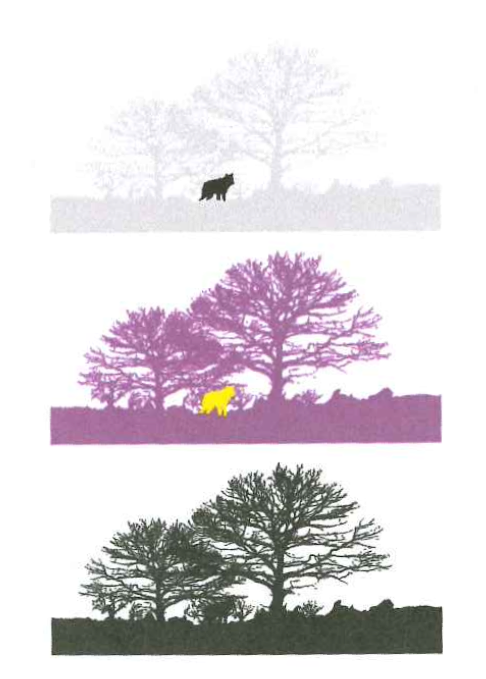

Figure 6.1 Cairo (2013)
Especially …
- Intensity (light/dark)
- Contrast
- Color
- Position or size
- Changes in…

Kahneman (2013)
Pre-attentive vision
- Detect quickly, with minimal effort
- Usually in a single glance/fixation
- vs. attentive vision
- Overt shifts of attention (eye movements)
- Covert shifts (“mind’s eye” movements)

Figure 6.4 Cairo (2013)
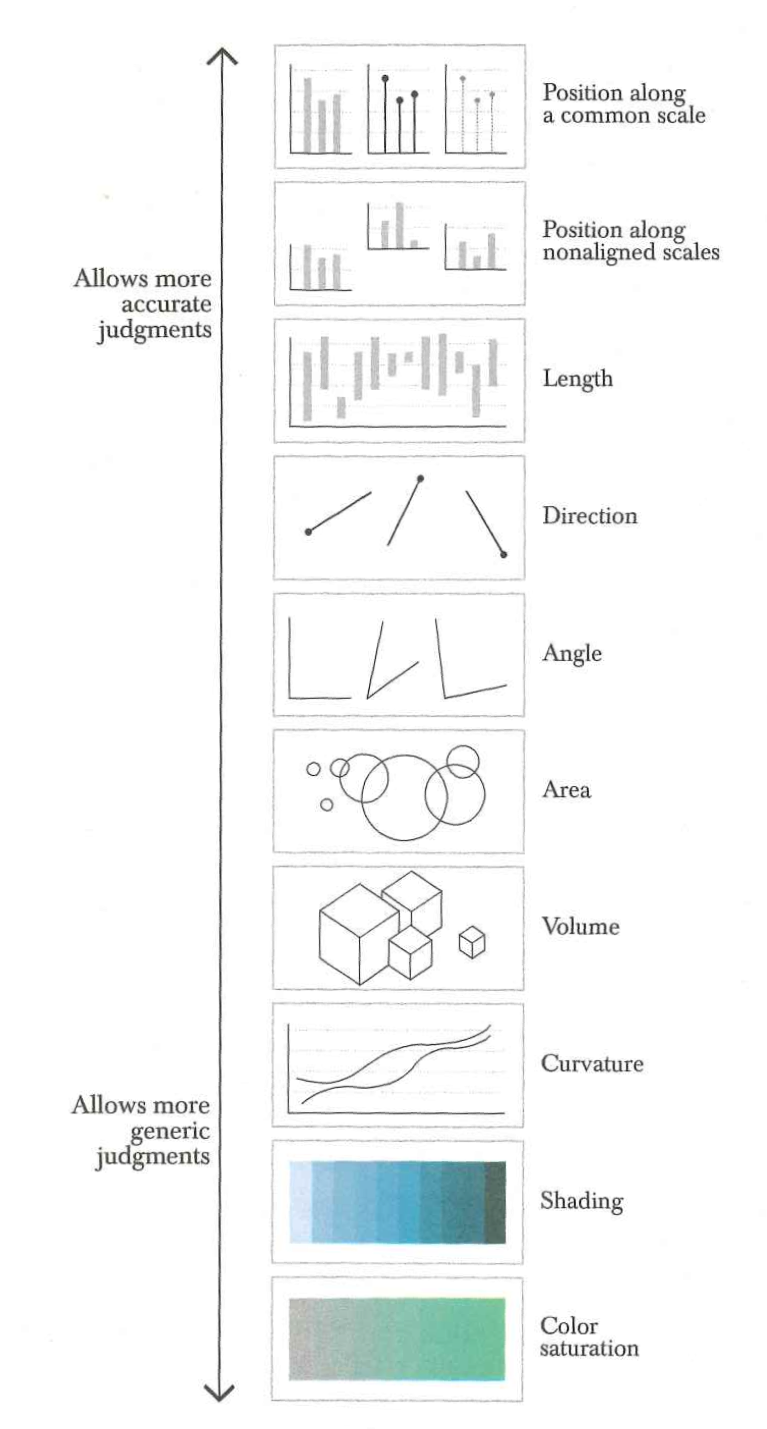
Some features easier/faster to judge
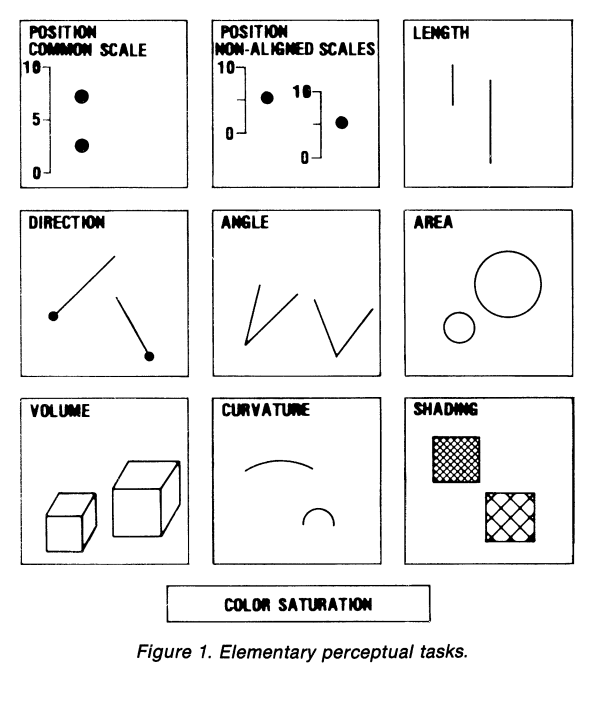
Figure 1 Cleveland & McGill (1984)
Gestalt school
- Gestalt: “whole form”
- Can psychological phenomena be understood from their parts?
- Or is the whole greater than the sum of the parts?
Reification
- Perception is constructive

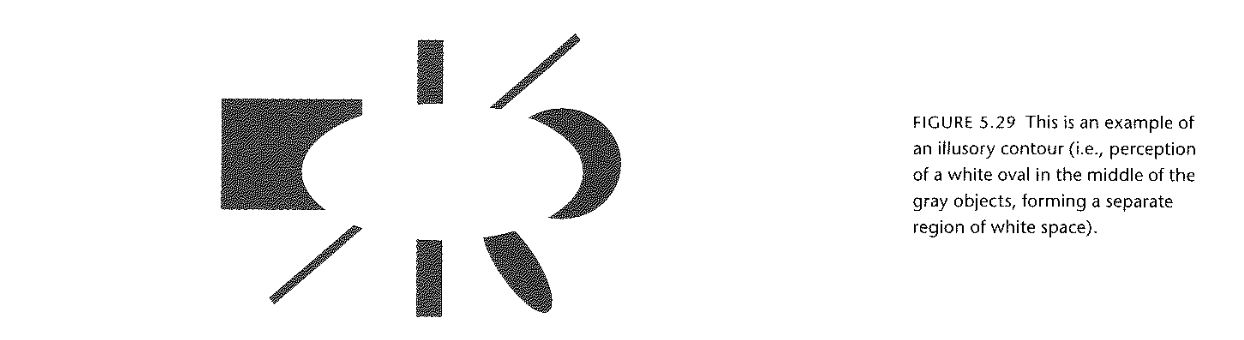
Figure 5.29 Few (2004)
Multistability
- Perception is multistable

Invariance
- And yet…
- Perception is invariant
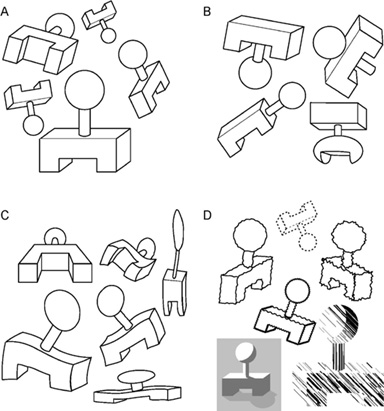
Gestalt “laws” of perceptual grouping
- Proximity
- Similarity
- Connectedness
- Closure
- Continuity
- Symmetry
Proximity

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestalt_psychology

Figure 6.5 Cairo (2013)
Similarity

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestalt_psychology
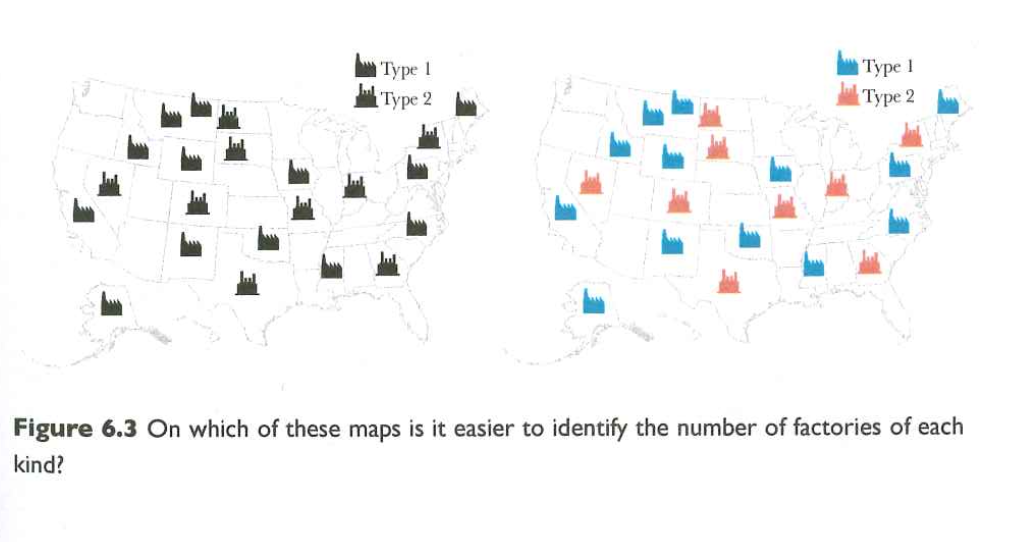
Figure 6.3 Cairo (2013)
Similar but not too similar
Closure
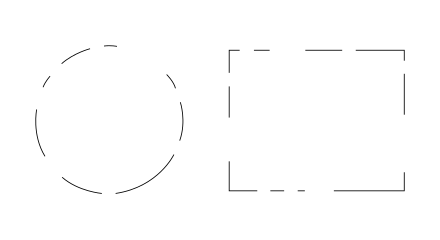
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestalt_psychology
Continuity

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestalt_psychology
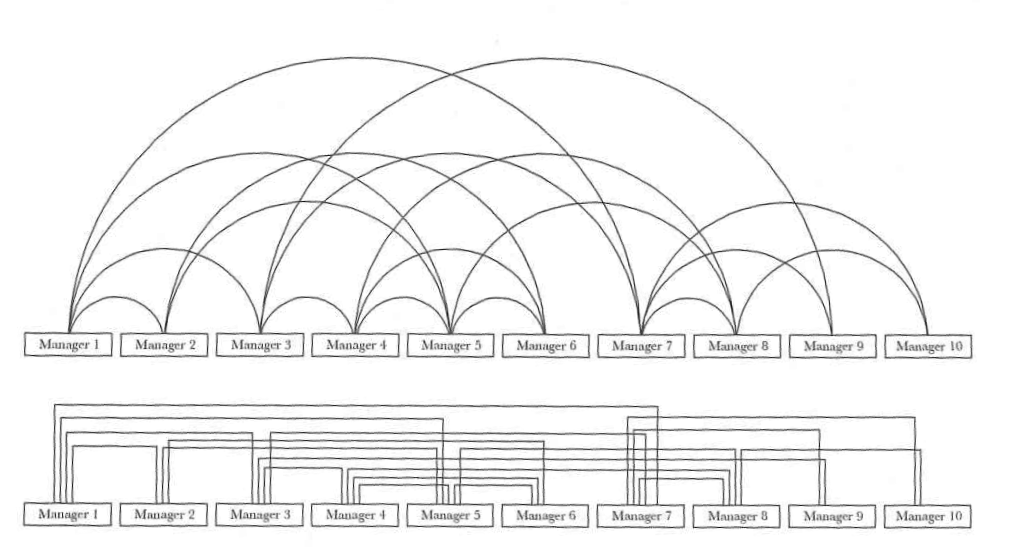
Figure 6.9 Cairo (2013)
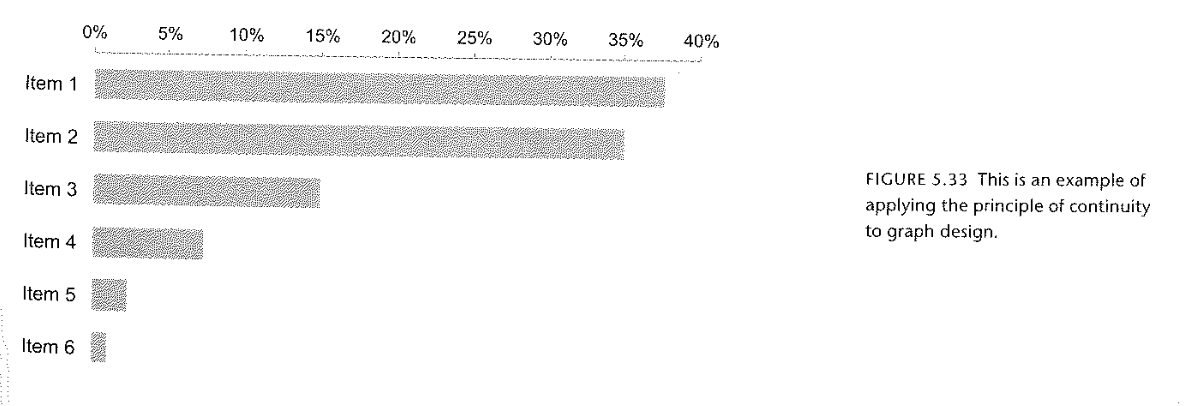
Figure 5.33 Few (2004)
Connectedness
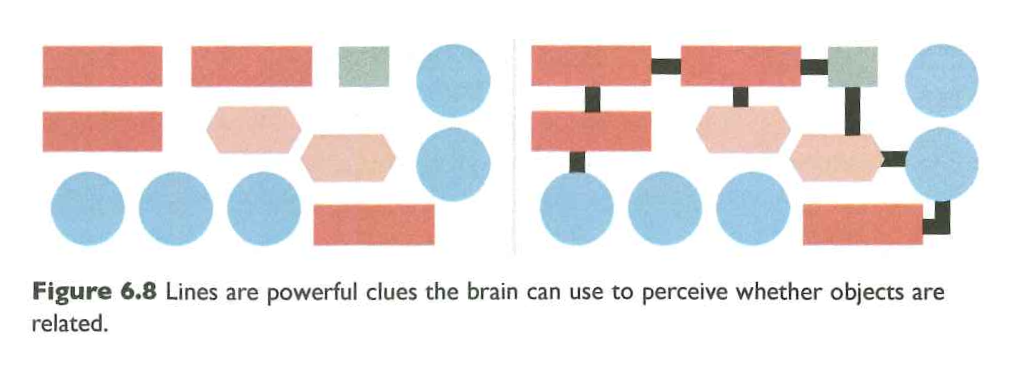
Figure 6.8 Cairo (2013)

Few (2004)
Symmetry
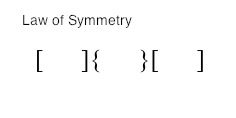
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestalt_psychology
Your turn
- Find a compelling illustration of one of the Gestalt phenomena (non-data visualization-related)
- Find an illustration of one of the Gestalt phenomena in a data visualization
- Add findings (and URLs) here:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1G8U_IPMP0x17Sfl-FQfF37DN19bDQFm0GO_UmQQzv7Q/edit?usp=sharing
Putting it all together
- Vision is reconstructive
- Pre-attentive vs. attentive vision
- Gestalt principles describe feature grouping
Next time
From cognition to understanding