Topic 4 Levels of analysis
Spatial and Temporal Resolution
Your turn
- What’s a micro (spatially small) influence on/aspect of behavior?
- What’s a macro (spatially large)…
- What’s a micro (temporally short)…
- What’s a macro (temporally long)…
Why does this matter?
- Different methods, different levels of analysis
- Challenge of linking phenomena across levels
- How does the micro affect macro or vice versa?
- Challenge of interpretation
Important skills: Being able to think about spatial and temporal levels of analysis inside and outside of neuroscience.
Spatial Resolution in Detail
- Within an individual
- molecular
- genetic
- receptor
- chemical
- neurotransmitter/hormonal
- cellular
- neuronal firing
- molecular
- Internal to individuals
- network
- lateral inhibition
- area
- V1 varies by ~2x
- region
- Wiring/connectivity differences
- system
- network
- External to individuals
- Social
- Friends, family, teachers, others
- Non-social
- Neighborhood, school, state/region, country
- Physical environment
- Social
Temporal Resolution in Detail
- Within one lifetime
- Microseconds
- detection position from acoustic stimulation
- Milliseconds
- action potential
- Seconds
- changes in EEG power
- short-term memory
- Microseconds
- Within one lifetime
- Minutes
- synaptic plasticity
- Hours
- memory consolidation
- Hormone (melatonin, cortisol) levels
- Days
- Minutes
- Within one lifetime
- Weeks
- Months
- Years
- education & training
- disease processes
- cultural change
- Across lifetimes
- Centuries
- cultural changes
- Millenia
- Natural & sexual selection
- Centuries
References
Sejnowski, Terrence J, Patricia S Churchland, and J Anthony Movshon. 2014. “Putting Big Data to Good Use in Neuroscience.” Nature Neuroscience 17 (11): 1440–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3839.
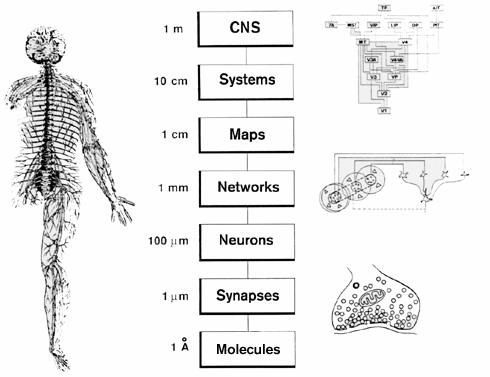
![[[@sejnowski2014putting]](http://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3839)](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnn.3839/MediaObjects/41593_2014_Article_BFnn3839_Fig1_HTML.jpg?as=webp)