Topic 5 Methods
Evaluating methods
- What question does method X answer?
- What are we measuring?
- Structure
- Activity
- Strengths & Weaknesses
- Cost (time/$)
- Invasiveness (surgery vs. no)
- Spatial/temporal resolution
- high/fine (small details, fast events)
- low/poor (big picture, slow events)
Types of methods
- Structural
- What are the parts?
- How do they connect?
- Functional (next time)
- What do the parts do?
Structural methods
Cellular methods
Golgi stain
- Camillo Golgi
- Complete nerve cells, but only 1-5% of total
- Soak tissue in Potassium Dichromate (\(K_2Cr_2O_7\)) then apply Silver Nitrate (\(AgNO_3\))
- Santiago Ramon y Cajal argued for neuron doctrine, shared 1906 Nobel Prize with Golgi

Figure 5.2: source: http://connectomethebook.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/Brainforest17_1119.jpg
Nissl stain
- Franz Nissl
- Only cell bodies
- Cellular distribution, concentration, microanatomy
- Density of staining ~ cell density/number

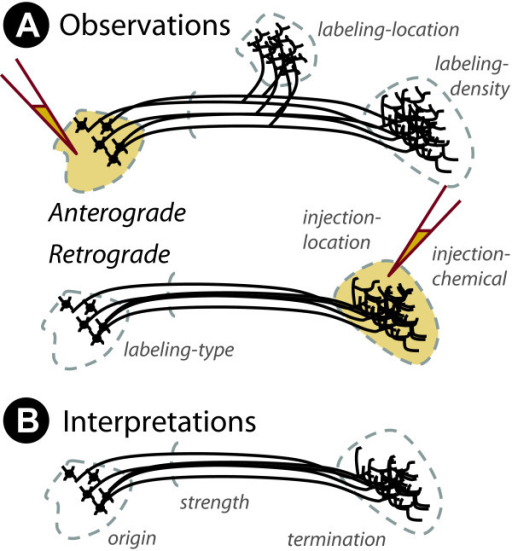
Histochemical tracers
- Neuron information flow polarized–flows in one direction
- ≠ electronic wires, but like pipes
- Tracers are substances that flow one direction down the neuron, allow starting/ending points to be traced
- Retrograde (from axon terminal to cell body)
- Anterograde (from cell body to axon terminal)
Whole-brain imaging
Computed axial tomography (CAT)
- Computed tomography CT
- X-ray based
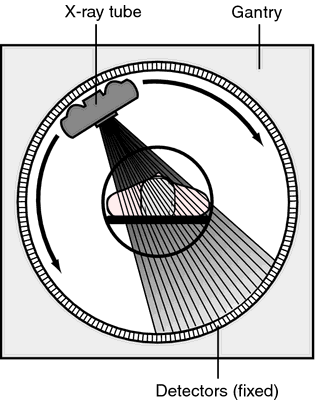
Figure 5.6: CT scanner: http://img.tfd.com/mk/T/X2604-T-22.png

Figure 5.7: How tomography works: https://cdn.hswstatic.com/gif/cat-scan-pineapple.jpg
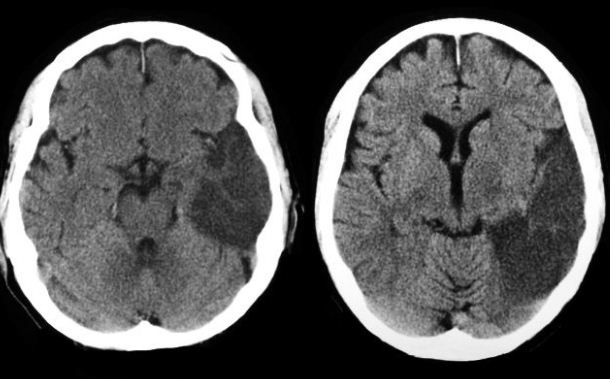
Figure 5.8: CT scan of stroke: http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-I5AIwDp1jJM/UF9gqPEw4vI/AAAAAAAB77M/VfLRw2JDEiY/s1600/mca+inferior+division+infarct+ct+brain.JPG
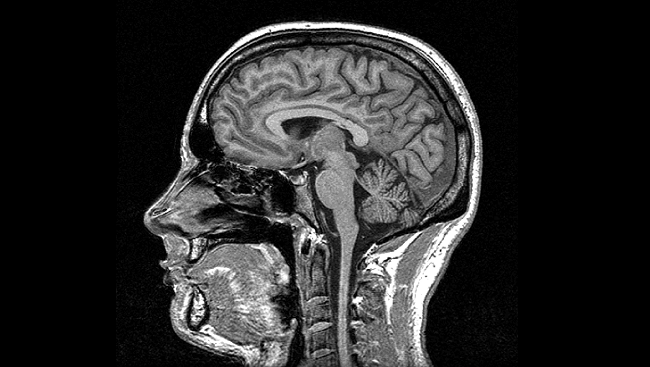
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic resonance
- Some common isotopes (e.g., H) & complex molecules have a magnetic dipole
- Axes align with strong magnetic field
- When alignment perturbed by radio frequency (RF) pulse, speed of realignment varies by tissue
- Realignment emits RF signals
- How MRI works
- Types
- Structural
- Functional
- Reveals tissue density/type differences
- Gray matter (neurons & dendrites & axons & glia) vs. white matter (mostly axons)
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
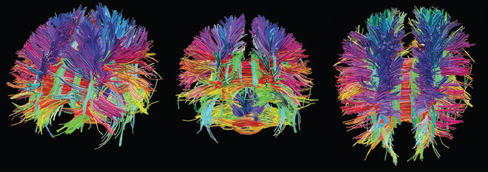
- Type of structural MRI
- Measures patterns of movement/diffusion of \(H_{2}O\)
- Reveals integrity/density of axon fibers
- Measure of connectivity
MR Spectroscopy

Figure 5.10: https://radiopaedia.org/cases/glioma-mr-spectroscopy
- Some complex molecules generate distinctive signals that MR detects
- Voxels (volume-based elements)
- like pixels in an image, but volumes of tissue
- Morphometry, measure (“metry”) form/morphology
- How does brain size or thickness vary by age, disease status, etc.?
Functional methods
Types of functional methods
- Recording from the brain
- Interfering with the brain
- Stimulating the brain
- Simulating the brain
Recording from the brain
- Single/multi unit recording
- Microelectrodes
- Units -> Small numbers of nerve cells
Single/multi-unit recording
- What does neuron X respond to?
- High temporal (ms) & spatial resolution (um)
- Invasive
- Used in non-human animals for purely research purposes
Electrocorticography (ECoG)
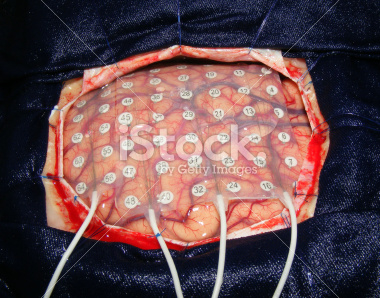
Figure 5.13: ECoG array: https://sites.uci.edu/alns/files/2015/03/eCOG-stock-photo-22578962-brain-surgery.jpg
- Used in human neurosurgery
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Radioactive tracers (glucose, oxygen) delivered intravenously
- Positron decay
- Experimental condition - control
- Average across individuals

Figure 5.14: Data from PET study on language processing: https://www.d.umn.edu/~jfitzake/Lectures/DMED/SpeechLanguage/CorticalS_LAreas/PosnerRaichlePETLanguageAreas.jpg
- Temporal (~ s) and spatial (mm-cm) resolution worse than fMRI
- Radioactive exposures + mildly invasive
- Dose < airline crew exposure in 1 yr
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
- Neural activity -> local \(O_2\) consumption increase
- Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) response
- Oxygenated vs. deoxygenated hemoglobin creates magnetic contrast
- Do regional blood \(O_2\) volumes (and flow) vary with behavior X?
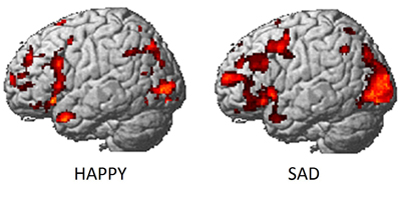
Figure 5.15: fMRI data on emotion processing: https://www.cmu.edu/news/stories/archives/2013/june/images/happysadbrainactivity_400x200.jpg
![fMRI data about retinotopy in V1 from [[@dougherty_visual_2003]](https://doi.org/10.1167/3.10.1)](include/img/doughtery-retinotopy-m_jov-3-10-1-fig001.jpg)
Figure 5.16: fMRI data about retinotopy in V1 from (Dougherty et al. 2003)
What participants viewed
- Non-invasive, but expensive
- Moderate but improving (mm) spatial, temporal (~sec) resolution
- Indirect measure of brain activity
- Hemodynamic Response Function (HRF)
- 1s delay plus 3-6 s ‘initial-dip’

Figure 5.17: Hemodynamic Response Function (HRF): https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/imgs/512/236/3109590/3109590_TONIJ-5-24_F1.png
Electroencephalography (EEG)
- How does it work?
- Electrodes on scalp or brain surface
- What do we measure?
- Combined activity of huge # of neurons
- High/fine temporal resolution (detect fast changes) but poor spatial resolution
Frequency analysis of EEG
- Analyze frequency bands
- LOW: deep sleep
- MIDDLE: Quiet, alert state
- HIGH:“Binding” information across senses

Figure 5.19: Source: https://i.stack.imgur.com/epLsO.png
Brain Computer Interface (BCI)
- Often based on EEG.
Magneto-encephalography (MEG)
- Like EEG, but measures magnetic fields
- High temporal resolution, low spatial resolution
- Magnetic field propagates with minimal distortion from brain/skull, unlike electric field
Manipulating the brain
- Nature’s “experiments”
- Stroke, head injury, tumor
- Neuropsychology
- If damage to X impairs performance on Y -> X critical for/controls Y
- Poor spatial/temporal resolution, limited experimental control
The case of Phineas Gage
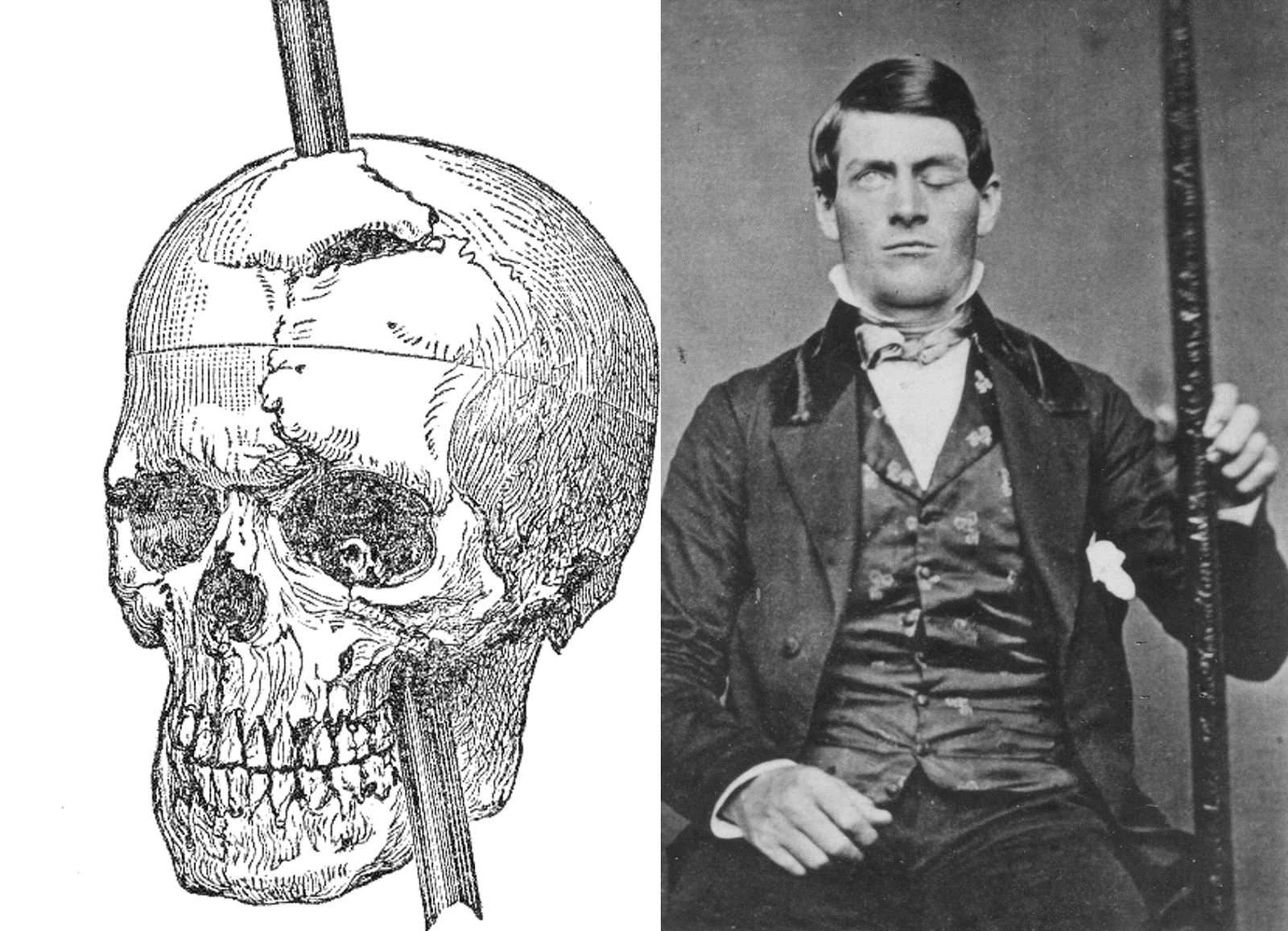
Figure 5.23: Phineas Gage: http://www.doctorsimpossible.com/the-curious-case-of-phineas-gage/

Figure 5.24: Sacks, O. The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat
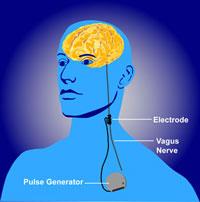
Stimulating the brain
- Pharmacological
- Electrical (transcranial Direct Current Stimulation - tDCS)
- Magnetic (Transcranial magnetic stimulation - TMS)
- Optically (optogenetics)
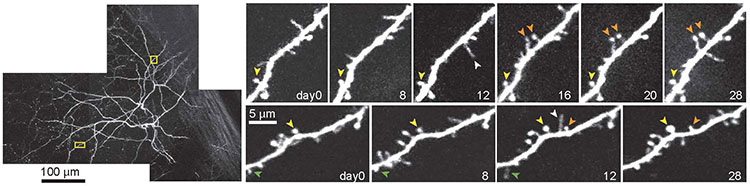
![[[@sejnowski2014putting]](http://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3839)](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnn.3839/MediaObjects/41593_2014_Article_BFnn3839_Fig1_HTML.jpg?as=webp)
![[[@Williamson2012-uj]](http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00184)](http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/18691/fnhum-06-00184-HTML/image_m/fnhum-06-00184-g003.jpg)
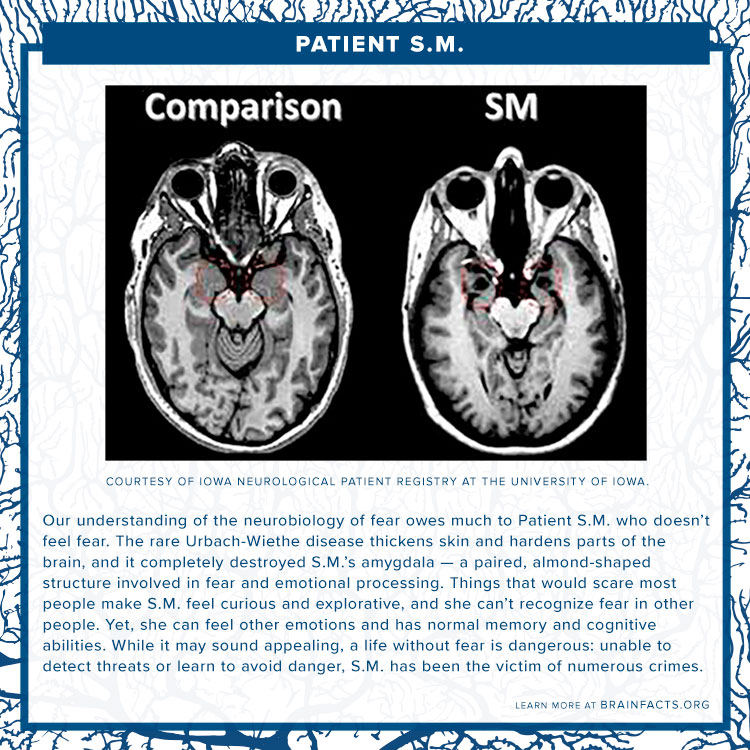
![[[@Maren2004-uz]](http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn1535)](https://media.springernature.com/w300/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnrn1535/MediaObjects/41583_2004_Article_BFnrn1535_Figa_HTML.jpg?as=webp)




![[[@Dayan2013-gp]](http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v16/n7/full/nn.3422.html)](https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnn.3422/MediaObjects/41593_2013_Article_BFnn3422_Fig4_HTML.jpg?as=webp)
![[[@Dayan2013-gp]](http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v16/n7/full/nn.3422.html)](https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fnn.3422/MediaObjects/41593_2013_Article_BFnn3422_Fig1_HTML.jpg?as=webp)