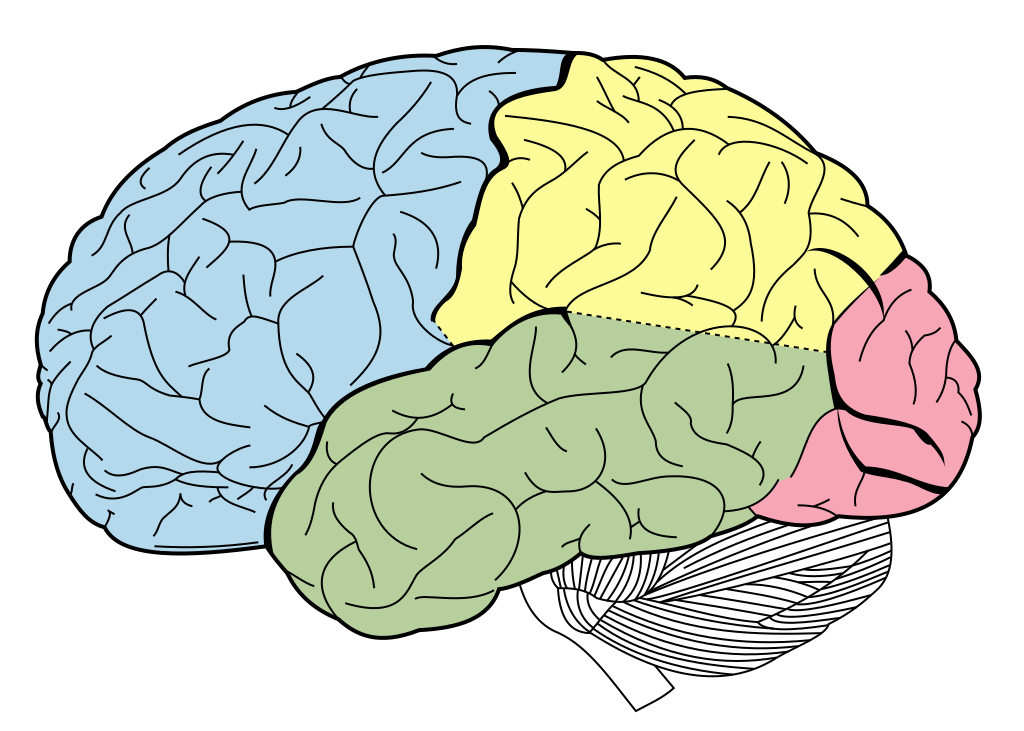
Topic 6 Neuroanatomy
Finding our way around
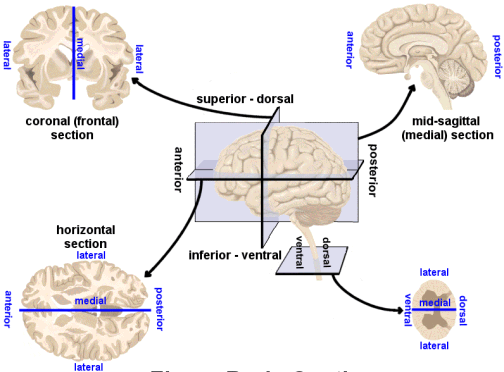
Directional terms
- Anterior/Posterior -> front/back
- Medial/Lateral -> inside/outside
- Superior/Inferior -> upward/downward
- Dorsal/Ventral -> back-ward/belly-ward
- Rostral/Caudal -> head-ward/tail-ward

Figure 6.1: Wikipedia

Figure 6.2: Wikipedia
Supporting structures
Meninges
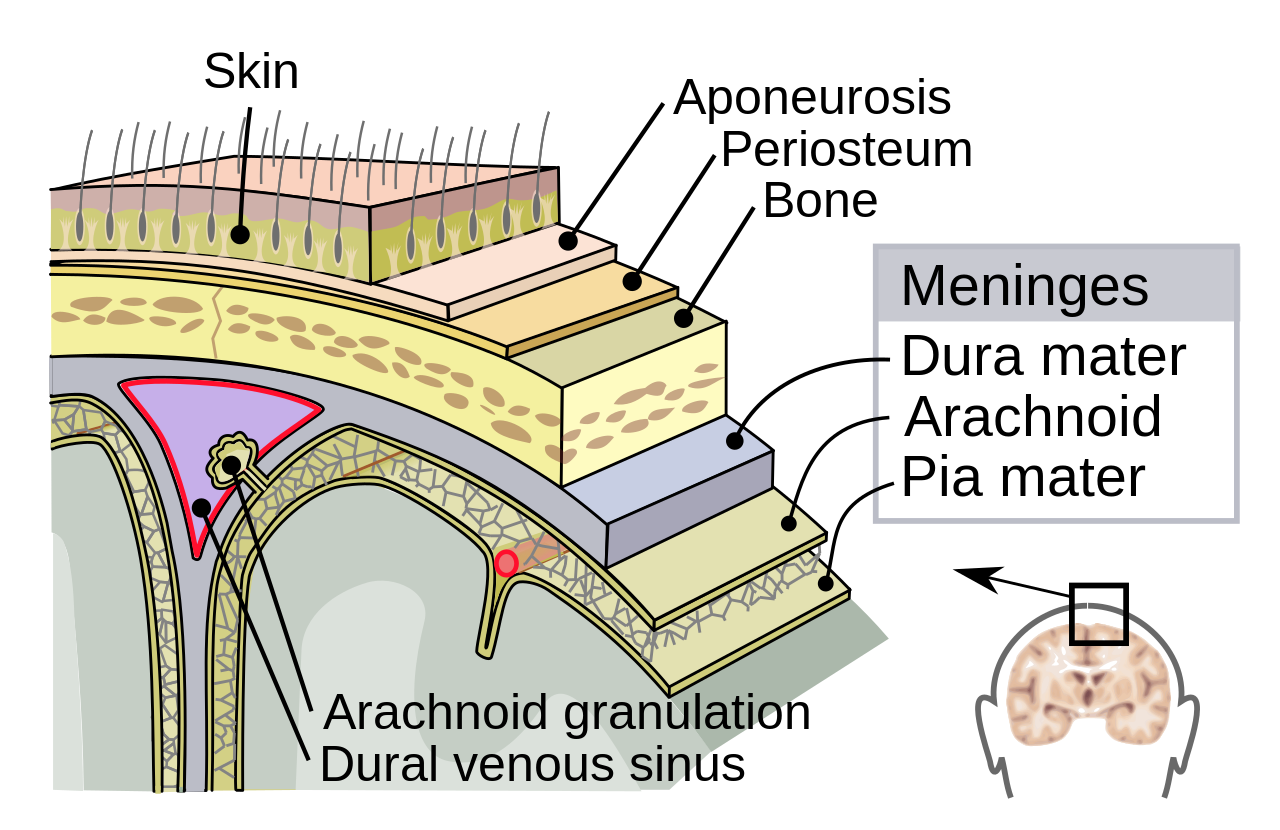
Figure 6.4: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8e/Meninges-en.svg/1280px-Meninges-en.svg.png
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater/membrane
- Subarachnoid space
- Pia mater
What disease is associated with inflammation of (e.g., ‘-itis’) of the meninges?
Ventricular system or Cerebral Ventricles
- Lateral (1st & 2nd)
- 3rd
- Cerebral aqueduct
- 4th
- Ventricles are filled with Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Hydrocephalus can occur there is a blockage in the flow of CSF through the cerebral ventricles.
Blood Supply
Arteries
- external & internal carotid; vertebral -> basilar
- Circle of Willis
- anterior, middle, & posterior cerebral
Circle of Willis helps equalize blood pressures among the ascending arteries from the heart.
Blood/brain barrier
- Isolates CNS from blood stream
- Active transport of molecules typically required
- Astrocytes contribute to
- (endothelial) cells forming blood vessel walls are tightly packed
- Exception is Area Postrema
- In brainstem (see AP in the figure below)
- Blood-brain barrier thin
- Detects toxins, evokes vomiting (emesis)
Organization of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- CNS
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Everything encased in bone
- PNS
- Everything else!
Interactive brain atlas
Figure 6.9: Interactive brain atlas: https://www.med.harvard.edu/aanlib/cases/caseNA/pb9.htm
Organization of the brain
| Major division | Ventricular Landmark | Embryonic Division | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forebrain | Lateral | Telencephalon | Cerebral cortex |
| Basal ganglia | |||
| Hippocampus, Amygdala | |||
| Third | Diencephalon | Thalamus | |
| Hypothalamus | |||
| Midbrain | Cerebral Aqueduct | Mesencephalon | Tectum, Tegmentum |
| Hindbrain | 4th | Rhombencephalon | Cerebellum, pons |
| – | Medulla oblongata |
Components of the brain
Hindbrain
- Structures adjacent to 4th ventricle

Figure 6.11: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b9/Gray708.svg/500px-Gray708.svg.png
Medulla oblongata

Figure 6.12: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b9/Gray708.svg/500px-Gray708.svg.png
- Fibers of passage (to/from spinal cord)
- Cranial nerves VI-XII
- Cardiovascular regulation
- Muscle tone
Cerebellum
- “Little brain”
- Dorsal to pons
- Movement coordination, classical conditioning (associative learning), + ???
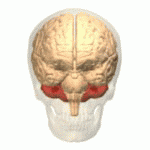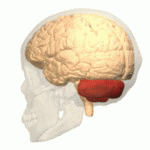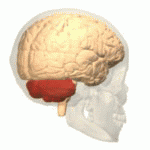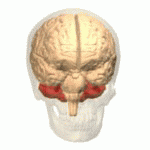
Figure 6.13: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerebellum
Pons
- Bulge on brain stem
- Neuromodulatory nuclei
- Relay to cerebellum
- Cranial nerve V
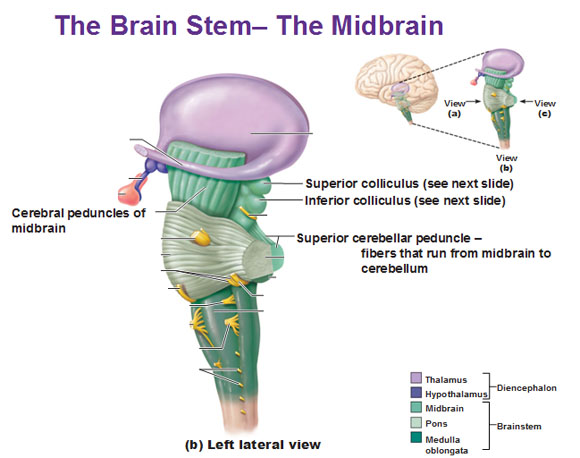
Midbrain
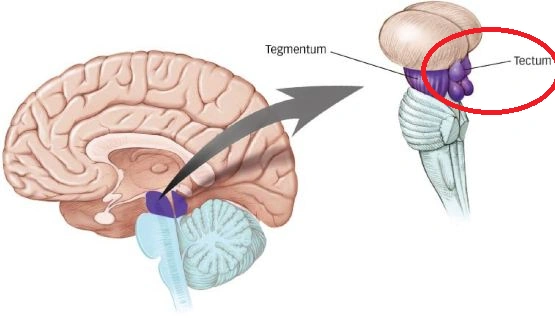
Figure 6.16: https://vignette.wikia.nocookie.net/brain-for-ai/images/b/bd/Tectum.png/revision/latest?cb=20170613125935
Tectum
- Tectum -> “roof”
- Superior colliculus (reflexive orienting of eyes, head, ears)
- Inferior colliculus (sound/auditory processing)
Tegmentum
- Tegmentum -> “floor”
- Species-typical movement sequences (e.g., cat: hissing, pouncing)
- Cranial nerves III, IV
- Nuclei that release modulatory neurotransmitters (“neuromodulators”)
- Dopamine (DA)
- Norepinephrine (NE)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
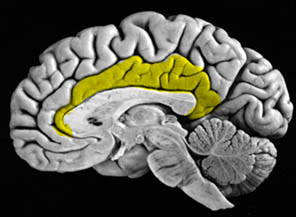
Pineal gland
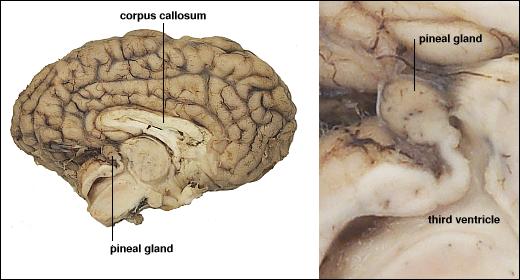
Figure 6.17: Pineal gland: http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/otherendo/pineal.html
Diencephalon (“between” brain)
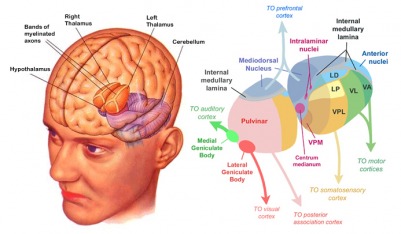
Thalamus
- Input to cortex
- Functionally distinct nuclei (collection of neurons)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), vision
- Medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), audition
Hypothalamus
- Five Fs: fighting, fleeing/freezing, feeding, and reproduction
- Controls Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Sympathetic branch
- Parasympathetic branch
- Controls endocrine system via pituitary gland (“master” gland)
- Anterior pituitary (indirect release of hormones)
- Posterior (direct release of hormones)
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
- Regulates circadian rhythms (via Suprachiasmatic Nucleus)
Telencephalon
- Basal (not basil) ganglia
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
- Skill and habit learning
- Sequencing of movement
- Example: Parkinson’s Disease
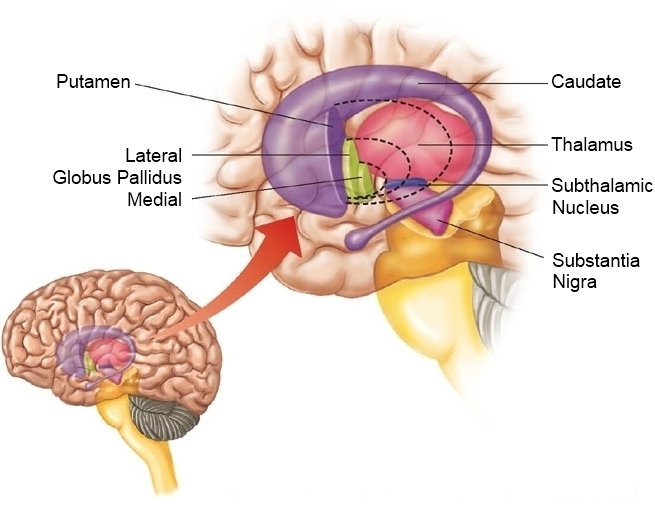
Figure 6.22: http://humanphysiology.academy/Neurosciences%202015/Images/5/basalganglia%20sehati_org.jpeg
- Striatum
- Dorsal
- Ventral
- Globus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Substantia nigra (in tegmentum)
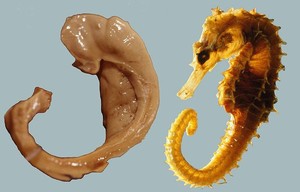
Hippocampus
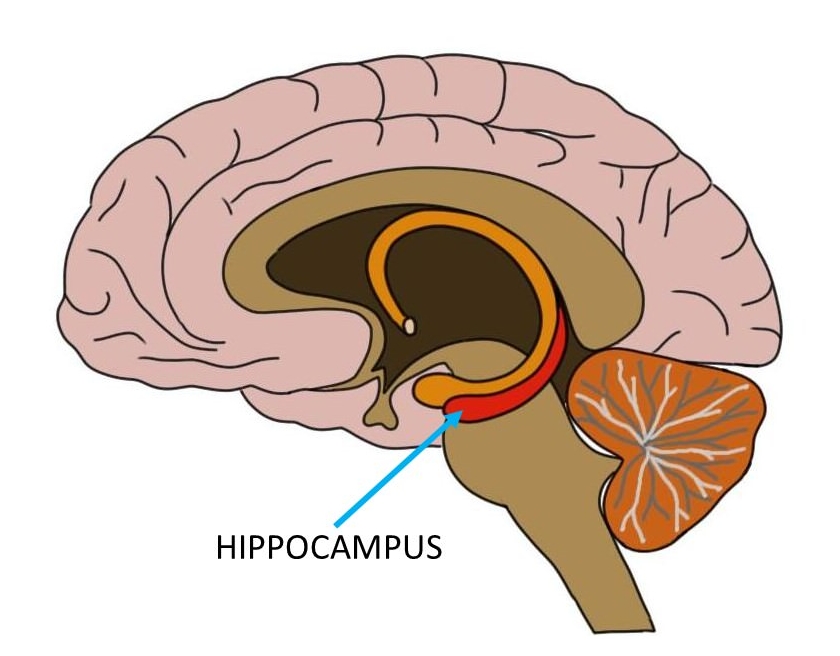
- From Greek for “sea horse”
- Immediately lateral to (inferior) lateral ventricles
- Medial temporal lobe
- Memories of specific facts or events, spatial locations
- Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Fornix projects to hypothalamus
- Mammillary bodies
Amygdala
- “almond”
- Influences physiological state, behavioral readiness, affect
- NOT the fear center! (LeDoux 2015).
Cerebral Cortex
Hemispheres
- Right cerebral hemisphere
- Left cerebral hemisphere
- Gyrus/gyri (bumps)
- Sulcus/sulci, fissures (grooves)
Landmarks
| Landmark | Identifies/separates |
|---|---|
| Medial longitudinal fissure (longitudinal fissure) | Divides hemispheres |
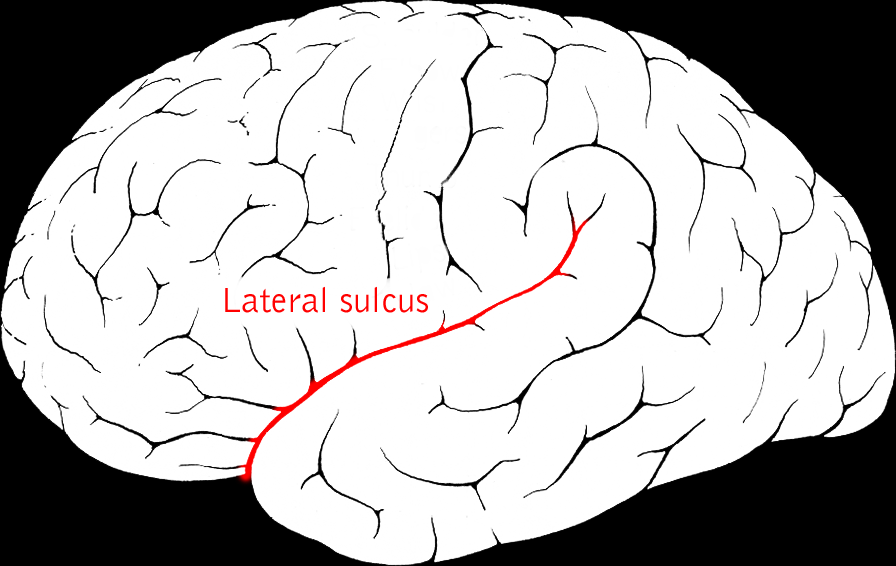
| Lateral sulcus/fissure aka Sylvian Fissure | Divides temporal lobe from frontal & parietal |
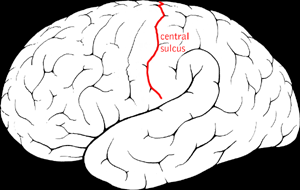
| Central sulcus aka Rolandic Fissure | Divides frontal from parietal lobe |
6.0.0.0.1 Frontal lobe
- Where is it?
- Anterior to central sulcus
- Superior to lateral fissure
- Dorsal to temporal lobe
- What does it do/contain?
- Pre-central gyrus (pre/anterior to central sulcus)
- What does it do/contain?
- Prefrontal cortex
- Planning, problem solving, working memory…?
- Primary olfactory cortex
- Gustatory cortex
- Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- Prefrontal cortex
Cingulate Gyrus {.smaller}
Inferior Frontal Gyrus (IFG)
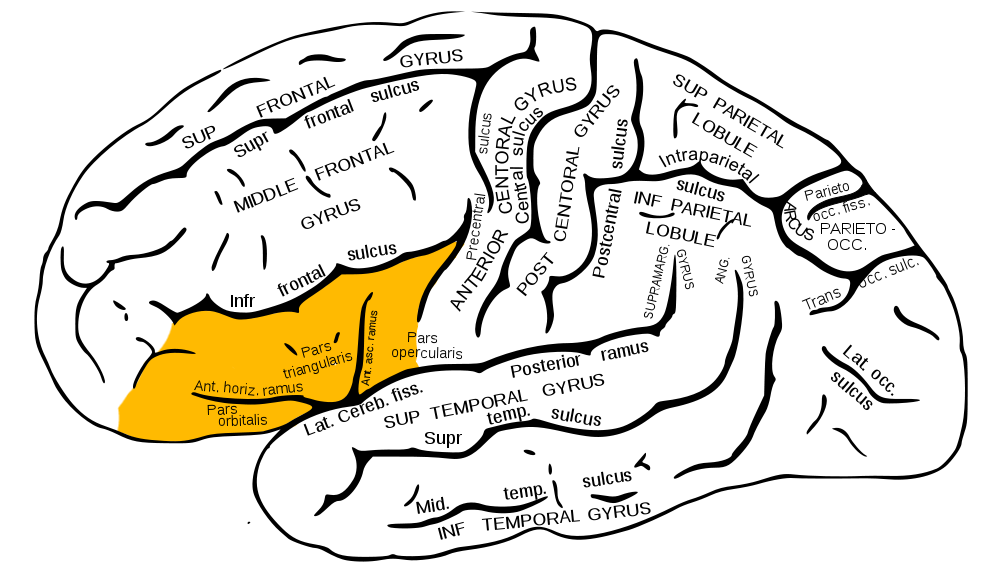
Figure 6.32: Inferior frontal gyrus: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b2/Gray726_inferior_frontal_gyrus.png
Middle Frontal Gyrus (MFG)
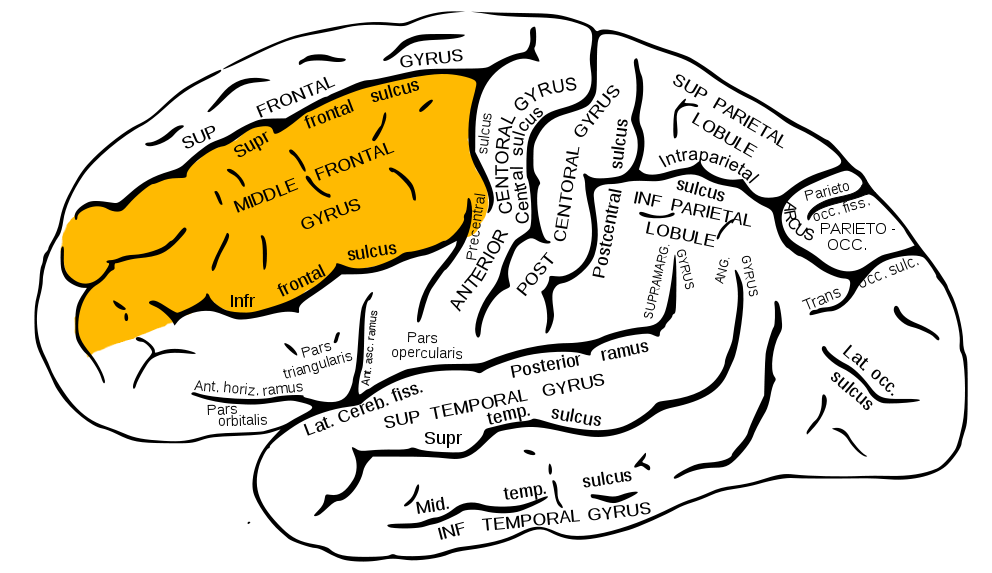
Figure 6.33: Middle frontal gyrus: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7f/Gray726_middle_frontal_gyrus.png
Temporal lobe
- Where is it?
- Ventral to frontal, parietal lobes
- Inferior to lateral fissure
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary auditory cortex (A-I)
- Object, face recognition
- Amygdala, hippocampus
- Storage/recall of memories about events, objects
Inferior Temporal Gyrus (ITG)
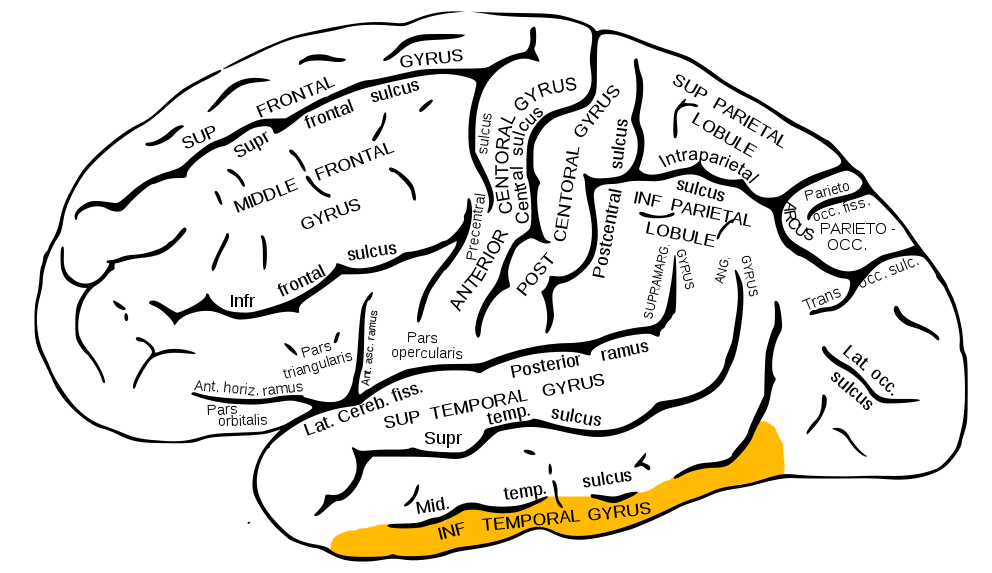
Figure 6.35: Inferior temporal gyrus: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/18/Gray726_inferior_temporal_gyrus.png
Entorhinal Cortex (ER)

Figure 6.36: Entorhinal cortex: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/15/Medial_surface_of_cerebral_cortex_-_entorhinal_cortex.png
Parietal lobe
- Where is it?
- Caudal to frontal lobe
- Dorsal to temporal lobe
- Posterior to central sulcus
- What does it do/contain?
- Perception of spatial relations, action planning
- Post-central gyrus
- Post-central -> “posterior to” central sulcus
- Primary somatosensory cortex (S-I)

Figure 6.39: Inferior Parietal Lobule: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e3/Gray726_inferior_parietal_lobule.png
Superior Parietal Lobule

Figure 6.40: Superior Parietal Lobule: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e3/Gray726_inferior_parietal_lobule.png
Occipital lobe
- Where is it?
- Caudal to parietal & temporal lobes
- What does it do/contain?
- Multiple visual areas in occipital lobe
Insular cortex (insula)
- Where is it?
- medial to temporal lobe
- deep inside lateral fissure
- What does it do/contain?
- Primary gustatory cortex
- self-awareness, interpersonal experiences, motor control
Summary: Lobes, landmarks, areas
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Central sulcus | Precentral gyrus | motor cortex |
| Corpus callosum | Cingulate gyrus | anterior cingulate cortex | |
| olfactory cortex | |||
| gustatory cortex |
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal | Lateral fissure | auditory cortex | |
| olfactory cortex | |||
| hipppocampus | |||
| amygdala |
| Lobe | Sulci | Gyri | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parietal | Central sulcus | Postcentral gyrus | somatosensory ctx |
| Occipital | visual ctx | ||
| Insula | Lateral fissure | gustatory ctx |
Brodmann Areas
- Regions of cerebral cortex that differ in cellular architecture.
- Numbering scheme–Brodmann Area 3 (BA3)
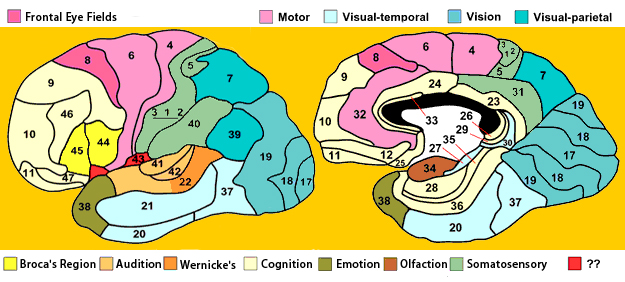
Figure 6.46: http://www.brain-maps.com/gehirn/brodmann_areale.jpg
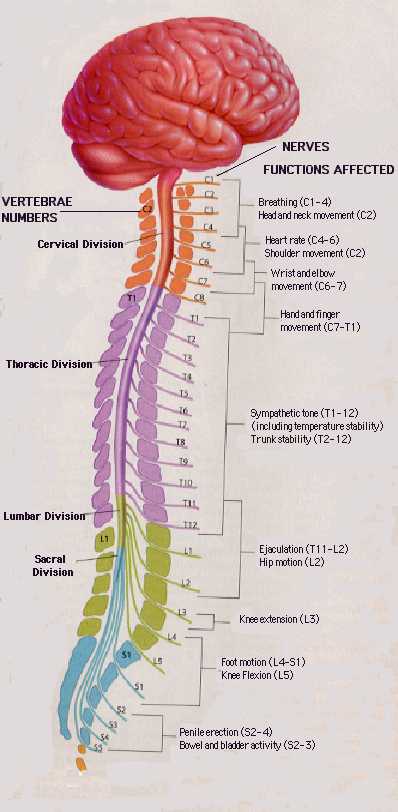
Spinal cord
- Rostral/Caudal axis
- Spinal column w/ vertebrae
- Cervical (8), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5), coccygeal (1)
- Spinal segments & 31 nerve pairs
- Cauda equina

By John A Beal, PhD Dep’t. of Cellular Biology & Anatomy, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport - <a rel=“nofollow” class=“external free” href=“http://www.healcentral.org/healapp/showMetadata?metadataId=40566">http://www.healcentral.org/healapp/showMetadata?metadataId=40566</a>;, CC BY 2.5, Link
- Organization of the spinal cord
- Dorsal/Ventral
- Dorsal root (sensory)
- Ventral root (mostly motor)
- Grey (interior) vs. white matter (exterior)
- Dorsal/Ventral

Figure 6.48: Cross-section of spinal cord: https://www.britannica.com/science/spinal-cord
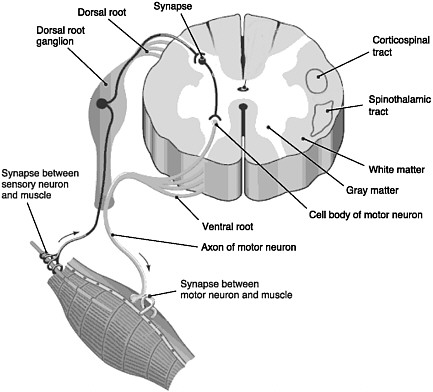
Figure 6.49: Schematic of spinal cord (grey/white shading reversed from actual spinal cord): https://www.nap.edu/openbook/0309095859/xhtml/images/p2000d3bdg31001.jpg
Organization of the PNS
- Somatic division
- Voluntary sensory & motor function
- Autonomic division
- Involuntary sensory & motor function
- Cranial nerves
- Spinal nerves
Cranial nerves
- Afferents (input/sensory), efferents (output/motor), or mixed/both
- On Old Olympus’ Towering Top…
- Some Say Marry Money…
- Innervate head and neck
- Olfactory (I), optic (II), (VIII) auditory, vagus (X), etc.
- Spinal nerves

Figure 6.50: Cranial nerves: https://www.britannica.com/science/cranial-nerve

Figure 6.51: Cranial nerve mnemonic: https://medizzy.com/feed/2893188
You will have to memorize the cranial nerves in other classes, but not this one.
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
- CNS & PNS components
- Controls “vegetative functions””
- Limited voluntary control
- Two divisions
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
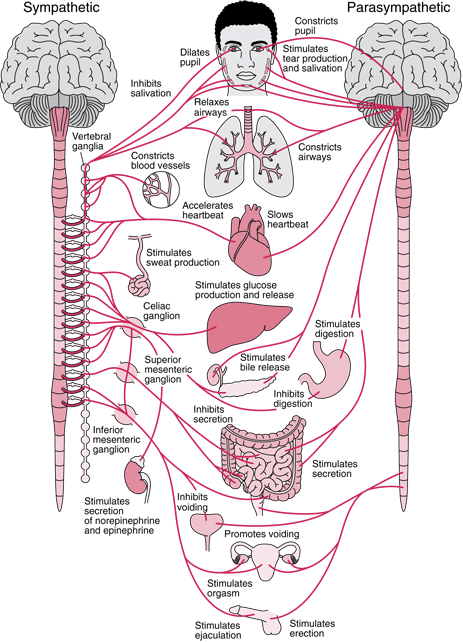
Figure 6.52: http://humanphysiology.academy/Neurosciences%202015/Images/2/NEU_autonomic_nervous_system%20Merck%20Manuals.gif


![[[@Abbott2006-jw]](http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn1824)](https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnrn1824/MediaObjects/41583_2006_Article_BFnrn1824_Fig2_HTML.jpg?as=webp)
![[[@Begg2013-fb]](http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2013.136)](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnrendo.2013.136/MediaObjects/41574_2013_Article_BFnrendo2013136_Fig2_HTML.jpg?as=webp)

![[[@Samanthi2019-jt]](https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-forebrain-midbrain-and-hindbrain/)](https://i2.wp.com/www.differencebetween.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Difference-Between-Forebrain-Midbrain-and-Hindbrain_Figure-1-e1557922693725.png?w=724&ssl=1)