Topic 18 Supplemental
2023-01-12
2023-01-17
“If understanding everything we need to know about the brain is a mile, how far have we walked?” – J. Lichtman
Leonardo da Vinci created wax casts of which fluid-filled structure in the forebrain?
- Pineal gland
- Cerebral cortex
- Cerebral ventricles
- Hippocampus
Decartes was a philosophical dualist. This means he believed that…
- Philosophers should engage in armed combat over their ideas
- Human behavior is influenced by physical and extra-physical (spiritual) forces
- The pineal gland is both an input and output structure
2023-01-19
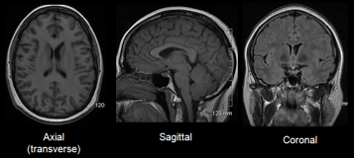
What kind of structural brain imaging technique does this image represent?

- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Event-related potentials (ERP)
Which of the following functional methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds?
- functional MRI
- EEG
- MEG
- single-unit recording
Which of the following methods has high/fine spatial resolution?
- functional MRI
- PET
- EEG
- single-unit recording
2023-01-24
(“All the Layers in Your Brain,” n.d.)
Announcements
- Quiz 1 this Thursday, January 26, 2023. Available on Canvas after class and until 10 PM.
- 10 questions + bonus (worth 10 points)
- Neuroscience colloquia
- Wednesday, January 25, 2023, 4:00 PM, Dmitriy Aronov, Columbia University, “Using food-caching birds to study the neuroscience of episodic memory”, 108 Wartik and https://psu.zoom.us/j/96831119776.
- March 1, 2023, Jennifer Rinker, Department of Neuroscience at The Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC)
What substance is generated in and flows through the cerebral ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord?
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Blood plasma
- Neuromodulators
Which of the cerebral ventricles is adjacent to the hindbrain (cerebellum, pons, and medulla)?
- Cerebral aqueduct
- Lateral ventricles
- 4th ventricle
2023-01-26
Announcements
- Quiz 1 TODAY Thursday, January 26, 2023. Available on Canvas after class and until 10 PM.
- 10 questions + bonus (worth 10 points)
- Neuroscience colloquia
- March 1, 2023, Jennifer Rinker, Department of Neuroscience at The Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC)
2023-01-31
The somatosensory cortex (S-I) is located in which lobe of the cerebral cortex?
- Frontal
- Insular
- Parietal
- Occipital
If sympathetic nervous system activation is like the accelerator pedal in a car, parasympathetic activation is like the _______?
- clutch pedal
- gear shift
- turn signal
- brake
The cauda equina is the region in the spine where…
- There are nerve fibers, but no spinal cord.
- Nerves exit the spine and connect with the head and neck region.
- The medulla oblongata connects with the spinal cord.
Some good examples of systems
““An example of a system can be a bus system found on the Penn State campus. There are different buses within the system that transport individuals to different areas via various routes. There can be many other components involved in the bus system such as: the bus drivers, how many stops there are on each route, the funding for maintenance of the buses, how the routes are determined, and the maximum capacity of the buses. the inputs of the system are the students at their original location, and the outputs of the system are the students at their desired location.”
““A vending machine is a system used to dispense food after a payment has been given… The input of the system includes the form of payment, whether it be in bills or coins, and the location of the food/drink as given by the push of a button. The outputs of the system are the change given back and the food/drink that is dispensed.”
“For the muscular system, the inputs would be the ability to contract the muscles and the individual components of the thick and thin filaments working in conjunction to create this motion. In addition to the inputs that act on and make the muscle contract, the output would be the action of the muscle and its function/what it performs.”
“Toasters would be categorized as an open system because they freely exchange energy and matter with their surroundings. The input would be electrical energy from whatever outlet it is plugged into, the mechanical energy used to press the lever downwards and start the cooking, as well as the untoasted piece of bread you place into it. The output would be the result of the electrical energy transferred into heat which then toasts the bread, so we have thermal energy and a now-toasted piece of bread.”
“A subway system can be defined as an electric railway that operates underground. The components of this system include an area of land underground, train tracks, train, cars, and subway stations. These components include seats within train cars, electrical wires along the tracks and throughout the subway tunnels, ticket booths within the subway station, etc.”
“The input for [a subway system] is power supplied to the train cars through electricity from wires or an electrified rail. The output is the movement of the trains. Once the electricity is received by the train car, it can begin moving in order to fulfill its purpose of moving people from one place to another throughout the area in which it operates.”
“Some components of the digestive system include the mouth, the stomach, the small and large intestine, and the colon. The inputs are the food and drink that we put into our bodies to gain nutrients for energy to use… The output is urination and defecation.”
2023-02-02
Figure 18.3: Neuronal migration from (bbscottvids 2009)
2023-02-06
Propagation is the way…
Figure 18.5: Superstition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_tmeHCO1IM
If only potassium ions \(K^+\) and organic anions \(A^-\) were in a neuron, what would the voltage across the neuron (its membrane potential) be?
- -90mV, the equilibrium potential for \(K^+\).
- +55mv, the equilibrium potential for \(Na^+\).
- 0mv, the equilibrium potential for solutions with equal concentrations of + and - ions.
2023-02-14
Announcements
- Exam 1 scores will be released tonight
- Next Tuesday, February 21
- Blog post 1 (of 3) due. Assignment details
- Quiz 2, available on Canvas after class.
EyeWire extra credit opportunity
Figure 18.7: EyeWire EyeWire (2021)
Tag one cube of neuron segments from EyeWire. Take a screenshot of your completed section. Submit it to via Canvas Megan for five (5) extra credit points. Due: Thursday, March 2, 2023.
2023-02-16
Figure 18.8: Wizard of Oz: https://www.youtube.com/embed/NZR64EF3OpA
Monoamine Song
Figure 18.9: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y5W60VwDkas
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mah_Nà_Mah_Nà
Monoamines, do-do do do-do Monoamines, do do do-do Monoamines, do do do do-do do do-do do do-do do do do do-do do
Monoamines, do-pa-mine is one Monoamines, norepi, too Monoamines, sero-tonin e-pinephrine, dop-a-mine, nor-epinephrine, melatonin, whoo!
Monoamines, mod-u-late neurons Monoamines, throughout the brain Monoamines, keep people happy, brains snappy, not sleepy, not sappy, do-do do-do do-do do
These images are examples of what structural imaging technique?
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Single unit recording
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed Axial Tomography (CAT)
What maintains the intracellular (inside)/extracellular (outside) concentration differences of K+ and Na+ ions?
- The myelin sheath.
- The force of diffusion.
- Ion flow through passive/leak channels.
- Action of the Na+/K+ pump (ATPase).
Which ventral midbrain region is one of the main sites for neurons that release neuromodulators (e.g., dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin)?
- Tegmentum.
- Basal ganglia.
- Lateral geniculate nucleus.
- Tectum.
Which of the following marks the medial boundary of the frontal lobe(s)?
- Longitudinal fissure.
- Lateral fissure.
- Central sulcus.
- Inferior temporal gyrus.
Nodes of Ranvier, or gaps in the myelination of an axon, serve which purpose?
- Allow space in the axon for neurotransmitter release.
- Increase the speed of propagation.
- Provide structural support to the neuron.
- Combine input from different dendrites
2023-02-21
Announcements
- Quiz 2 today (on Canvas, after class)
- Blog post 1 (of 3) due today by 5:00 PM
- Exam 2 next Tuesday, February 28, in-class
Black widow spider venom causes paralysis by impeding the normal function of which neurotransmitter system?
- GABA (GABA)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
With one exception, the monoamine neurotransmitters bind to what type of receptors?
- ionotropic
- voltage-gated
- nicotinic
- metabotropic
2023-02-23
The SAM axis consists of all of the following components except:
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Adrenal medulla
- Midbrain
The HPA axis consists of all of the following components except:
- Adrenal cortex
- Anterior pituitary
- Posterior pituitary
- Hypothalamus
Oxytocin is often called the ‘love’ hormone because:
- Animals without oxytocin receptors fail to form pair-bonds, mate, or care for their young.
- The oxytocin system is activated when animals respond to external threats from mating rivals.
- Oxytocin release occurs during orgasm and triggers the milk let-down reflex in nursing mothers.
2023-04-11
Which type of muscle fiber is also a sensory organ?
- extrafusal
- intrafusal
- exteroceptive
- extrapyramidal
2023-04-13
Announcements
- Quiz 4 next Thursday, April 20
- Exam 4 on Tuesday, May 2, 10:10a-12:00p, Health & Human Development 254
Lasik surgery reshapes this part of the eye that accounts for 2/3 of the eye’s total refractive power.
A. Cornea B. Retina C. Lens
2023-04-18
Announcements
- Quiz 4 this Thursday (on Canvas, after class)
- Exam 4 on Tuesday, May 2, 10:10a-12:00p, Health & Human Development 254
- In-class lab next Tuesday, April 25.
Why does Gilmore say the retina is anatomically ‘inside-out’?
A. The dorsal stream and the ventral stream project to different cortical targets B. Information from the left visual field projects to the right hemisphere C. Photoreceptors lie at the back of the eye, away from the path of light D. Long wavelength ‘red-ish’ lights can only be seen outside
Visual information from the retina projects to the ______ which controls circadian rhythms.
A. Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus B. Dorso-medial nucleus of the thalamus C. Superior colliculus/optic tectum D. Suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus
Hubel and Wiesel did not find many cells in V1 that had center-surround receptive fields because…
A. Many cells in V1 have elongated, rectangular-shaped, receptive fields B. V1 cells don’t have receptive fields C. V1 doesn’t respond to visual information that strongly D. The visual cortex doesn’t respond strongly under anesthesia
2023-04-20
Announcements
- Quiz 4 TODAY (on Canvas, after class)
- Exam 4 on Tuesday, May 2, 10:10a-12:00p, Health & Human Development 254
- In-class lab next Tuesday, April 25.
What neurotransmiter is the main chemical trigger for the NMDA receptor?
A. Dopamine B. Acetylcholine C. Glutamate D. Oxytocin
All of the following are types of associative learning EXCEPT
A. Instrumental conditioning B. Observational learning C. Sensitization D. Implicit learning
The idea that memories are stored by physical changes in the brain is a relatively recent idea, TRUE or FALSE?
A. True B. False