Meta-analysis
2024-11-04 Mon
Prelude
McCutcheon (2019b)
McCutcheon (2019a)
Overview
Announcements
- Due Friday
Today
Meta-analysis
- Discuss
- Wilson (2014)
Meta-analysis
- Imagine lots of replications
- Combining multiple studies, ideally published and unpublished
- Why unpublished, too?
- Question: What is the distribution of effect sizes?
- Why effect sizes?
- Question: What is the quality of the evidence?
- Related to Cochrane Systematic Reviews
Let’s simulate one
Example
van Agteren, J., Iasiello, M., Lo, L., Bartholomaeus, J., Kopsaftis, Z., Carey, M. & Kyrios, M. (2021). A systematic review and meta-analysis of psychological interventions to improve mental wellbeing. Nature Human Behaviour. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01093-w.
Our current understanding of the efficacy of psychological interventions in improving mental states of wellbeing is incomplete. This study aimed to overcome limitations of previous reviews by examining the efficacy of distinct types of psychological interventions, irrespective of their theoretical underpinning, and the impact of various moderators, in a unified systematic review and meta-analysis.
Agteren et al. (2021)
Four-hundred-and-nineteen randomized controlled trials from clinical and non-clinical populations (n = 53,288) were identified for inclusion. Mindfulness-based and multi-component positive psychological interventions demonstrated the greatest efficacy in both clinical and non-clinical populations.
Agteren et al. (2021)
Meta-analyses also found that singular positive psychological interventions, cognitive and behavioural therapy-based, acceptance and commitment therapy-based, and reminiscence interventions were impactful.
Agteren et al. (2021)
Effect sizes were moderate at best, but differed according to target population and moderator, most notably intervention intensity. The evidence quality was generally low to moderate. While the evidence requires further advancement, the review provides insight into how psychological interventions can be designed to improve mental wellbeing.
Agteren et al. (2021)
Figure 2 from Agteren et al. (2021)
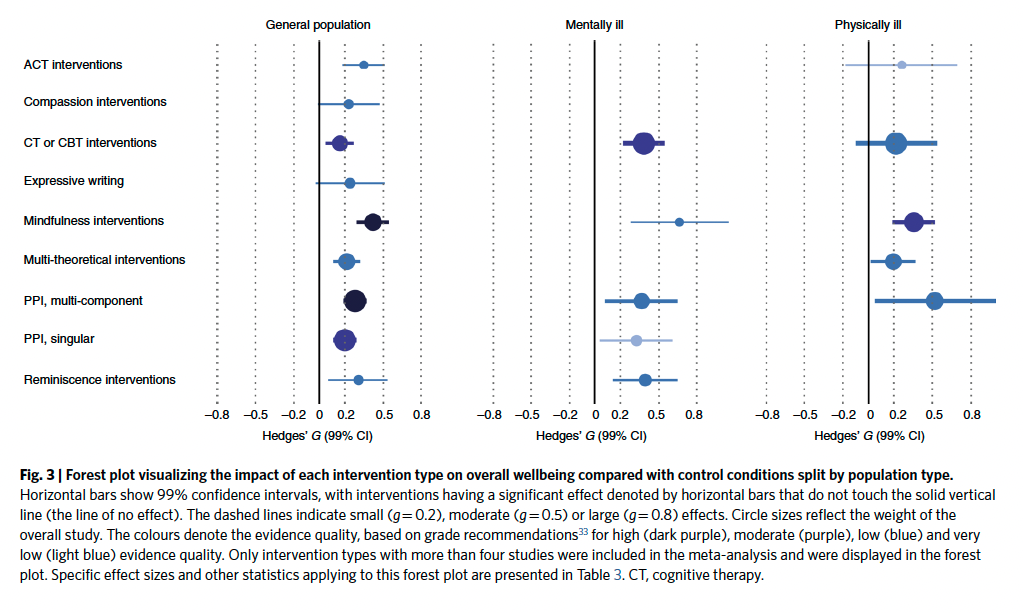
Figure 3 from Agteren et al. (2021)
Example 2
Richardson, M., Abraham, C., & Bond, R. (2012). Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 353–387. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026838
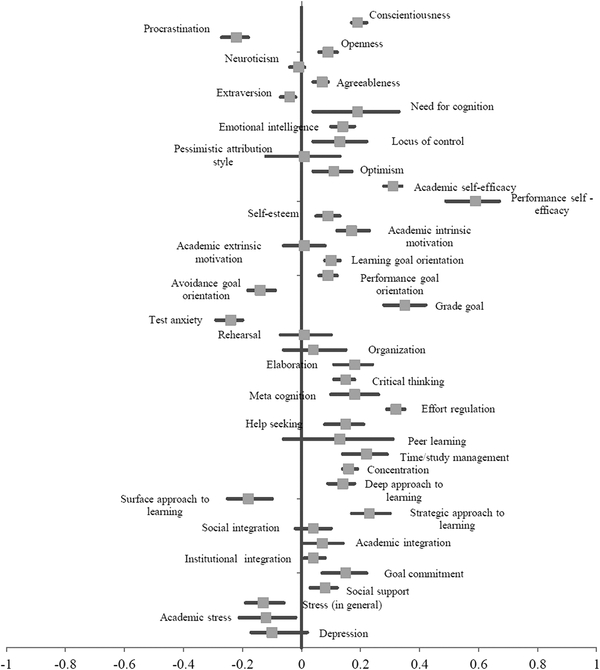
Richardson, Abraham, & Bond (2012). Figure 1: Results of the primary meta-analyses for the non-intellective correlates of GPA: r + and 95% confidence intervals.
“When challenges are familiar, students can draw upon past experiences to formulate expectations about specific performances. This has been referred to as performance self-efficacy…”
Richardson et al. (2012)

Crislip (2012)
“I never met a man I didn’t like” is a quote attributed to Will Rogers. The full quote is “I joked about every prominent man in my lifetime, but I never met one I didn’t like”. Rogers considered this line as an epitaph for his tombstone, but the shortened version is what appears on his gravestone in Claremore, Oklahoma.
Google AI
Flaws with meta-analysis
- Garbage-in, garbage-out?
The evidence quality was generally low to moderate… (Agteren et al., 2021)
- See The newcastle-ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses (n.d.) for one scheme for rating study quality.

Jefferson et al. (2023)

Jefferson et al. (2023)
Flaws with meta-analysis (continued)
- What about publication bias?
Policy Points:
- Currently, there is massive production of unnecessary, misleading, and conflicted systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Instead of promoting evidence-based medicine and health care, these instruments often serve mostly as easily produced publishable units or marketing tools.
- Suboptimal systematic reviews and meta-analyses can be harmful given the major prestige and influence these types of studies have acquired.
Ioannidis (2016)
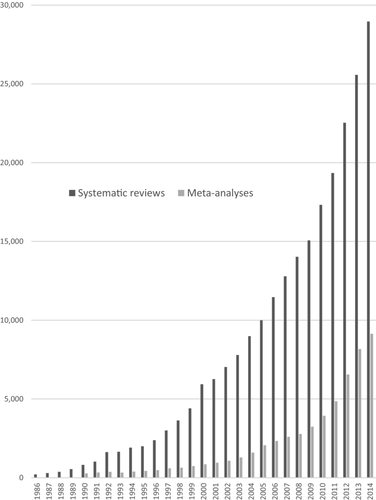
Figure 1 from Ioannidis (2016). Number of PubMed-Indexed Articles Published Each Year Between 1986 and 2014 That Carry the Tag “Systematic Review” or “Meta-analysis” for Type of Publication
Conclusions
The production of systematic reviews and meta-analyses has reached epidemic proportions. Possibly, the large majority of produced systematic reviews and meta-analyses are unnecessary, misleading, and/or conflicted.
Ioannidis (2016)
Publication bias poses a challenge for accurately synthesizing research findings using meta-analysis. A number of statistical methods have been developed to combat this problem by adjusting the meta-analytic estimates…
Sladekova, Webb, & Field (2023)
Next time
Many-Analysts
- Read
- Silberzahn et al. (2018)
- Class notes
